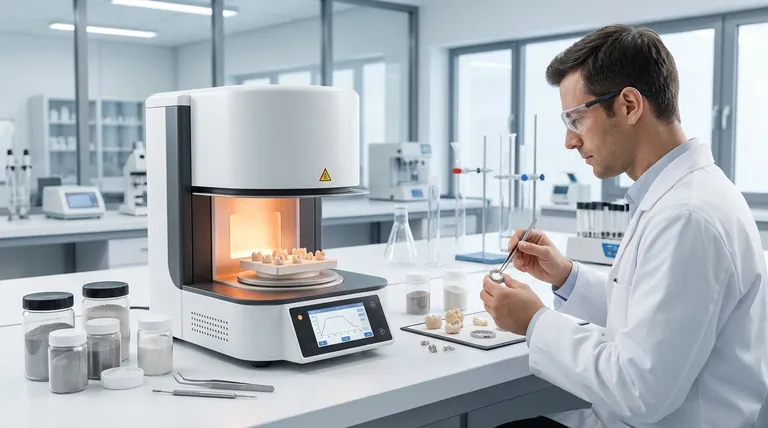
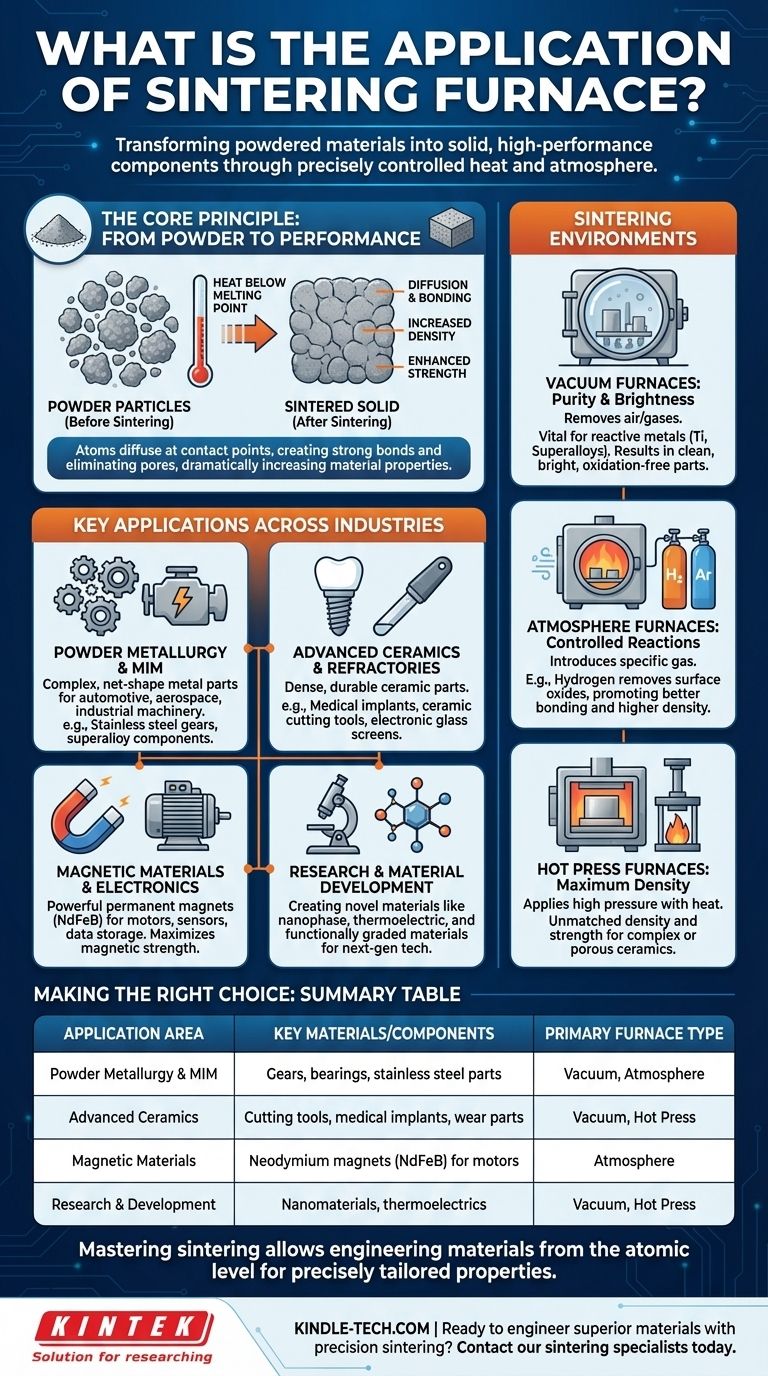
In essence, a sintering furnace is used to transform powdered materials into a solid, coherent mass through the application of heat. Its applications are vast, spanning the production of high-strength metal parts, advanced ceramics, electronics, medical implants, and magnetic components for industrial and scientific use.
The fundamental purpose of a sintering furnace is not merely to heat a material, but to use precisely controlled heat and atmosphere to bond powder particles together, dramatically increasing the material's density, strength, and overall performance.

The Core Principle: Why Sintering is Essential
Sintering is a foundational process in modern materials science and manufacturing. It enables the creation of high-performance components from materials that are difficult or impossible to shape using traditional melting and casting methods.
From Powder to Performance
Imagine pressing snowflakes together until they fuse into a solid block of ice. Sintering works on a similar principle, but at a microscopic level with metal, ceramic, or composite powders.
The process involves heating the compacted powder to a temperature below its melting point. At this temperature, the atoms at the contact points between particles diffuse, creating strong bonds and gradually eliminating the pores between them.
Solving Key Manufacturing Challenges
This method is critical for working with materials that have extremely high melting points, such as tungsten or certain ceramics. It also allows for the creation of unique alloy compositions and composite materials that cannot be produced by melting.
Key Applications Across Industries
The versatility of sintering makes it indispensable in numerous high-tech fields. The furnace type and process parameters are tailored specifically to the material and desired outcome.
Powder Metallurgy and Metal Injection Molding (MIM)
This is a primary application, used to create complex, net-shape metal parts for automotive, aerospace, and industrial machinery. Examples include gears, bearings, and structural components made from stainless steel, superalloys, and other high-strength metals.
Advanced Ceramics and Refractories
Sintering is essential for producing dense, durable ceramic parts. This includes everything from ceramic cutting tools and wear-resistant components to medical implants and the glass screens on electronic devices.
Magnetic Materials and Electronics
The creation of powerful permanent magnets, such as neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB), relies heavily on sintering. The process aligns the material's magnetic domains, maximizing its magnetic strength for use in motors, sensors, and data storage.
Research and Material Development
In scientific institutes and universities, sintering furnaces are workhorses for creating novel materials. This includes developing nanophase materials, thermoelectric devices, and functionally graded materials with unique properties for next-generation technologies.
Understanding Different Sintering Environments
The atmosphere inside the furnace is as critical as the temperature. Different environments are used to either protect the material or actively participate in the sintering process.
Vacuum Furnaces: For Purity and Brightness
A vacuum sintering furnace removes air and other gases that could react with and contaminate the material at high temperatures. This is vital for reactive metals like titanium and superalloys.
The result is superior quality parts that are clean, bright, and free from oxidation, requiring less post-processing.
Atmosphere Furnaces: For Controlled Reactions
An atmosphere sintering furnace introduces a specific gas, such as hydrogen or argon. A hydrogen atmosphere, for example, can actively remove surface oxides from metal powders, promoting better bonding and resulting in higher density.
This controlled environment is essential for sintering materials where specific chemical reactions on the surface are desired during the process.
Hot Press Furnaces: For Maximum Density
A hot press sintering furnace applies high pressure simultaneously with heat. This mechanical force aids in closing the pores between particles, resulting in materials with exceptional density and strength.
This method is particularly effective for producing complex or porous ceramic structures and achieving properties that are not possible with pressureless sintering alone.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, sintering is a precise and demanding process. Success depends on carefully controlling numerous variables to achieve the desired outcome.
The Need for Extreme Precision
The final properties of a sintered part are highly sensitive to the raw powder characteristics, compaction pressure, heating rate, final temperature, hold time, and furnace atmosphere. Any deviation can lead to defects or suboptimal performance.
Material and Process Compatibility
Not all materials can be sintered effectively. Furthermore, the choice of furnace environment is critical. Using the wrong atmosphere can ruin a batch of parts, for example, by causing unwanted chemical reactions or contamination.
Furnace Loading and Throughput
As noted in industrial guidelines, the way parts are loaded into a furnace (furnace loading) is a science in itself. Improper loading can cause uneven heating, leading to warped parts or inconsistent densities across a batch, impacting overall production efficiency.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct sintering approach depends entirely on your material, budget, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is mass production of clean, high-strength metal parts: A vacuum sintering furnace is the industry standard for its quality, consistency, and ability to handle a wide range of alloys.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of iron-based components: An atmosphere furnace with a nitrogen/hydrogen mix is often the most economical and efficient choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength in advanced ceramics or composites: A hot press sintering furnace provides capabilities that are unmatched by other methods, despite its lower throughput.
Ultimately, mastering the sintering process allows you to engineer materials from the atomic level up, creating components with precisely tailored properties.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Materials/Components | Primary Furnace Type |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Metallurgy & MIM | Gears, bearings, stainless steel parts | Vacuum, Atmosphere |
| Advanced Ceramics | Cutting tools, medical implants, wear parts | Vacuum, Hot Press |
| Magnetic Materials | Neodymium magnets (NdFeB) for motors | Atmosphere |
| Research & Development | Nanomaterials, thermoelectrics | Vacuum, Hot Press |
Ready to engineer superior materials with precision sintering? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and consumables, serving industries from aerospace to medical research. Whether you need a vacuum furnace for reactive metals or an atmosphere system for cost-effective production, our expertise ensures you achieve the density, strength, and purity your projects demand. Contact our sintering specialists today to discuss your specific material and application goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What makes zirconia translucent? The Science Behind Modern Dental Aesthetics
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations



















