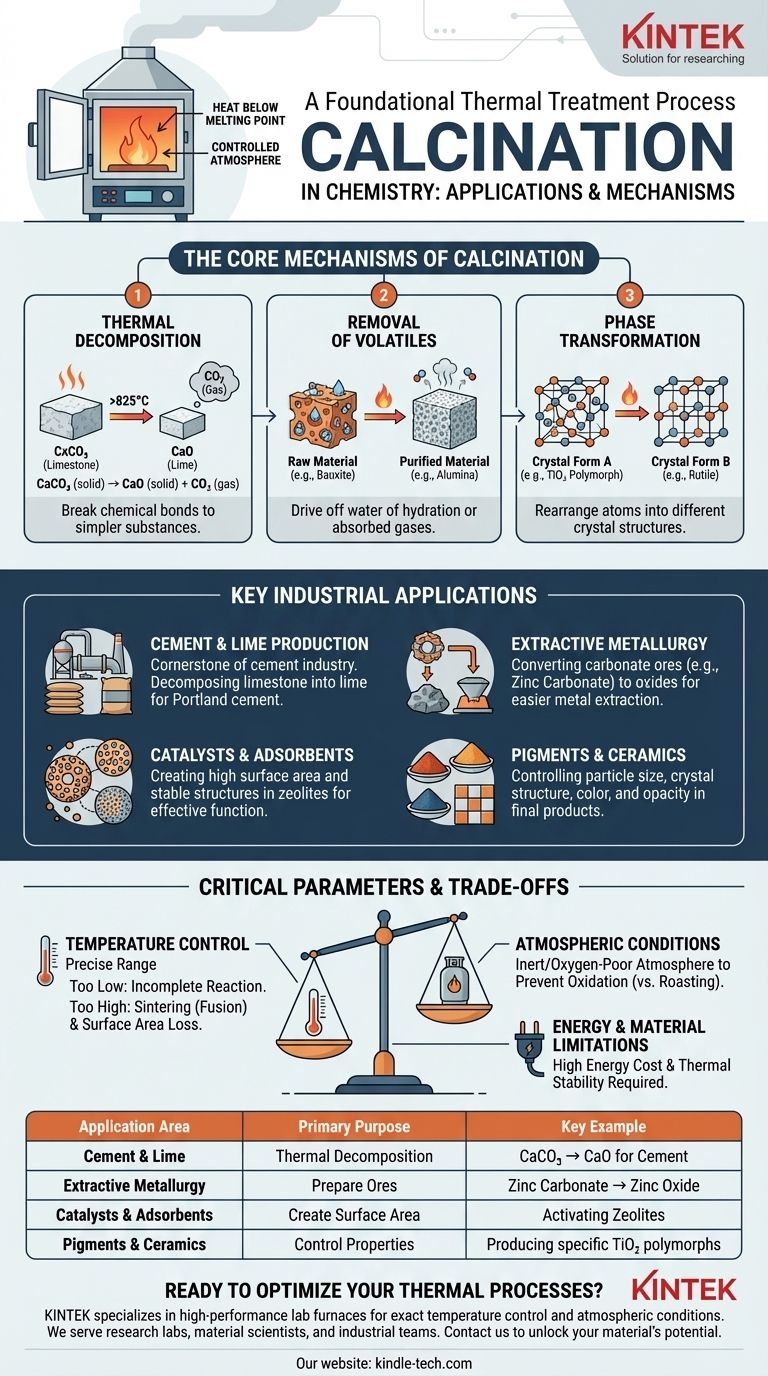
In essence, calcination is a foundational thermal treatment process in chemistry. It involves heating a solid material to a high temperature, typically below its melting point, in a controlled atmosphere or in the absence of air. This is done not to melt the substance, but to cause thermal decomposition, drive off volatile components like water and carbon dioxide, or trigger a phase transition in its crystal structure.
The core purpose of calcination is not simply to heat a material, but to fundamentally alter its chemical composition and physical structure in a precise, controlled way to make it suitable for a specific industrial application.
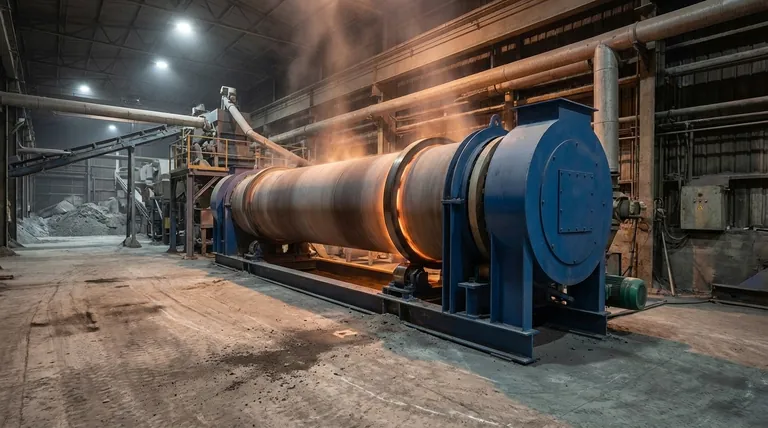

The Core Mechanisms of Calcination
To understand its applications, you must first grasp the fundamental changes that calcination induces in a material. The process typically achieves one of three primary objectives.
Thermal Decomposition
This is the most common goal of calcination. The applied heat provides enough energy to break chemical bonds within a compound, breaking it down into simpler substances.
The classic example is the production of lime (calcium oxide, CaO) from limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃). Heating limestone above 825°C drives off carbon dioxide, leaving behind the desired lime.
CaCO₃ (solid) → CaO (solid) + CO₂ (gas)
Removal of Volatiles
Many raw materials contain volatile substances, most commonly water of hydration (chemically bound water) or absorbed gases.
Calcination purifies the material by driving these volatiles out. For example, bauxite ore is calcined to remove water, converting aluminum hydroxides into aluminum oxide (alumina), a critical step before producing aluminum metal.
Phase Transformation
Heating a solid can cause its atoms to rearrange into a different crystal structure, a process known as a phase transition. The different crystal forms (polymorphs) of a substance can have vastly different physical and chemical properties.
For instance, calcination is used to convert titanium dioxide (TiO₂) into its desired crystal form (e.g., rutile) for use as a pigment, as this controls its opacity and brightness.
Key Industrial Applications
The principles of calcination are applied across numerous large-scale industries where the properties of solid materials are paramount.
Cement and Lime Production
This is the largest industrial application of calcination by volume. The decomposition of limestone into lime is the cornerstone of the cement industry, as lime is the primary ingredient in Portland cement.
Extractive Metallurgy
Before a metal can be extracted from an ore, the ore must often be prepared. Calcination is used to convert carbonate ores into their corresponding oxides.
It is generally much easier and more energy-efficient to reduce a metal oxide to the pure metal than it is to reduce a metal carbonate directly. For example, zinc carbonate (smithsonite) is calcined to zinc oxide before being smelted.
Catalysts and Adsorbents
The performance of catalysts and adsorbents (like zeolites) depends heavily on their surface area and porous structure.
Calcination is a critical step in their manufacturing. It's used to remove precursor chemicals, stabilize the material's framework, and create the high surface area and specific pore sizes necessary for them to function effectively.
Pigments and Ceramics
In the production of inorganic pigments, ceramics, and refractories, calcination provides precise control over the final product's properties.
The process determines particle size, crystal structure, and purity, which directly impacts characteristics like color, opacity, hardness, and thermal stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Critical Parameters
While powerful, calcination is a precise process where slight deviations can lead to undesirable outcomes. Success requires managing a careful balance of factors.
Temperature Control is Paramount
The calcination temperature is the most critical variable. Too low a temperature results in an incomplete reaction, leaving impurities or unreacted starting material.
Conversely, too high a temperature can cause sintering, where the solid particles begin to fuse. This drastically reduces the material's surface area, which is catastrophic for applications involving catalysts or adsorbents.
Atmospheric Conditions Matter
Calcination is formally defined by its controlled, often inert or oxygen-poor, atmosphere. This distinguishes it from roasting, which is a similar high-temperature process performed in the presence of excess air to promote oxidation.
Using an inert atmosphere (like nitrogen) prevents unwanted side reactions, ensuring the material undergoes the desired decomposition or phase change without being oxidized.
Energy and Material Limitations
Calcination is an energy-intensive process due to the high temperatures required. This represents a significant operational cost, especially at industrial scales.
Furthermore, it is only suitable for materials that are thermally stable up to their decomposition temperature and do not melt or vaporize prematurely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Calcination is a versatile tool, but its application must be tailored to the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is bulk chemical production: Use calcination for large-scale thermal decomposition, such as converting limestone into lime for cement.
- If your primary focus is preparing an ore for metal extraction: Apply calcination to convert carbonate or hydrated ores into their more easily reducible oxides.
- If your primary focus is engineering advanced material properties: Employ calcination as a precision tool to control crystal structure and create high surface area in catalysts, pigments, and adsorbents.
Ultimately, mastering calcination is about understanding how to apply controlled thermal energy to unlock the precise chemical and physical potential hidden within a solid material.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Primary Purpose of Calcination | Key Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cement & Lime Production | Thermal decomposition of carbonates | Converting limestone (CaCO₃) to lime (CaO) for cement |
| Extractive Metallurgy | Prepare ores for metal extraction | Converting zinc carbonate ore to zinc oxide before smelting |
| Catalysts & Adsorbents | Create high surface area and stable structure | Activating zeolites by removing precursors and stabilizing pores |
| Pigments & Ceramics | Control crystal structure and particle properties | Producing specific TiO₂ polymorphs for opacity and color in pigments |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Processes?
Calcination is a precise science, and the right equipment is critical for achieving the desired material properties—whether you're developing catalysts, processing ores, or engineering advanced ceramics. KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and thermal processing equipment designed for exact temperature control and atmospheric conditions, ensuring your calcination processes are efficient, repeatable, and scalable.
We serve: Research laboratories, material scientists, and industrial teams focused on metallurgy, catalysis, ceramics, and chemical production.
Let us help you unlock the full potential of your materials. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific calcination needs and discover the ideal solution for your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- Is pyrolysis costly? Unlocking the True Economics of Waste-to-Energy Technology
- What is the history of pyrolysis technology? From Wood Distillation to Modern Waste Valorization
- What is pyrolysis characteristics? Unlocking Waste-to-Energy Potential
- What is the difference between pyrolysis and fast pyrolysis? Maximize Biochar or Bio-Oil Yield
- What are the disadvantages of fast pyrolysis? The key challenges of bio-oil production
- What is fast pyrolysis of wood? A Rapid Process to Maximize Bio-Oil Yield
- What are the modes of pyrolysis? Choose the Right Method for Your Target Product
- What is the use of pyrolysis product? Convert Waste into Fuel, Biochar & Syngas



















