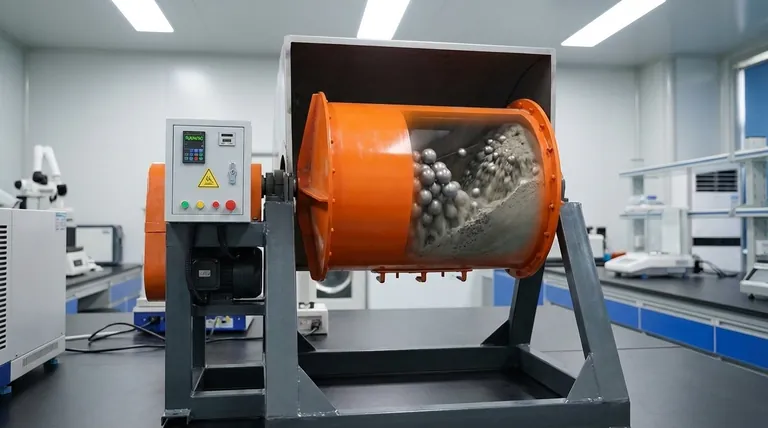
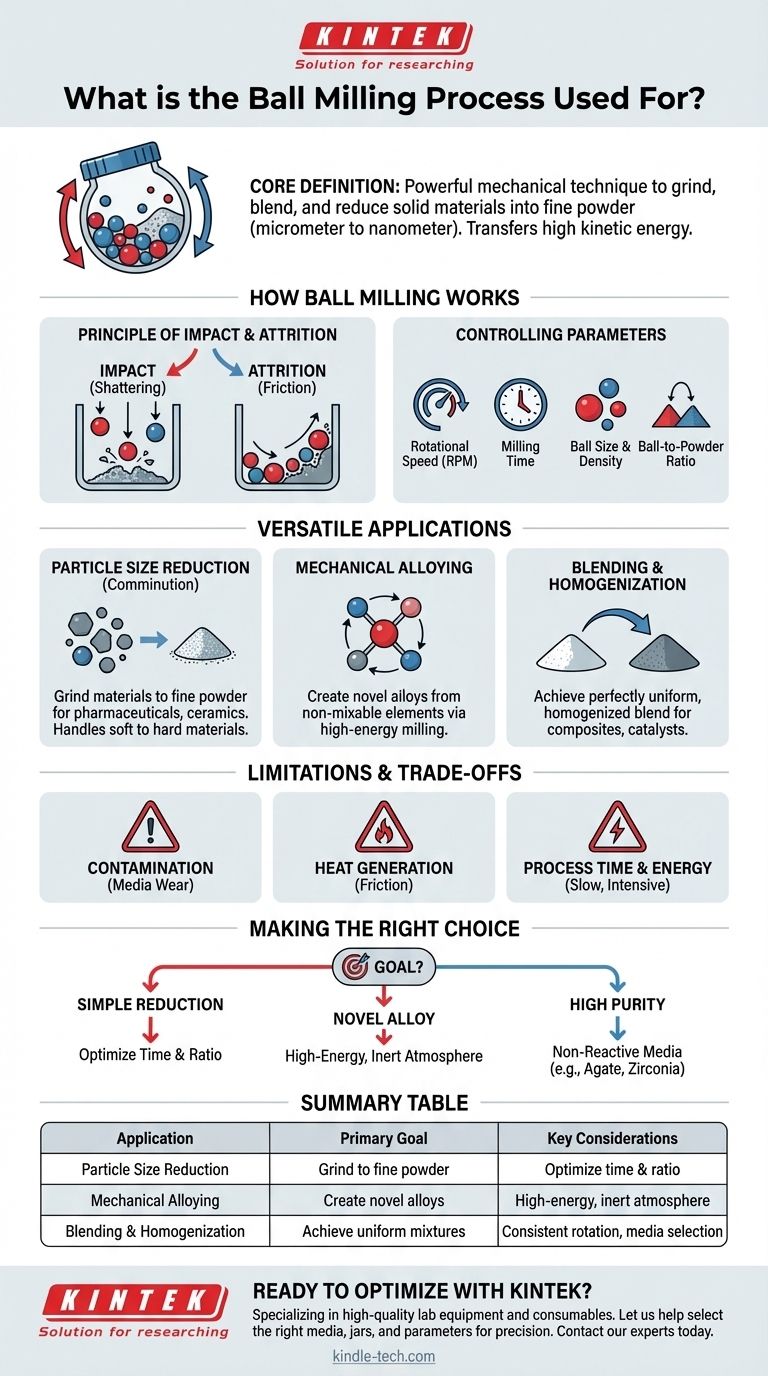
At its core, the ball milling process is a powerful mechanical technique used to grind, blend, and reduce the size of solid materials into a fine powder. It is highly versatile, capable of processing a wide range of substances, from soft organic compounds to extremely hard ceramics and metals. This is achieved by placing the material into a rotating jar along with heavy grinding media (the "balls"), which repeatedly crush and grind the material down to the micrometer or even nanometer scale.
The essential purpose of ball milling is to transfer high kinetic energy from grinding media to a sample material. This controlled energy transfer is what drives particle size reduction, material blending, and even the creation of novel alloys through a process called mechanical alloying.

How Ball Milling Achieves Material Transformation
Ball milling is more than a simple crushing action. It's a dynamic physical process governed by controlled forces that systematically break down a material's structure.
The Fundamental Components
The system consists of three key parts: the milling jar (the container), the grinding media (balls made of a hard material like steel, zirconia, or agate), and the sample material itself. The jar is rotated at high speeds, causing the balls and material inside to tumble and collide.
The Principle of Impact and Attrition
Two primary forces are at work. High-energy impact occurs when the grinding balls fall from the top of the rotating jar, shattering the material particles. Attrition (friction) occurs as the balls and particles rub against each other and the jar wall, shearing and grinding them into even finer pieces.
Controlling the Final Particle Size
The final properties of the milled powder are not left to chance. They are precisely controlled by adjusting key parameters like the rotational speed (RPM), the milling time, the size and density of the balls, and the ball-to-powder weight ratio.
The Versatile Applications of Ball Milling
The ability to control the milling process makes it a crucial tool in numerous scientific and industrial fields. Its applications go far beyond simple grinding.
Particle Size Reduction (Comminution)
This is the most common use of ball milling. It is essential in industries like pharmaceuticals, pigment manufacturing, and ceramics, where a specific and uniform particle size is critical for product performance. The process can handle everything from soft and fibrous to brittle and extremely hard materials.
Mechanical Alloying
This advanced application uses high-energy ball milling to create novel alloys from elements that would not normally mix. The repeated fracturing and cold-welding of particles forces the different atoms into a solid solution, forming materials with unique properties that are impossible to create through traditional melting.
Blending and Homogenization
Ball milling is an extremely effective method for mixing different powdered materials to achieve a perfectly uniform, or homogenized, blend. This is vital for producing composite materials, catalysts, and other multi-component products.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, ball milling is not without its challenges. Understanding these limitations is key to achieving successful results and maintaining the integrity of your sample.
Potential for Contamination
The constant impact and attrition can cause the grinding media and the jar to wear down. This wear can introduce trace amounts of unwanted material, or contamination, into your sample powder. Selecting grinding media made of a material harder than your sample is a critical first step to minimize this.
Heat Generation
The milling process generates significant heat due to friction. For heat-sensitive materials, this can lead to unwanted chemical reactions, phase changes, or degradation. Cooling systems or controlled "wet milling" (using a liquid medium) can help mitigate this issue.
Process Time and Energy
Ball milling can be a slow and energy-intensive process. Achieving very fine particle sizes, especially at the nano-scale, can sometimes require continuous operation for many hours or even days.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To use ball milling effectively, you must align the process parameters with your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is simple particle size reduction: Concentrate on optimizing the milling time and the ball-to-powder ratio for efficient grinding.
- If your primary focus is creating a novel alloy: You will need a high-energy milling setup and must consider milling under a specific atmosphere (like argon) to prevent oxidation.
- If your primary focus is maintaining high purity: The most critical decision is choosing non-reactive, low-wear grinding media and jars, such as those made from agate or zirconia.
Ultimately, mastering the variables of the ball milling process provides precise control over the fundamental properties of your materials.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size Reduction | Grind materials to fine powder | Optimize milling time and ball-to-powder ratio |
| Mechanical Alloying | Create novel alloys from elements | Use high-energy milling and inert atmosphere |
| Blending & Homogenization | Achieve uniform powder mixtures | Ensure consistent rotation and media selection |
| Limitations | Challenges to manage | Contamination risk, heat generation, process time |
Ready to Optimize Your Material Processing with Precision Ball Milling?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs. Whether you're working in pharmaceuticals, ceramics, or advanced materials research, our expertise ensures you achieve the perfect particle size, alloy composition, or blend homogeneity.
Let us help you select the right grinding media, jars, and milling parameters to minimize contamination, control heat, and maximize efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and drive your projects forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Stainless Steel Laboratory Ball Mill for Dry Powder and Liquid with Ceramic Polyurethane Lining
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Four-Body Horizontal Jar Mill
- Hybrid High Energy Vibratory Ball Mill for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the disadvantages of a ball mill? High Energy Use, Noise, and Contamination Risks
- What is the key role of a planetary ball mill for IZO targets? Achieve Atomic-Level Uniformity in Material Preparation
- Why use ball milling for NMC cathode materials? Achieve Precision Particle Sizing for Composite Cathodes
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in eggshell fertilizer production? Unlock Superior Chemical Reactivity
- How does a high-energy planetary ball mill facilitate the synthesis of sulfide glassy electrolytes? Achieve Amorphization



















