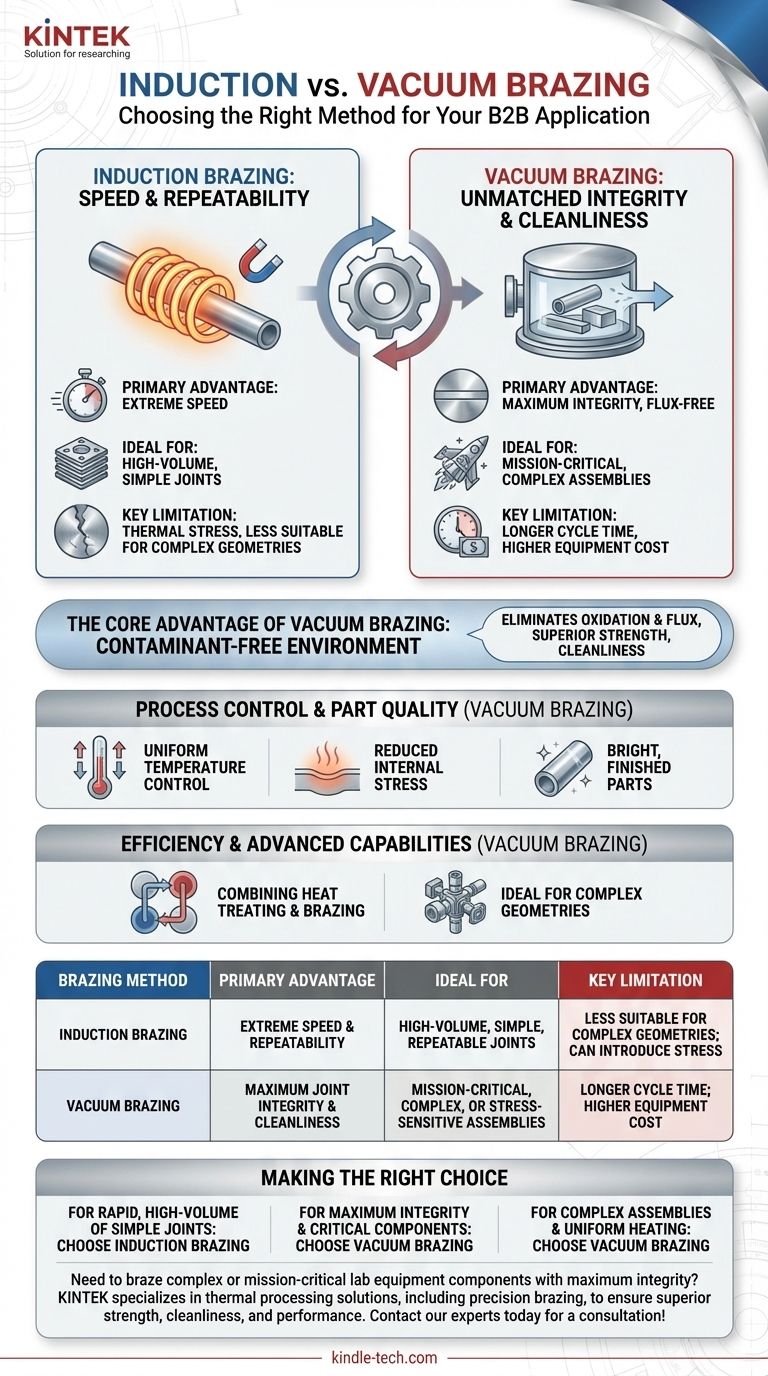
In short, the primary advantage of induction brazing is its speed and repeatability, making it highly effective for high-volume production runs where the same joint is created over and over. This process uses an electromagnetic field to rapidly heat a very localized area, allowing for precise, consistent, and fast joining of components like carbide tips onto steel shafts.
While induction brazing excels at speed for specific applications, achieving the absolute highest level of joint integrity, cleanliness, and strength—especially in complex or mission-critical assemblies—often requires a different approach: vacuum brazing.

The Core Advantage: Unmatched Joint Integrity and Cleanliness
The defining feature of vacuum brazing is the environment in which it occurs. By removing the atmosphere from a sealed furnace, the process eliminates the root cause of many common brazing defects and unlocks a superior level of quality.
Contaminant-Free Environment
A vacuum effectively removes atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This prevents the formation of oxides on the metal surfaces during the heating cycle, which is a common failure point in other brazing methods.
The result is an exceptionally clean work surface that promotes excellent wetting and flow of the brazing filler metal.
Flux-Free Joints
Because the vacuum prevents oxidation, there is no need for flux—a chemical agent used in other processes to clean the joint area. This completely eliminates the risk of corrosive flux being trapped within the joint, which can compromise its long-term integrity.
Superior Strength and Performance
The combination of an ultra-clean surface and excellent filler metal flow results in braze joints that are free of voids and inclusions. This creates a final bond with exceptionally high integrity and strength, often matching the properties of the base metals themselves.
Process Control and Part Quality
Vacuum brazing is not just about the environment; it is also about the precise thermal control it offers throughout the entire cycle. This control has a direct impact on the final quality of the part.
Uniform Temperature Control
The furnace heats the entire assembly slowly and uniformly. This ensures that all parts of the component, regardless of thickness or complexity, reach the brazing temperature at the same time, preventing distortion and ensuring a consistent joint.
Reduced Internal Stress
Slow, controlled heating and cooling cycles are a hallmark of the vacuum process. This gentle thermal treatment minimizes the residual stresses that can be introduced by rapid, localized heating methods, improving the overall mechanical and thermal properties of the finished assembly.
Bright, Finished Parts
Components emerge from a vacuum furnace bright and clean, with no oxidation or discoloration. This often eliminates the need for post-brazing cleaning operations, saving both time and cost.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single process is perfect for every application. While vacuum brazing offers supreme quality, induction brazing provides speed.
Vacuum brazing's primary trade-offs are cycle time and cost. The slow heating and cooling, combined with the time needed to create the vacuum, results in longer cycles compared to induction. The equipment is also more complex and expensive.
Induction brazing, conversely, is extremely fast. Its ability to heat a localized area in seconds is its key advantage. However, this speed can introduce thermal stress, and it is less suitable for complex assemblies or for joining materials in a single, stress-free operation.
Efficiency and Advanced Capabilities
For complex engineering requirements, vacuum brazing provides capabilities that other processes cannot easily match.
Combining Heat Treating and Brazing
The controlled furnace environment allows other thermal processes, such as hardening, annealing, or age hardening, to be performed in the same cycle as the brazing. This consolidates manufacturing steps, improves efficiency, and ensures consistent material properties.
Ideal for Complex Geometries
The uniform heating of vacuum brazing makes it the ideal method for joining intricate, multi-component assemblies or parts with internal channels. It ensures the entire assembly is joined perfectly without overheating or damaging sensitive areas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct brazing method depends entirely on the priorities of your project.
- If your primary focus is rapid, high-volume production of simple, repeatable joints: Induction brazing is an excellent and highly efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint integrity, cleanliness, and strength for critical components: Vacuum brazing is the definitive, superior method.
- If your primary focus is processing complex assemblies or materials sensitive to thermal stress: The controlled, uniform heating of vacuum brazing is essential for success.
Ultimately, choosing the right process is about aligning the method's capabilities with your specific engineering and quality requirements.
Summary Table:
| Brazing Method | Primary Advantage | Ideal For | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Induction Brazing | Extreme speed and repeatability | High-volume, simple, repeatable joints | Less suitable for complex geometries; can introduce stress |
| Vacuum Brazing | Maximum joint integrity and cleanliness | Mission-critical, complex, or stress-sensitive assemblies | Longer cycle time; higher equipment cost |
Need to braze complex or mission-critical lab equipment components with maximum integrity?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment and consumables. Our expertise in thermal processing solutions, including brazing, ensures your assemblies achieve superior strength, cleanliness, and performance. Let's discuss how we can meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace IGBT Experimental Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of brazing? Join Dissimilar Metals with Strong, Leak-Proof Bonds
- Can dissimilar metals be brazed or braze welded? A Guide to Strong, Reliable Joints
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is vacuum brazed? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity Metal Joining



















