Sintering is a manufacturing process that uses heat and pressure to compact a powdered material into a solid, unified mass. Critically, this is achieved without raising the temperature to the primary material's melting point, instead fusing the particles together at their contact surfaces. This method is fundamental to creating strong, often complex parts from powders.
The core principle of sintering is simple: you can create a dense, solid object from a powder by heating it just enough for the particles to bond together. This avoids the energy and complexity of fully melting the material, making it a highly efficient and versatile method for producing intricate components at scale.
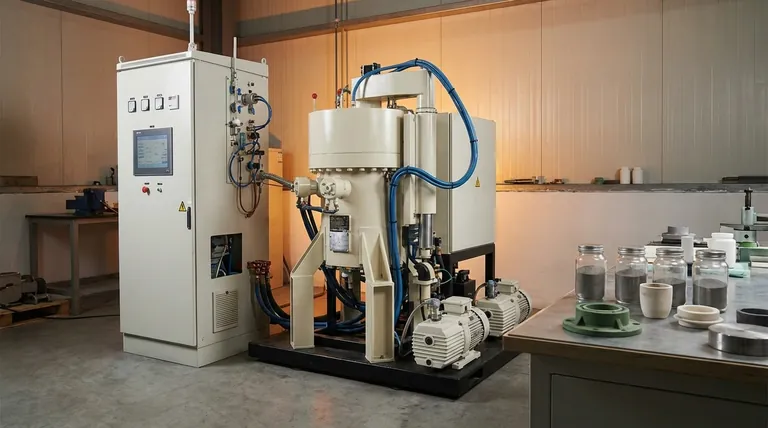

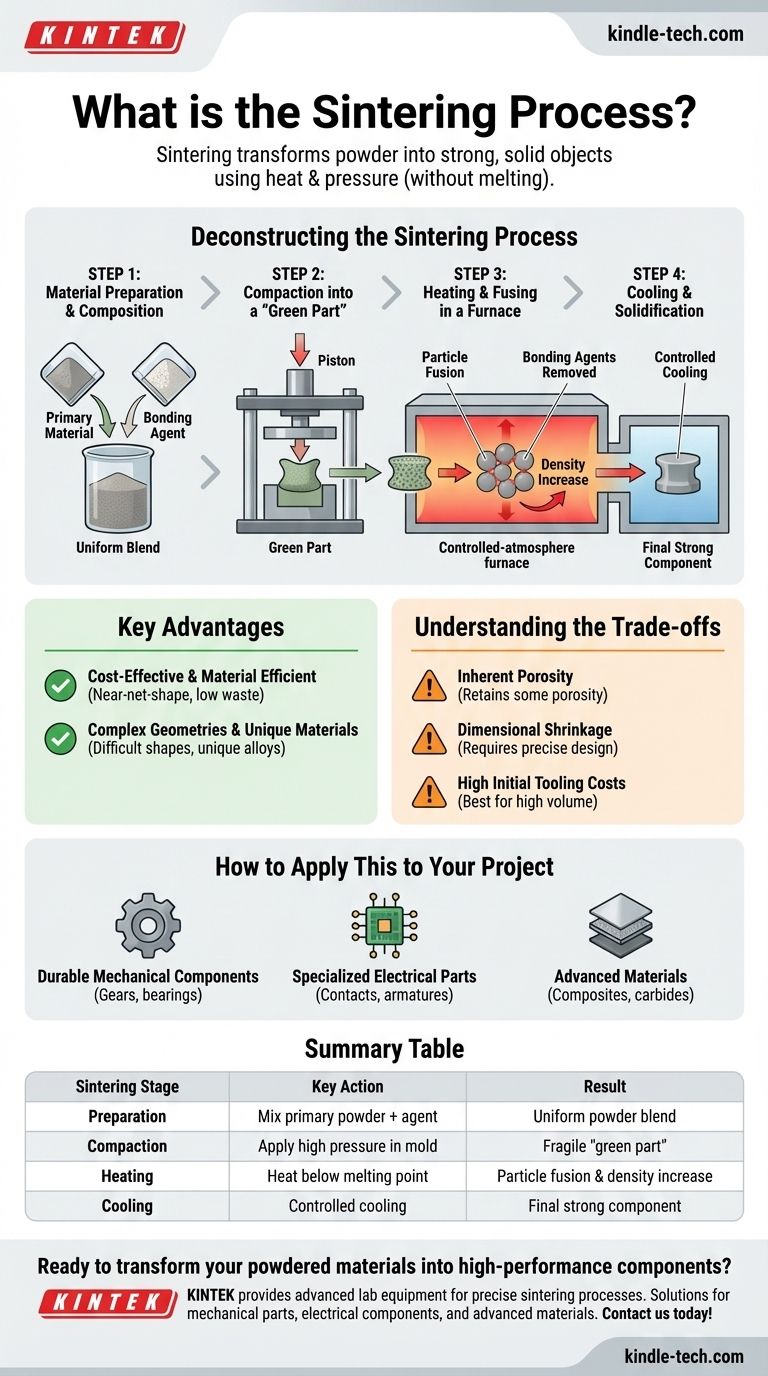
Deconstructing the Sintering Process
Sintering is best understood as a multi-stage thermal treatment that transforms loose powder into a coherent, engineered part. Each step is critical to achieving the final desired properties.
Step 1: Material Preparation and Composition
The process begins with a carefully formulated powder. This is often a blend of a primary material, such as a metal or ceramic powder, mixed with a bonding agent or lubricant.
This agent, which can be wax, a polymer, or another additive, helps the powder particles stick together during the initial forming stage.
Step 2: Compaction into a "Green Part"
The prepared powder mixture is loaded into a mold or die. It is then subjected to high pressure, which compacts the powder into the desired shape.
This initial, fragile component is known as a "green part." It has the correct geometry but lacks the mechanical strength of the final product.
Step 3: Heating and Fusing in a Furnace
The green part is placed into a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated. This thermal cycle has two key phases.
First, the temperature rises to burn off or evaporate the bonding agents. Second, the temperature continues to increase to a point just below the primary material's melting point. At this temperature, the particles begin to fuse at their surfaces, a process that significantly reduces the porous spaces between them.
Step 4: Cooling and Solidification
After being held at the sintering temperature for a set time, the component is carefully cooled. As it cools, the newly formed bonds solidify, creating a single, unified mass.
This final part is dense, strong, and closely matches the intended design, though some predictable dimensional shrinkage occurs during the process.
Key Advantages of the Sintering Method
Sintering is not just a niche technique; it is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing because it offers distinct advantages over other methods like machining or casting.
Cost-Effectiveness and Material Efficiency
By avoiding the high energy costs required to fully melt materials, sintering is often more economical, especially for high-volume production. It is also a near-net-shape process, meaning it produces very little waste material compared to subtractive methods like machining.
Complex Geometries and Unique Materials
The process excels at creating parts with intricate or complex shapes that would be difficult or prohibitively expensive to produce otherwise.
Furthermore, it allows for the creation of unique alloys and composites by mixing powders of materials that would not easily combine in a molten state.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While powerful, sintering is not the ideal solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Inherent Porosity
Even after sintering, parts typically retain a small amount of porosity. This can affect mechanical properties like tensile strength and fatigue resistance when compared to parts made from fully dense, forged materials. In some applications, like self-lubricating bearings, this porosity is a desired feature.
Dimensional Shrinkage
The densification that occurs during sintering causes the part to shrink. This change must be precisely calculated and factored into the design of the initial mold and green part to ensure the final component meets dimensional tolerances.
High Initial Tooling Costs
The molds and dies required for the compaction stage are robust and precisely engineered, representing a significant upfront investment. This makes sintering most cost-effective for medium- to high-volume production runs where the tooling cost can be amortized across many parts.
How to Apply This to Your Project
The decision to use sintering depends entirely on your material, geometry, and production volume goals.
- If your primary focus is producing durable mechanical components: Sintering is ideal for creating cost-effective gears, bearings, sprockets, and cams in large quantities.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing specialized electrical parts: The process is excellent for producing components like electrical contacts and armatures where unique material blends are needed for specific magnetic or conductive properties.
- If your primary focus is developing advanced materials: Sintering is a key enabling technology for creating metal-matrix composites, cemented carbides, and ceramics that cannot be formed through traditional melting.
Ultimately, sintering provides an elegant and efficient pathway from powdered raw material to a strong, functional component.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Action | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Preparation | Mix primary powder with bonding agent | Uniform powder blend ready for molding |
| 2. Compaction | Apply high pressure in a mold | Formation of fragile 'green part' |
| 3. Heating | Heat in furnace below melting point | Particle fusion and density increase |
| 4. Cooling | Controlled cooling of the part | Solidification into final strong component |
Ready to transform your powdered materials into high-performance components?
KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise sintering processes. Whether you're developing durable mechanical parts, specialized electrical components, or advanced materials, our solutions help you achieve superior results with efficiency and reliability.
Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can support your sintering projects and bring your designs to life!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance
- How does a vacuum environment system contribute to the hot pressing sintering of B4C-CeB6? Unlock Peak Ceramic Density
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve 98.9% Density in Al2O3-TiC Laminated Ceramics



















