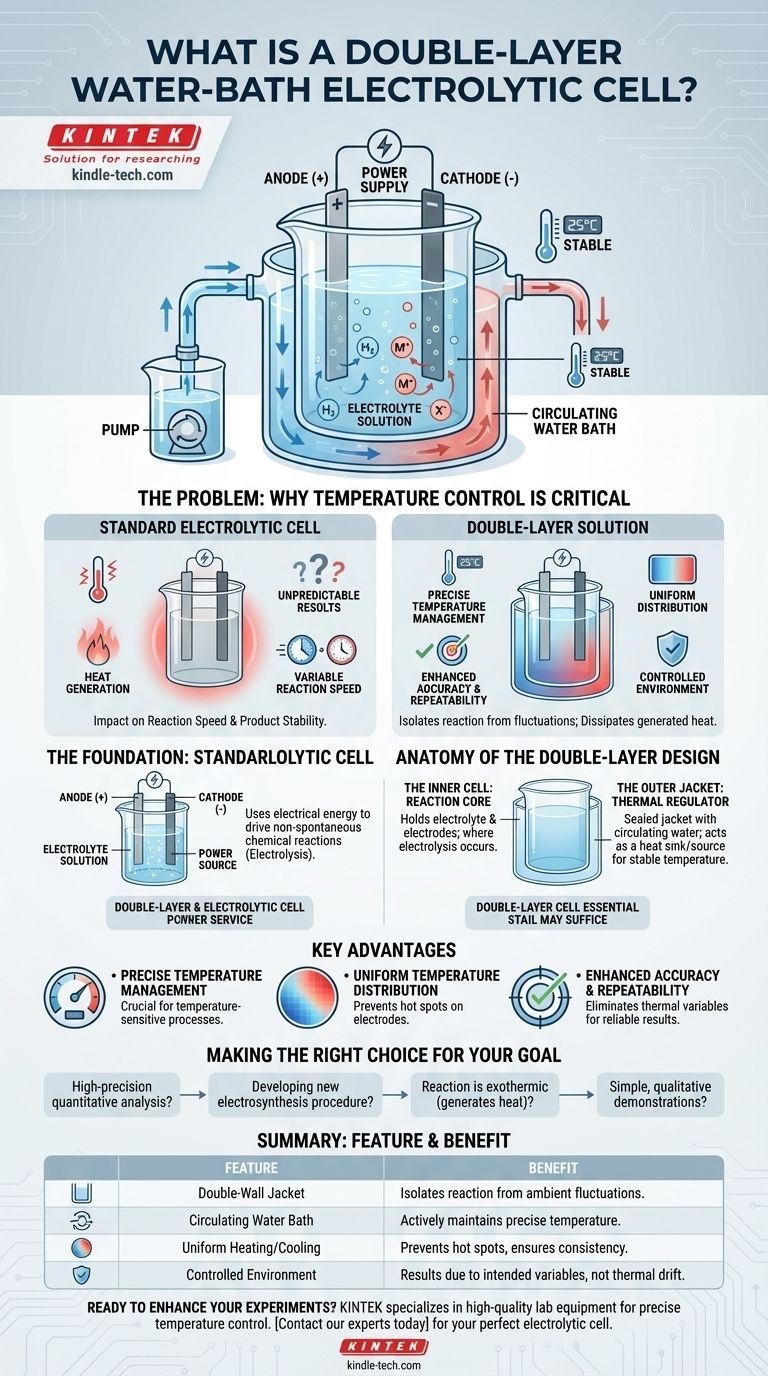
A double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell is a specialized piece of laboratory equipment designed for running electrolysis experiments under precisely controlled temperature conditions. It consists of an inner container for the chemical reaction, which is surrounded by an outer jacket, or container, through which a temperature-controlled liquid (like water) is circulated. This design isolates the reaction from ambient temperature fluctuations and dissipates any heat generated by the process itself.
The fundamental purpose of a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell is to eliminate temperature as a variable in an experiment. By creating a stable thermal environment, it ensures that the results of electrolysis are more accurate, repeatable, and directly attributable to the intended electrochemical process.

The Foundation: Understanding a Standard Electrolytic Cell
What It Does
An electrolytic cell is a device that uses electrical energy to drive a chemical reaction that would not happen on its own. This process is called electrolysis.
The externally applied electricity provides the energy needed to overcome the reaction's activation barrier, often to decompose stable chemical compounds into their constituent elements.
Core Components
A standard cell contains two electrodes, an anode (positive) and a cathode (negative), submerged in a liquid solution called an electrolyte. An external power source forces a non-spontaneous redox reaction to occur.
The Problem: Why Temperature Control is Critical
Impact on Reaction Speed
Like most chemical reactions, the rate of electrolysis is highly sensitive to temperature. Higher temperatures typically increase reaction speed, while lower temperatures slow it down.
Without stable temperature, it's impossible to know if changes in your results are due to your experimental variables or simply a shift in the room's temperature.
Heat Generation and Product Stability
The process of electrolysis itself can generate significant heat. This self-heating can alter the reaction conditions, potentially leading to unwanted side reactions or the degradation of the desired product.
A lack of temperature control can compromise the purity and yield of the electrolysis process, making results unreliable.
The Solution: Anatomy of the Double-Layer Design
The double-layer water-bath cell directly solves the problem of thermal instability through its simple and effective two-part structure.
The Inner Cell: The Reaction Core
This is the central container where the actual electrolysis takes place. It holds the electrolyte solution and the electrodes, functioning just like a standard electrolytic cell.
The Outer Jacket: The Thermal Regulator
This external layer forms a sealed jacket around the inner cell. A constant-temperature liquid, typically water from a circulating bath, flows through this jacket.
This continuous flow acts as a heat sink or source, actively removing excess heat generated by the reaction or warming the cell to maintain a specific target temperature. This ensures the temperature inside the inner cell remains uniform and constant.
Key Advantages of the Double-Layer System
Precise Temperature Management
The primary advantage is the ability to set and maintain the reaction temperature with high precision. This is crucial for temperature-sensitive processes like organic electrosynthesis or when studying reaction kinetics.
Uniform Temperature Distribution
The circulating water bath ensures that the entire inner cell is heated or cooled evenly. This prevents localized "hot spots" on electrode surfaces, which could otherwise lead to inconsistent results and lower efficiency.
Enhanced Accuracy and Repeatability
By eliminating thermal fluctuations, the double-layer cell ensures that any observed effects are due to the intended variables of the experiment. This makes experiments far more accurate and repeatable, which is the cornerstone of sound scientific research.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
- If your primary focus is high-precision quantitative analysis: The double-layer cell is essential to guarantee that temperature variations do not skew your measurements.
- If you are developing a new electrosynthesis procedure: Controlling temperature is critical for optimizing product yield and minimizing impurities.
- If your reaction is known to be exothermic (generates heat): The water bath provides a necessary cooling mechanism to maintain stable conditions.
- If you are conducting simple, qualitative demonstrations not sensitive to temperature: A standard, single-wall electrolytic cell may be sufficient and more cost-effective.
Ultimately, choosing the right tool is the first step toward achieving reliable and meaningful experimental outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Double-Wall Jacket | Isolates reaction from ambient temperature fluctuations. |
| Circulating Water Bath | Actively heats or cools to maintain a precise, set temperature. |
| Uniform Heating/Cooling | Prevents hot spots on electrodes for consistent results. |
| Controlled Environment | Ensures experimental outcomes are due to intended variables, not thermal drift. |
Ready to enhance the accuracy and repeatability of your electrolysis experiments?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including double-layer water-bath electrolytic cells designed for precise temperature control. Whether you're optimizing an electrosynthesis procedure or conducting sensitive quantitative analysis, our equipment helps you achieve reliable, publication-ready results.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect electrolytic cell for your laboratory's specific needs and ensure your research is built on a foundation of thermal stability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double-Layer Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
People Also Ask
- How can water and gas leaks be prevented in a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? A Guide to Proactive Maintenance
- What safety precautions are necessary for temperature control when using a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Experiments
- What are the procedures for after using a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Ensure Equipment Longevity and Data Accuracy
- What are the typical volumes and aperture configurations for a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Optimize Your Electrochemical Setup
- What is the overall structure of the H-type double-layer optical water bath electrolytic cell? Precision Design for Controlled Experiments