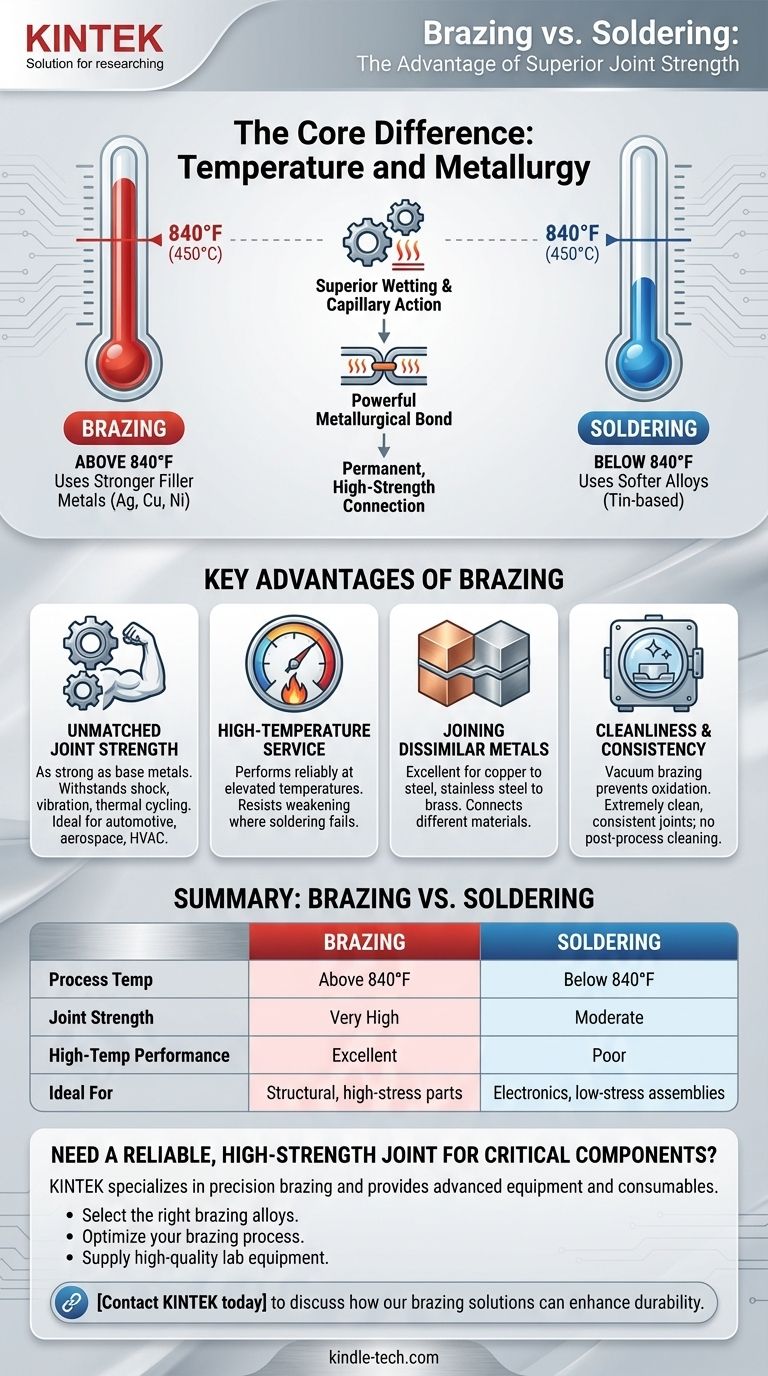
The fundamental advantage of brazing over soldering is superior joint strength. Brazing occurs at a much higher temperature—above 840°F (450°C)—which allows it to use stronger filler metals. This process creates a metallurgical bond that results in a finished joint that is often as strong, or even stronger, than the base metals being joined.
The choice between brazing and soldering is a direct trade-off between the required strength of the joint and the heat tolerance of the components. Brazing delivers exceptional strength for demanding applications, while soldering is a lower-temperature alternative for less strenuous or heat-sensitive work.
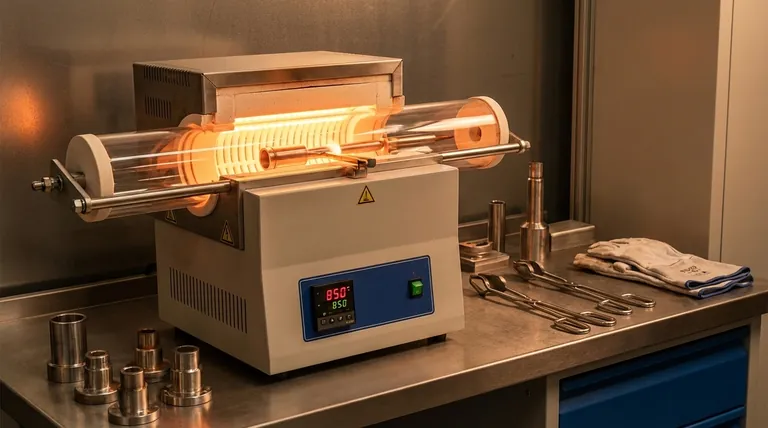

The Core Difference: Temperature and Metallurgy
The distinction between brazing and soldering is defined by a single factor: temperature. This difference dictates the type of filler metal used and, consequently, the mechanical properties of the final joint.
The 840°F (450°C) Threshold
By industry definition, any process using a filler metal that melts below 840°F is considered soldering. Any process using a filler metal that melts above 840°F without melting the base metals is considered brazing.
Impact on Filler Metals
The higher working temperature of brazing allows for the use of robust filler alloys, typically containing silver, copper, or nickel. Soldering relies on softer, lower-melting-point alloys like those based on tin.
How This Creates Stronger Bonds
The intense heat of brazing promotes superior wetting and capillary action, allowing the filler metal to be drawn deeply into the joint. This creates a powerful metallurgical bond between the filler and the base metals, resulting in a permanent, high-strength connection.
Key Advantages of Brazing
The high-temperature nature of brazing translates directly into several critical performance benefits, making it the preferred method for demanding industrial applications.
Unmatched Joint Strength
A properly brazed joint is exceptionally strong and ductile. It can withstand significant shock, vibration, and thermal cycling, making it ideal for industries like automotive, aerospace, and HVAC where joint failure is not an option.
High-Temperature Service
Because brazed joints are created at high temperatures, they can also perform reliably at elevated service temperatures where a soldered joint would weaken and fail.
Joining Dissimilar Metals
Brazing is an excellent method for joining different types of metals, such as copper to steel or stainless steel to brass, which can be difficult or impossible to join with other methods like welding.
Cleanliness and Consistency
When performed in a controlled atmosphere or vacuum, a process known as vacuum brazing prevents oxidation. This produces extremely clean, strong joints with excellent part-to-part consistency and no need for post-process cleaning.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While brazing offers superior strength, its use of high heat is not always an advantage. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The Risk of High Heat
The high temperatures required for brazing can negatively affect the base metals. It can cause heat distortion or alter the material's temper and hardness, which must be accounted for during the design and engineering phase.
Why Soldering Remains Essential
Soldering's primary advantage is its low temperature. This makes it the only suitable choice for joining heat-sensitive electronic components, where the high heat of brazing would cause immediate and irreversible damage.
Process Complexity
Brazing generally requires more precise heat control, cleaner base materials, and tighter joint tolerances than soldering. This can make the process more complex and require more skilled operation, particularly for advanced techniques like vacuum brazing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct process requires you to align the method's capabilities with your project's primary goal.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and durability: Brazing is the definitive choice, especially for parts subject to high stress, vibration, or temperature.
- If you are joining heat-sensitive electronic components: Soldering is the correct and only safe process, as its lower temperature prevents damage.
- If you require a leak-proof seal in a high-pressure system: Brazing offers a more robust and reliable seal for applications like HVAC refrigerant lines or automotive fluid systems.
- If your primary focus is a simple, low-stress assembly: Soldering is often a more economical and straightforward solution when maximal strength is not a critical requirement.
Choosing the right joining method is fundamental to guaranteeing the long-term integrity and performance of your assembly.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | Above 840°F (450°C) | Below 840°F (450°C) |
| Joint Strength | Very High; as strong as base metals | Moderate |
| High-Temp Performance | Excellent | Poor |
| Ideal For | Structural, high-stress, high-temperature parts | Electronics, low-stress assemblies, heat-sensitive components |
| Joint Cleanliness | Excellent (especially with vacuum brazing) | Good |
Need a reliable, high-strength joint for your critical components?
Brazing is the definitive solution for demanding applications where joint failure is not an option. KINTEK specializes in precision brazing and provides the advanced equipment and consumables needed to achieve flawless, high-integrity bonds.
Let our experts help you:
- Select the right brazing alloys for your specific metals and performance requirements.
- Optimize your brazing process for maximum strength and consistency.
- Supply the high-quality lab equipment you need for successful results.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our brazing solutions can enhance the durability and performance of your assemblies.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- What are the benefits of a tube furnace? Achieve Superior Temperature & Atmosphere Control
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is the high temperature of a tube furnace? Unlock the Right Model for Your Application
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















