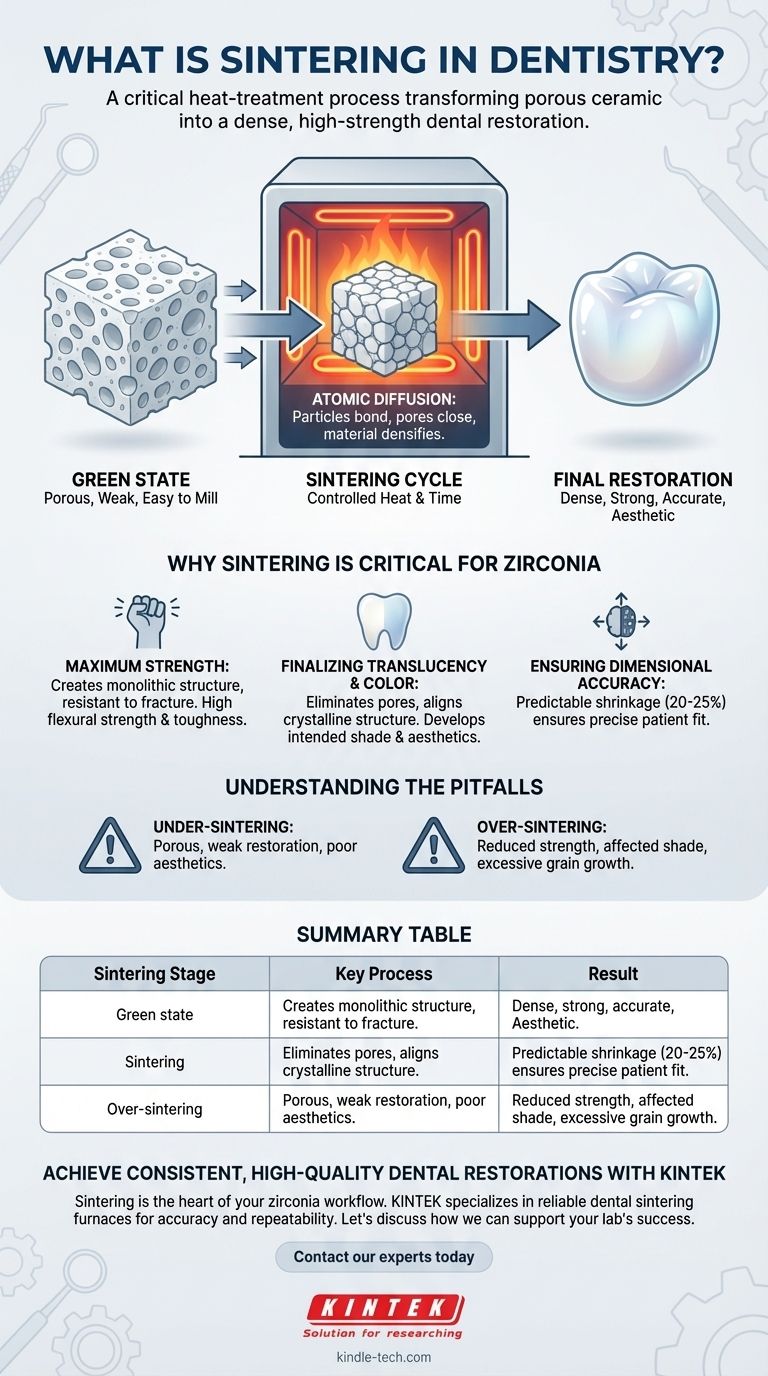
In dentistry, sintering is a critical heat-treatment process that transforms a porous, chalk-like block of ceramic material into a dense, high-strength final restoration. This process is most commonly associated with zirconia, where it is responsible for the material's exceptional durability and esthetics. It essentially fuses individual ceramic particles together without melting them.
Sintering is not simply baking; it is a precisely controlled transformation. This process is what converts an oversized, fragile, milled shape into a strong, accurately sized, and clinically viable dental crown, bridge, or implant abutment.

The Transformation: From "Green State" to Final Form
To understand sintering, you must first understand the material's initial state after it has been milled by a CAD/CAM system.
What is the "Green State"?
The "green state" refers to the material before sintering. In this stage, zirconia is soft, porous, and easily milled into a detailed anatomical shape.
Think of it as a block of highly compacted powder. The particles are pressed together but not yet chemically or physically fused. This makes the material weak and unsuitable for any clinical use.
The Role of Heat and Time
The green-state restoration is placed into a specialized, high-temperature furnace. The furnace follows a precise heating program, known as a sintering cycle.
As the temperature rises, the individual ceramic particles begin to bond at their points of contact. This process, driven by atomic diffusion, eliminates the pores between the particles.
The Result: Densification and Shrinkage
The primary outcome of sintering is densification. As the voids between particles are removed, the material becomes incredibly dense and solid.
This densification causes the restoration to shrink predictably. Zirconia typically shrinks by 20-25%. This shrinkage is a known factor, and the design software automatically enlarges the initial restoration design to compensate perfectly.
Why Sintering is Critical for Zirconia
Sintering is the step that unlocks the material properties that make zirconia a cornerstone of modern restorative dentistry.
Achieving Maximum Strength
The fusion of particles creates a monolithic structure that is highly resistant to fracture. Sintering is directly responsible for zirconia's high flexural strength and fracture toughness, allowing it to be used for long-span bridges and restorations in high-stress areas.
Finalizing Translucency and Color
The process also has a major impact on aesthetics. In the green state, zirconia is completely opaque. Sintering reduces light scattering by eliminating pores and aligning the material's crystalline structure.
This is what develops the final translucency and allows the pre-applied coloring ions to express the intended tooth shade.
Ensuring Dimensional Accuracy
The success of the entire digital workflow depends on predictable shrinkage. An accurate sintering cycle ensures the final restoration shrinks to the exact dimensions specified in the digital design, guaranteeing a precise fit for the patient.
Understanding the Pitfalls and Trade-offs
The sintering cycle is a delicate balance of temperature, heating rate, and time. Deviating from the manufacturer's validated parameters can severely compromise the final restoration.
The Risk of Under-Sintering
If the temperature is too low or the hold time is too short, the material will not fully densify. This results in a porous, weak restoration with poor aesthetics that is highly susceptible to premature failure.
The Risk of Over-Sintering
If the temperature is too high or the hold time is too long, it can cause excessive grain growth within the zirconia's microstructure. This can paradoxically reduce strength and negatively impact the material's translucency and shade.
Contamination and Inaccuracy
A contaminated or poorly calibrated furnace can also ruin the outcome. Debris inside the furnace can discolor the restoration, while an inaccurate temperature can lead to under- or over-sintering, destroying the restoration's integrity and fit.
Making the Right Choice for Predictable Results
Mastering the sintering process means following validated protocols precisely to ensure consistent, high-quality outcomes.
- If your primary focus is strength and longevity: Always use the exact sintering cycle recommended by the zirconia manufacturer for that specific material.
- If your primary focus is optimal aesthetics: Ensure your furnace is clean and calibrated regularly, as temperature accuracy directly impacts the final shade and translucency.
- If your primary focus is efficiency: Only use "speed" or "fast" sintering cycles if they are explicitly validated by the manufacturer for the specific zirconia puck you are using.
Ultimately, understanding sintering empowers you to control the final properties of your ceramic restorations, turning a digital design into a clinical success.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Process | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Green State | Milled zirconia block, porous and weak | Easy to shape, but not clinically usable |
| Sintering Cycle | Heating in a specialized furnace (atomic diffusion) | Particles bond, pores close, material densifies |
| Final Restoration | Predictable 20-25% shrinkage, shade development | Dense, strong, accurate, and aesthetic restoration |
Achieve consistent, high-quality dental restorations with KINTEK.
Sintering is the heart of your zirconia workflow, and precision is non-negotiable. KINTEK specializes in dental lab equipment, including reliable sintering furnaces designed for accuracy and repeatability. Whether your focus is ultimate strength, perfect aesthetics, or efficient production, the right equipment ensures your restorations meet the highest clinical standards every time.
Let's discuss how we can support your lab's success. Contact our experts today to find the perfect sintering solution for your specific zirconia materials and workflow needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Horizontal High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a muffle furnace or oven used for thermal annealing after silver nanowire deposition? Unlock Peak Conductivity
- Why do ceramics need to be sintered? Unlock Strength and Durability Through High-Temperature Fusion
- What is ashing in chemistry? Enhance Analytical Accuracy with Ashing Techniques
- What role does a high-temperature box furnace play during the re-austenitization of 17-4 PH? Transform SLM Performance
- What is the sintering process of coating? Building Durable, Solid Layers from Powder


















