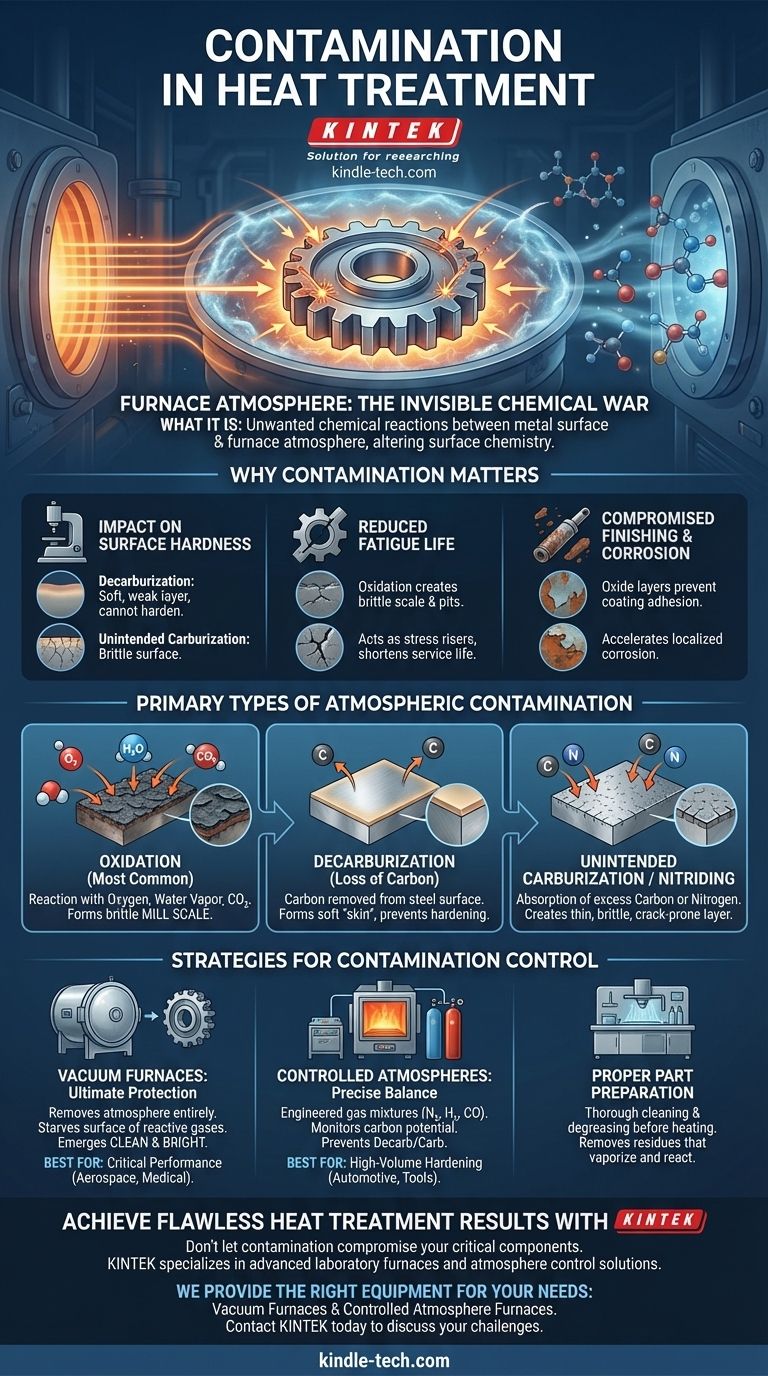
In heat treatment, contamination is any unwanted chemical reaction between the surface of a metal part and its surrounding environment, primarily the furnace atmosphere. These reactions alter the surface chemistry and microstructure of the part, often degrading its intended mechanical properties like hardness, fatigue life, and corrosion resistance. The goal of modern heat treatment is as much about controlling these surface reactions as it is about controlling temperature.
The core challenge of heat treatment is not just about heating and cooling metal; it's about managing the invisible chemical war that rages at the part's surface. Failing to control the furnace atmosphere means you are not controlling the final properties of your component.
Why Contamination is a Critical Concern
Contamination isn't merely a cosmetic issue; it directly undermines the purpose of the heat treatment process itself. The changes it causes can lead to premature component failure.
Impact on Surface Hardness
Many heat treatments, like hardening steel, rely on a precise carbon content at the surface. Contamination directly attacks this.
Decarburization is the loss of carbon from the surface, creating a soft, weak layer that cannot be hardened properly. Unintended carburization is the opposite, where excess carbon is absorbed, potentially making the surface too brittle.
Reduced Fatigue Life
Contamination like oxidation creates a rough, brittle layer of scale on the surface. This scale can flake off, leaving microscopic pits and cracks.
These surface defects act as stress risers, creating initiation points for fatigue cracks to form and grow under cyclic loading, significantly shortening the component's service life.
Compromised Finishing and Corrosion
A contaminated surface is chemically different from the base metal. This can cause problems with subsequent manufacturing steps.
Oxide layers can prevent proper adhesion for coatings like paint or plating. They can also create galvanic cells that accelerate localized corrosion.
The Primary Types of Atmospheric Contamination
At elevated temperatures, metal surfaces are highly reactive. The gases inside the furnace are the primary agents of contamination.
Oxidation: The Most Common Threat
Oxidation is the reaction of the metal surface with oxygen, water vapor (H₂O), or carbon dioxide (CO₂). This is the most common form of contamination.
It forms a layer of metallic oxide, often called mill scale. This scale must typically be removed through costly secondary operations like sandblasting or acid pickling.
Decarburization: The Loss of Carbon
For steels, decarburization is a major concern. It occurs when gases in the atmosphere react with and remove carbon from the surface layers of the steel.
The result is a soft "skin" on the part that will not respond to hardening. This is particularly damaging for components that rely on high surface hardness for wear resistance, such as gears and bearings.
Unintended Carburization or Nitriding
The opposite problem can also occur. If the furnace atmosphere has an excessively high concentration of carbon-monoxide or nitrogen-bearing gases (like ammonia), the metal surface can absorb these elements.
While sometimes done intentionally (in processes called carburizing or nitriding), this unintended absorption can create a thin, extremely brittle surface layer that is prone to chipping or cracking.
Strategies for Contamination Control
Preventing contamination requires isolating the hot metal part from a reactive atmosphere. The method chosen depends on the material, the process, and the required quality of the final part.
Vacuum Furnaces: The Ultimate Protection
The most effective way to prevent atmospheric contamination is to remove the atmosphere entirely.
In a vacuum furnace, air is pumped out before heating begins. This starves the surface of reactive gases like oxygen, ensuring the part emerges clean and bright with its original surface chemistry intact.
Controlled Atmospheres: A Precise Balance
For many applications, creating a precisely engineered atmosphere is a more cost-effective solution.
These atmospheres use specific mixtures of gases (like nitrogen, hydrogen, and carbon monoxide) to create an environment that is chemically neutral or even beneficial to the part's surface. The "carbon potential" of the gas is carefully monitored and controlled to prevent decarburization or unintended carburization.
Proper Part Preparation
Contamination doesn't only come from the furnace atmosphere. It can also come from the parts themselves.
Residues from cutting fluids, rust inhibitors, or even fingerprints can vaporize at high temperatures and cause unwanted surface reactions. Thorough cleaning and degreasing of parts before heat treatment is a critical first step.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct level of atmospheric control is a balance between metallurgical requirements, final part quality, and cost.
- If your primary focus is critical performance and finish (aerospace, medical): A vacuum furnace is non-negotiable. It provides the highest level of purity and guarantees that the surface properties are not compromised.
- If your primary focus is consistent, high-volume hardening (automotive gears, tools): A controlled atmosphere furnace offers the best balance of performance and cost, allowing for precise control over surface carbon.
- If your primary focus is bulk treatment where surface finish is not critical (annealing raw stock): Simpler furnaces with less atmospheric control may be acceptable, but you must account for post-processing steps like shot blasting to remove scale.
Ultimately, controlling the invisible furnace atmosphere is the key to achieving visible, reliable, and consistent results in your heat-treated components.
Summary Table:
| Type of Contamination | Primary Cause | Key Negative Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Oxidation | Reaction with O₂, H₂O, or CO₂ | Forms brittle scale, reduces fatigue life |
| Decarburization | Loss of carbon from steel surface | Creates a soft layer, prevents proper hardening |
| Unintended Carburization/Nitriding | Absorption of excess carbon/nitrogen | Creates a brittle surface, prone to chipping |
Achieve Flawless Heat Treatment Results with KINTEK
Don't let contamination compromise the integrity of your critical components. KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory furnaces and atmosphere control solutions designed to prevent oxidation, decarburization, and other surface reactions.
We provide the right equipment for your needs:
- Vacuum Furnaces: For the ultimate protection of high-value parts in aerospace and medical applications.
- Controlled Atmosphere Furnaces: For precise, high-volume hardening of automotive and tooling components.
Our experts can help you select the perfect system to guarantee consistent hardness, improved fatigue life, and a superior finish—eliminating costly secondary processing.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your heat treatment challenges and ensure your components perform reliably.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the vacuum heat treatment cycle? Achieve Superior Material Purity and Precision
- What is vacuum furnace high temperature? Unlock the Range for Your Material Processing
- Why do you vacuum for heat treatment? Achieve Flawless, High-Performance Metal Components
- What are the advantages of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Superior Purity and Control in Heat Treatment
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost



















