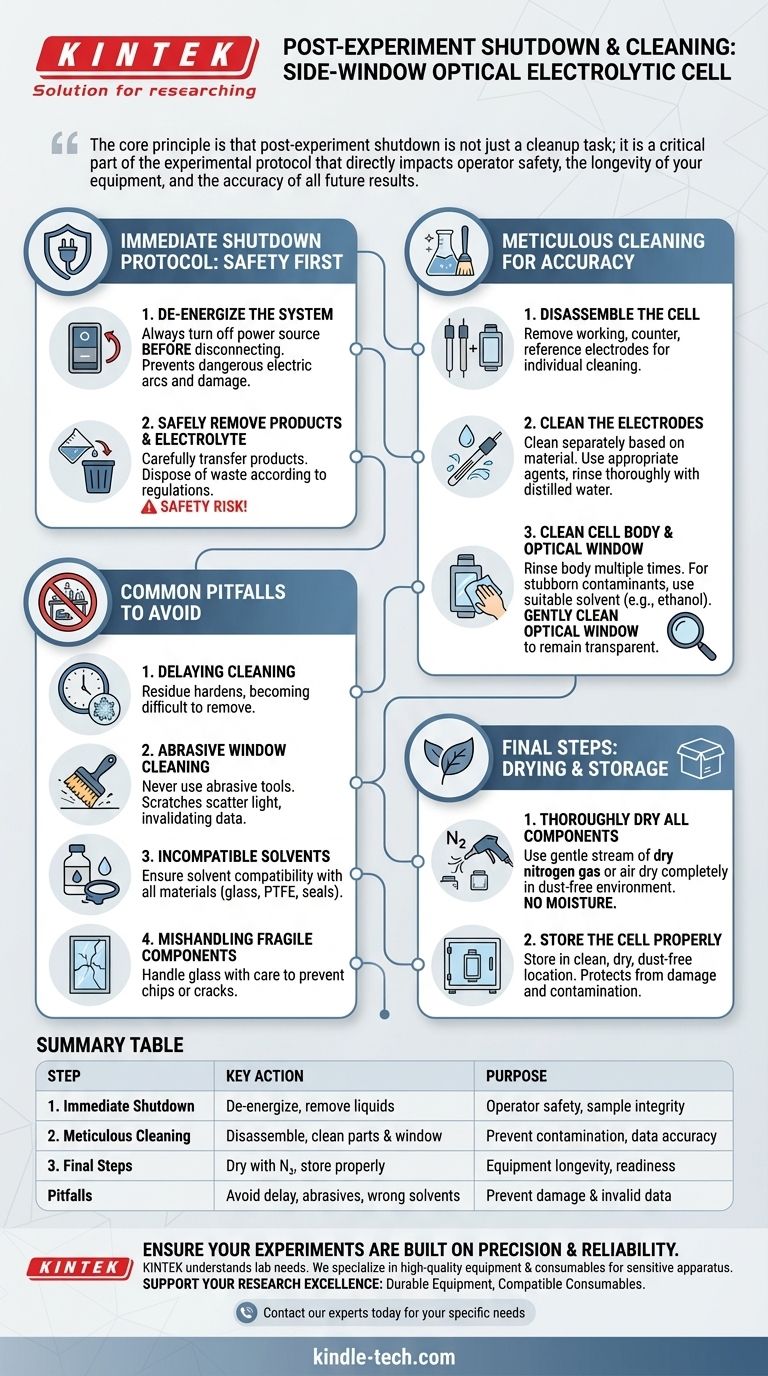
The correct procedure for shutting down and cleaning a side-window optical electrolytic cell is a systematic, multi-step process focused on safety, sample integrity, and equipment preservation. It begins with de-energizing the system, followed by the careful removal of all liquids, a thorough cleaning of the disassembled components, and finally, proper drying and storage.
The core principle is that post-experiment shutdown is not just a cleanup task; it is a critical part of the experimental protocol that directly impacts operator safety, the longevity of your equipment, and the accuracy of all future results.
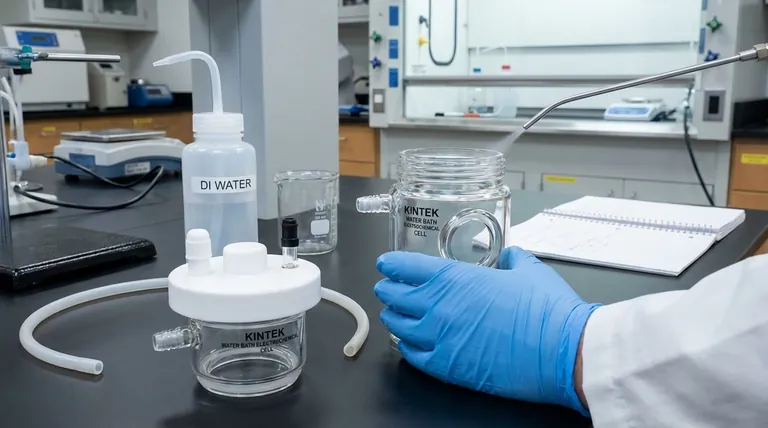

The Immediate Shutdown Protocol: Safety First
The first steps after your experiment concludes are centered on making the system safe to handle and preserving your results.
Step 1: De-energize the System
Always turn off the power source before disconnecting any electrical leads from the electrolytic cell. This is the most critical safety step.
Failing to do so can create an electric arc, which poses a significant safety risk to the operator and can damage both the potentiostat and the electrode connections.
Step 2: Safely Remove Products and Electrolyte
Once the cell is de-energized, carefully remove the post-reaction mixture.
Any products intended for further analysis should be transferred to appropriate storage containers. The remaining waste liquid and electrolyte must be handled and disposed of according to your institution's environmental safety regulations.
Meticulous Cleaning for Future Accuracy
Immediate and thorough cleaning prevents the buildup of residue, which can contaminate future experiments and is much harder to remove once it has dried.
Step 1: Disassemble the Cell
Carefully disassemble the cell components. This includes removing the working, counter, and reference electrodes from the cell body.
Handling each part individually allows for more effective cleaning and inspection.
Step 2: Clean the Electrodes
Clean the electrodes separately according to their specific material requirements. This prevents cross-contamination and ensures their surfaces are pristine for the next use.
Use appropriate cleaning agents to remove any dirt, oxides, or residue, then rinse them thoroughly with distilled or deionized water.
Step 3: Clean the Cell Body and Optical Window
Begin by rinsing the cell body multiple times with distilled or deionized water to remove the bulk of the residual electrolyte.
For more stubborn contaminants, a soak with a suitable organic solvent like ethanol may be necessary. Crucially, pay special attention to the optical window, cleaning it gently to ensure it remains perfectly transparent and free of scratches.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes during cleaning can be as detrimental as errors during the experiment itself. Being aware of these common pitfalls is essential.
Pitfall 1: Delaying the Cleaning Process
Never let the cell sit uncleaned for an extended period. Electrolyte salts and reaction byproducts can crystallize and harden, making them extremely difficult to remove without harsh methods that could damage the cell.
Pitfall 2: Abrasive Cleaning of the Optical Window
The optical window is a precision component. Never use abrasive brushes or powders to clean it.
Scratches or residue on the window will scatter light, rendering any future optical measurements inaccurate and invalidating your data.
Pitfall 3: Using Incompatible Solvents
Ensure any cleaning solvent you use is compatible with all materials of your cell, which may include glass, PTFE, and various sealing O-rings. An incompatible solvent can cause materials to swell, degrade, or leach contaminants.
Pitfall 4: Mishandling Fragile Components
Many electrolytic cells are constructed from glass. Always handle the cell body with care to prevent chips or cracks, which can compromise its seal and structural integrity.
Final Steps: Drying and Storage
The final stage ensures the cell is ready for its next use and protected from environmental contamination.
Step 1: Thoroughly Dry All Components
After a final rinse with distilled water, dry all parts of the cell. The preferred method is using a gentle stream of dry nitrogen gas.
Alternatively, you can allow the components to air dry completely in a clean, dust-free environment. Ensure no moisture remains, as it can cause corrosion or affect the next experiment's chemistry.
Step 2: Store the Cell Properly
Once dry, reassemble the cell or store the components in a clean, dry, and dust-free location. Proper storage protects the cell, particularly the optical window, from dust and accidental damage.
Making the Right Choice for Your Protocol
Your emphasis may change slightly depending on the specific demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is operator safety: Your first and most critical action is always to turn off the power source before touching any connections.
- If your primary focus is experimental reproducibility: Your priority should be immediate and meticulous cleaning of the electrodes and the optical window to eliminate any trace of contamination.
- If your primary focus is equipment longevity: Pay close attention to gentle handling, using compatible solvents, and ensuring proper, dust-free storage.
Ultimately, a disciplined shutdown and cleaning procedure is the hallmark of professional, reliable, and repeatable scientific research.
Summary Table:
| Step | Key Action | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Immediate Shutdown | De-energize system, remove electrolyte/products | Operator safety, sample integrity |
| 2. Meticulous Cleaning | Disassemble cell, clean electrodes & optical window | Prevent contamination, ensure data accuracy |
| 3. Final Steps | Dry components (e.g., with N₂ gas), store properly | Equipment longevity, readiness for next use |
| Common Pitfalls | Delaying cleaning, abrasive window cleaning | Avoid damage and invalid data |
Ensure Your Experiments are Built on a Foundation of Precision and Reliability
A proper shutdown and cleaning protocol is critical for the safety of your team and the integrity of your data. KINTEK understands the precise needs of laboratory professionals. We specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including items essential for the care of sensitive apparatus like optical electrolytic cells.
Let us support your research excellence:
- Durable Equipment: Reliable components built for repeatable performance.
- Compatible Consumables: The right solvents and materials to protect your investment.
Ready to enhance your lab's protocols and equipment? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Thin-Layer Spectral Electrolysis Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
People Also Ask
- What are the typical volumes and aperture configurations for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Optimize Your Electrochemical Setup
- What optical features does the H-type electrolytic cell have? Precision Quartz Windows for Photoelectrochemistry
- What is the overall structure of the H-type double-layer optical water bath electrolytic cell? Precision Design for Controlled Experiments
- What is the structure of an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? A Guide to Precise Electrochemical Separation
- What are the standard opening specifications for an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? Asymmetrical Ports for Precise Electrochemistry



















