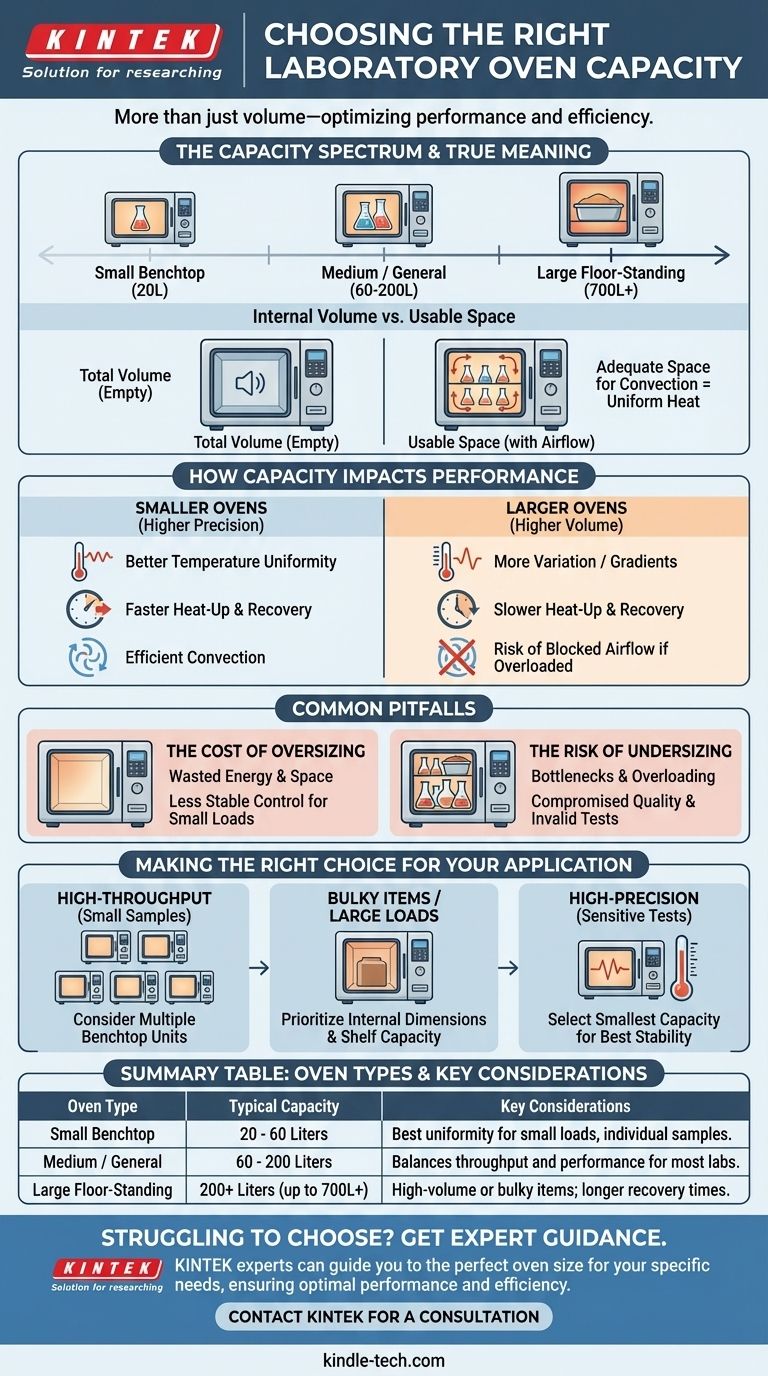
The capacity of a laboratory oven is not a single number, but a range that varies dramatically based on the model and its intended use. Capacities typically start from small benchtop units around 20 Liters (less than 1 cubic foot) and can extend to large, floor-standing models exceeding 700 Liters (over 24 cubic feet).
Choosing the correct oven capacity is not just about fitting your items inside. The critical challenge is selecting a volume that ensures optimal performance—specifically temperature uniformity and recovery—for your specific application without wasting energy or lab space.

Understanding What "Capacity" Truly Means
The stated volume is only the beginning of the story. True capacity is a function of usable space and how that space impacts the oven's primary function of delivering stable, uniform heat.
Internal Volume (Liters or Cubic Feet)
This is the most common metric advertised by manufacturers. It refers to the total empty space inside the oven's chamber. This figure helps you categorize ovens into general sizes, such as small benchtop models for individual use or large-capacity units for high-throughput work.
Usable Space vs. Total Volume
Crucially, you cannot use 100% of the internal volume. Laboratory ovens rely on convection heating—the circulation of hot air—to ensure all samples reach the target temperature uniformly. For this to work, you must leave adequate space around your samples for air to flow.
Overloading an oven by packing it too tightly blocks this airflow, creating cold spots and compromising the accuracy of your drying, curing, or sterilization process.
Shelf Capacity and Loading
The practical capacity is also defined by the number of shelves and their individual weight limits. Consider not just the total volume but how your specific glassware, components, or samples will be arranged on the shelves provided.
How Capacity Directly Impacts Oven Performance
A larger chamber is not inherently better. The oven's volume is directly tied to its thermal performance characteristics, which are critical for achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Temperature Uniformity
Maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the entire chamber is one of the most important functions of a lab oven. Larger ovens inherently have a more difficult time achieving tight uniformity, as there is a greater volume of air to heat and circulate. For highly sensitive materials, a smaller, well-designed oven often provides superior stability.
Heat-Up and Recovery Times
A larger volume of air takes more energy and time to heat up initially. More importantly, every time you open the door, cool air enters the chamber. A larger oven will take significantly longer to recover its setpoint temperature, which can slow down your workflow and affect sample consistency.
The Role of Convection and Venting
As noted, convection is key to removing moisture during a drying process. The circulated air picks up humidity, which is then expelled through a vent. If an oven is overloaded, this process becomes inefficient, dramatically increasing drying times and potentially leaving samples improperly treated.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Choosing the wrong size has practical consequences that go beyond just fitting your samples. Understanding these trade-offs is key to making a sound investment.
The Cost of Oversizing
Selecting an oven that is too large for your typical workload is inefficient. It consumes more electricity to heat the unused space, has a larger physical footprint in your lab, and may provide less stable temperature control for small sample loads.
The Risk of Undersizing
An undersized oven creates a workflow bottleneck, forcing you to run more cycles than necessary. More critically, it encourages users to overload the chamber to save time, which directly compromises the quality and reliability of the results. This can invalidate tests and ruin sensitive materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Analyze your primary need to determine the ideal capacity.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput processing of many small samples: Consider multiple smaller benchtop ovens, which can offer greater flexibility and better temperature recovery than one single large unit.
- If your primary focus is drying large or bulky items: Prioritize the oven's internal dimensions and shelf weight capacity, ensuring your specific items will fit with adequate clearance for airflow.
- If your primary focus is high-precision heating for sensitive tests: Select the smallest capacity that will comfortably meet your needs, as this often provides the best temperature uniformity and stability.
Ultimately, selecting the right oven capacity is about matching the physical space to your scientific requirements to ensure repeatable and accurate results.
Summary Table:
| Oven Type | Typical Capacity Range | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Small Benchtop | 20 - 60 Liters | Ideal for individual samples, offers best temperature uniformity for small loads. |
| Medium / General Purpose | 60 - 200 Liters | Balances throughput and performance for most standard lab applications. |
| Large Floor-Standing | 200+ Liters (up to 700L+) | Designed for high-volume processing or large/bulky items; longer heat recovery. |
Struggling to choose the right lab oven capacity for your specific application?
KINTEK specializes in laboratory equipment and consumables, helping labs like yours achieve precise and reliable results. Our experts can guide you to the perfect oven size—ensuring optimal temperature uniformity, efficient workflow, and energy savings—based on your exact samples and throughput needs.
Don't let the wrong oven size compromise your work. Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Scientific Electric Heating Blast Drying Oven
- 1200℃ Muffle Furnace Oven for Laboratory
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
- Laboratory Vortex Mixer Orbital Shaker Multifunctional Rotation Oscillation Mixer
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer PTFE Beaker and Lids
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a laboratory drying oven in catalyst treatment? Ensure Structural Integrity & High Performance
- What is the role of a blast drying oven in COF synthesis? Driving High-Crystallinity Solvothermal Reactions
- What is the function of a laboratory drying oven in Zr2.5Nb alloy pretreatment? Ensure Precise Corrosion Test Results
- How does a controlled drying process ensure the quality of radiochromic films? Achieve Precise Dosimetric Results
- How does a laboratory constant temperature drying oven contribute to the processing of synthesized Zinc Oxide precipitates?



















