In short, furnace brazing's primary advantage is its ability to produce strong, clean, and dimensionally stable joints in a highly controlled and repeatable manner. By heating entire assemblies uniformly within a protective atmosphere or vacuum, it excels at joining complex geometries, dissimilar materials, and multiple joints simultaneously, making it a superior choice for high-precision and high-volume manufacturing.
The challenge in metal joining is not just bonding two pieces together, but doing so without compromising the integrity of the parent materials, introducing contaminants, or causing heat-induced distortion. Furnace brazing solves this by moving the process into a controlled chamber, ensuring unparalleled consistency, cleanliness, and design freedom.
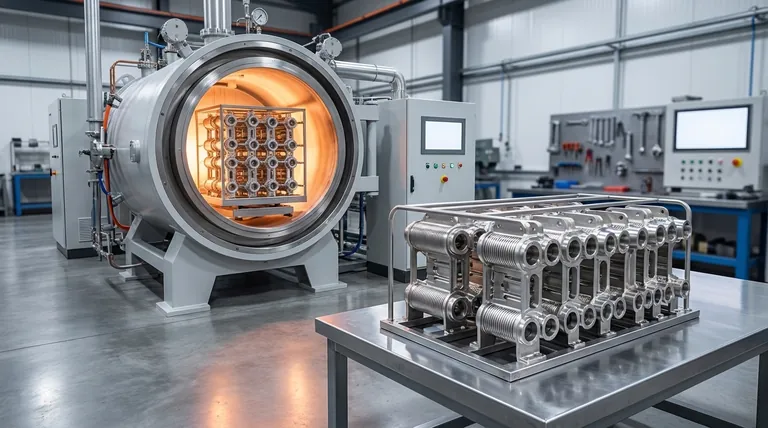

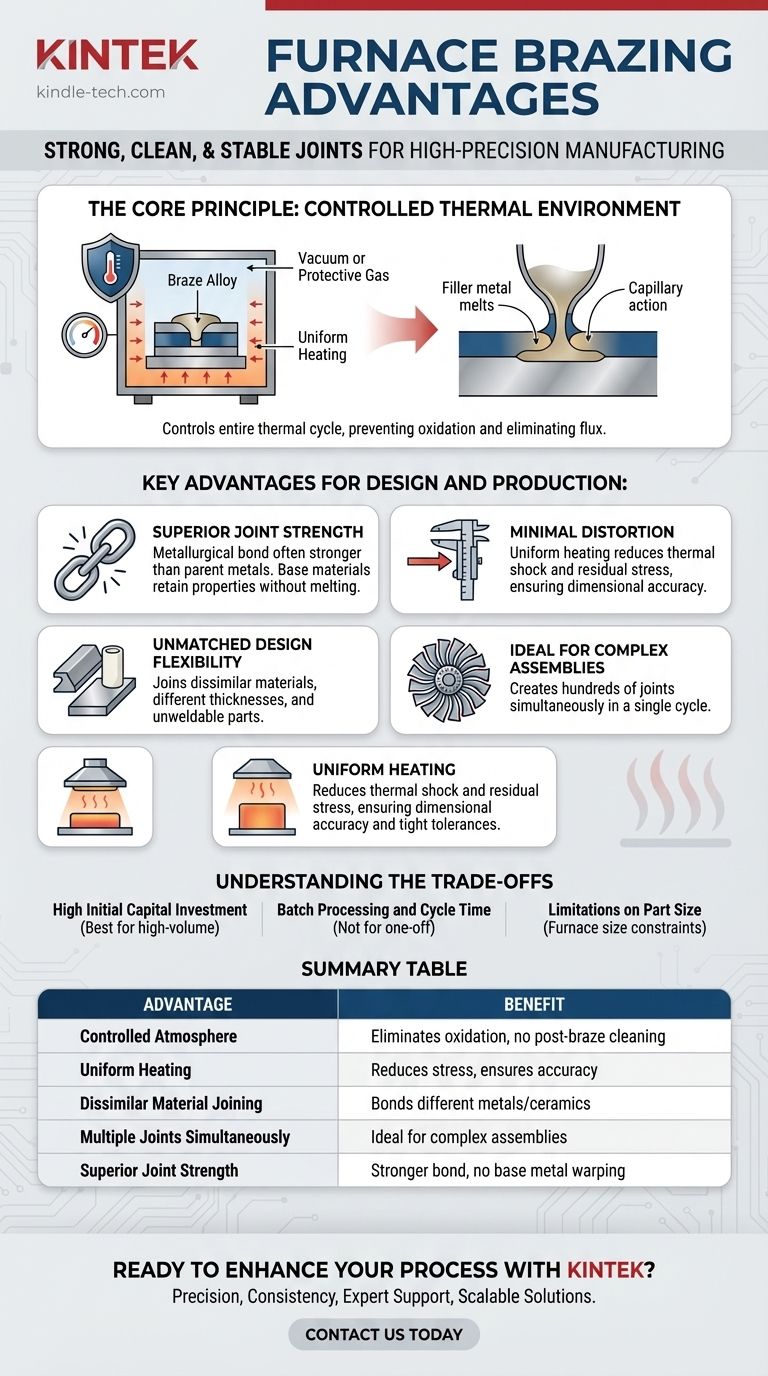
The Core Principle: A Controlled Thermal Environment
Furnace brazing fundamentally changes the joining process by controlling every aspect of the thermal cycle. This control is the source of its most significant advantages.
How the Process Works
Parts are first assembled with a filler metal, known as a braze alloy, placed at the intended joints. The entire assembly is then loaded into a furnace. The furnace is sealed, and the atmosphere is controlled—either by creating a vacuum or introducing a protective gas—before the components are heated to the brazing temperature. The filler metal melts and is drawn into the joints by capillary action, creating a strong bond as the assembly cools.
Eliminating Contamination and Flux
The protective atmosphere or vacuum is critical because it prevents oxidation of the metal surfaces during the high-temperature cycle. This eliminates the need for chemical fluxes, which are often required in other brazing methods to clean the joint area. The result is an exceptionally clean joint that requires little to no post-braze cleaning, saving time and reducing process steps.
Ensuring Temperature Uniformity
Unlike torch brazing or welding where heat is applied locally, a furnace heats the entire assembly uniformly. This slow, even heating and cooling cycle drastically reduces thermal shock and residual stress within the parts.
Key Advantages for Design and Production
The controlled environment of furnace brazing unlocks capabilities that are difficult or impossible to achieve with other methods.
Superior Joint Strength and Integrity
Furnace brazing creates a metallurgical bond that can be stronger than the parent metals themselves. Because the filler metal has a lower melting point, the parent metals are never melted or warped. This process ensures the base materials retain their original properties.
Minimal Distortion and Residual Stress
Uniform heating and cooling is the single greatest advantage for high-precision work. It ensures assemblies maintain their dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances. This makes furnace brazing the ideal method for delicate components or complex assemblies where any distortion would lead to failure.
Unmatched Design Flexibility
Engineers are given enormous freedom. The process allows for joining dissimilar materials (such as copper to steel or even metals to ceramics), parts with widely different thicknesses, and materials that are considered unweldable.
Ideal for Complex Assemblies
A single furnace cycle can create one joint or several hundred joints at once. This makes it possible to manufacture highly complex parts, like heat exchangers or turbine assemblies, that would be impractical to produce by welding or other means.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, furnace brazing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
High Initial Capital Investment
Furnaces, especially high-vacuum systems, represent a significant upfront cost. The process is most economical when used for medium- to high-volume production where the cost can be amortized over many parts.
Batch Processing and Cycle Time
Furnace brazing is a batch process. The entire cycle of loading, evacuating the chamber, heating, brazing, and cooling can be time-intensive. While efficient for many parts at once, it is not suited for one-off jobs or rapid, single-piece prototyping where setup time is a concern.
Limitations on Part Size
The size of the components that can be brazed is ultimately limited by the physical dimensions of the furnace's internal chamber.
Is Furnace Brazing Right for Your Application?
To determine if furnace brazing is the optimal choice, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is part quality and precision: Furnace brazing is superior for creating strong, clean joints with minimal distortion, especially for delicate or high-tolerance assemblies.
- If your primary focus is design freedom: This process excels at joining complex geometries, dissimilar materials, or creating hundreds of joints in a single operation.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production cost: Furnace brazing offers excellent economy of scale by reducing labor, eliminating post-processing, and increasing throughput for batch production.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or on-site repairs: Other methods like manual torch brazing or welding may be more practical and cost-effective due to the high setup cost and batch-oriented nature of furnace brazing.
Ultimately, furnace brazing empowers engineers to produce complex, high-integrity components at scale in a way that other joining methods simply cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Controlled Atmosphere | Eliminates oxidation and flux, resulting in exceptionally clean joints with no post-braze cleaning. |
| Uniform Heating | Reduces thermal shock and residual stress, ensuring dimensional accuracy and tight tolerances. |
| Dissimilar Material Joining | Enables bonding of different metals and even metals to ceramics, offering unmatched design flexibility. |
| Multiple Joints Simultaneously | Ideal for complex assemblies, allowing hundreds of joints to be created in a single furnace cycle. |
| Superior Joint Strength | Creates a metallurgical bond stronger than the parent metals, without melting or warping the base materials. |
Ready to Enhance Your Manufacturing Process with Precision Furnace Brazing?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables, including high-performance furnace brazing solutions tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're joining complex geometries, dissimilar materials, or aiming for high-volume production with minimal distortion, our expertise ensures you achieve strong, clean, and dimensionally stable joints every time.
Why Choose KINTEK for Your Furnace Brazing Needs?
- Precision and Consistency: Our equipment delivers uniform heating and controlled atmospheres for repeatable, high-quality results.
- Expert Support: Our team offers technical guidance to optimize your brazing process for maximum efficiency and part integrity.
- Scalable Solutions: From medium- to high-volume production, we provide systems that grow with your manufacturing demands.
Don't let joint quality or design limitations hold back your projects. Contact us today to discover how KINTEK's furnace brazing solutions can transform your metal joining process and deliver unparalleled performance for your laboratory or production facility.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- At what temperature does molybdenum evaporate? Understanding Its High-Temperature Limits



















