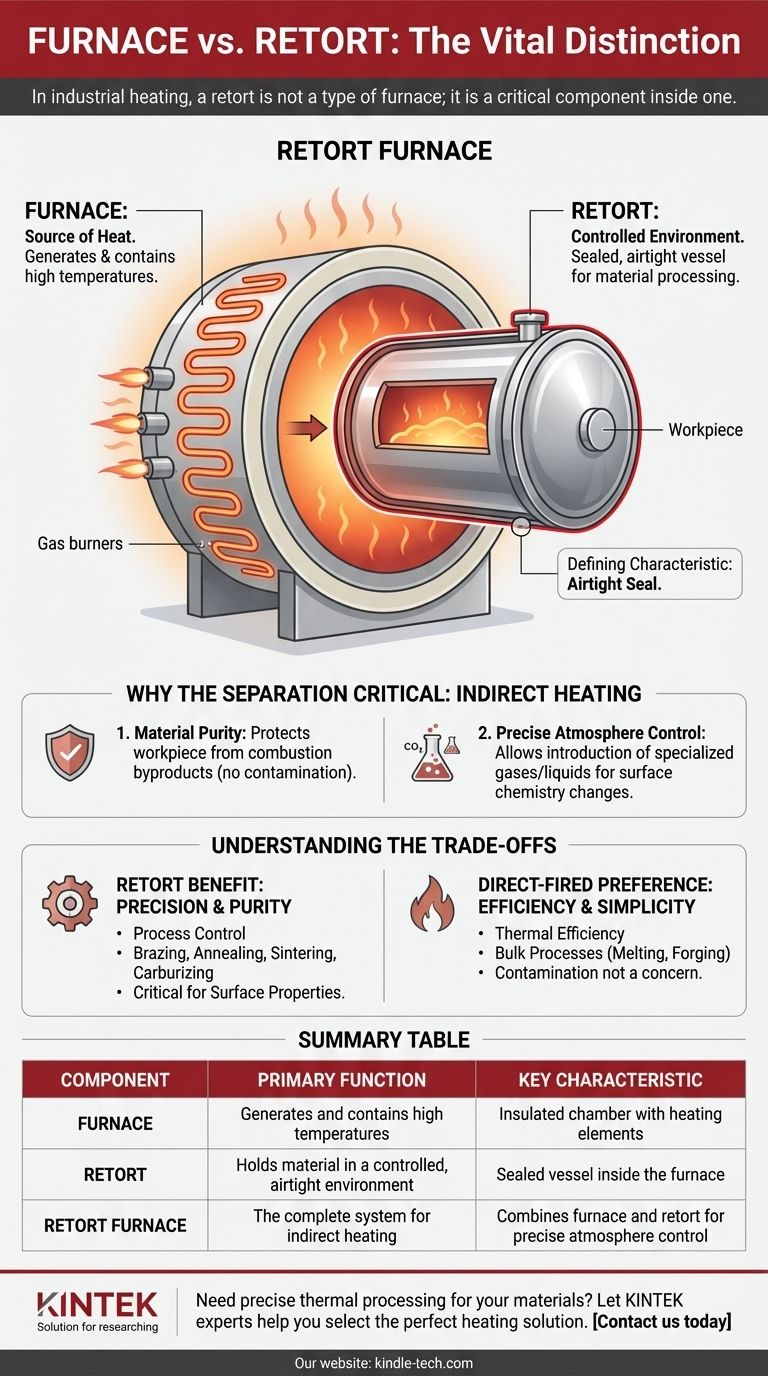
In industrial heating, a retort is not a type of furnace; it is a critical component inside one. A retort is the sealed, airtight vessel that holds the material being processed, while the furnace is the surrounding insulated chamber that provides the heat. The confusion arises because the entire apparatus—the furnace containing the retort—is often called a "retort furnace."
The core distinction is one of function, not of type. A furnace generates heat, while a retort creates a controlled, isolated environment for the material within that heat. Thinking of a retort as a specialized, sealed pot placed inside a powerful oven helps clarify their relationship.

Deconstructing the "Retort Furnace"
To understand the difference, it's best to break down a typical retort furnace into its two primary functional parts: the furnace and the retort itself. They work together as a system to achieve indirect heating.
The Furnace: The Source of Heat
The "furnace" component is the outer structure. Its sole job is to generate and contain high temperatures safely and efficiently.
This part consists of a heavily insulated box or chamber, along with heating elements. These heaters are typically either electric resistance coils or gas burners that heat the space around the retort.
The Retort: The Controlled Environment
The "retort" is the specialized vessel that sits inside the furnace. It is the chamber that directly contains the workpiece or material being heat-treated.
The defining characteristic of a retort is that it is gas-tight or "airtight." This seal is the reason for its existence. It can be designed as a horizontal tube or a vertical chamber, depending on the application.
Why the Separation is Critical
The separation between the heat source (furnace) and the material (in the retort) is the key to this technology. This indirect heating method provides two crucial advantages.
First, it protects the workpiece from the byproducts of combustion if the furnace is gas-fired. This prevents contamination and ensures material purity.
Second, because the retort is sealed, it allows for precise atmosphere control. Specialized gases (like nitrogen, argon, or hydrogen) or even liquids can be introduced to the retort. This controlled atmosphere can prevent oxidation or actively change the surface chemistry of the material, a process essential for many types of advanced heat treating.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use a retort furnace is a decision to prioritize control over other factors. This involves clear engineering trade-offs compared to simpler, direct-heating furnaces.
The Benefit of a Retort: Precision and Purity
The primary advantage is process control. When you need to protect a material from oxygen or subject it to a specific chemical environment at high temperatures, a retort is non-negotiable.
This is critical for applications like brazing, annealing sensitive alloys, sintering powdered metals, and carburizing steel, where the surface properties of the final product are paramount.
The Limitation: Thermal Inefficiency and Complexity
Indirect heating is inherently less energy-efficient. Heat must be generated in the furnace chamber, transfer (via radiation and convection) to the outer wall of the retort, and then conduct through the retort wall to reach the material. Each step involves some thermal loss.
Retort furnaces are also more complex and often more expensive to build and maintain due to the need for high-integrity seals and atmosphere management systems.
When Direct Heating is Preferred
For processes where material contamination from the heat source is not a concern, a direct-fired furnace is often a better choice.
In these systems, the flame and combustion gases come into direct contact with the material. This is more thermally efficient and simpler, making it ideal for bulk processes like melting scrap metal, forging large billets, or firing ceramics where a controlled atmosphere is unnecessary.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding this distinction allows you to select the correct industrial heating process based on your specific objective. The question is not "furnace or retort," but rather "what kind of thermal process do I need?"
- If your primary focus is material purity and controlled atmosphere: You require a process using a retort, found within a piece of equipment called a retort furnace or muffle furnace.
- If your primary focus is simple, high-volume bulk heating: A direct-fired furnace without a retort is likely the more efficient and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, knowing the role of the retort empowers you to choose a process that delivers either maximum efficiency or exacting chemical precision.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Furnace | Generates and contains high temperatures | Insulated chamber with heating elements |
| Retort | Holds material in a controlled, airtight environment | Sealed vessel inside the furnace |
| Retort Furnace | The complete system for indirect heating | Combines the furnace and retort for precise atmosphere control |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials?
Choosing the right equipment is critical for achieving your desired results, whether you need the efficiency of a direct-fired furnace or the exacting control of a retort system. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs with high-performance furnaces and retorts designed for material purity and process reliability.
Let our experts help you select the perfect heating solution for your application. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a reaction furnace contribute to the synthesis of uranium nitride precursor (U2N3) powder? High-Purity Controls
- What are the advantages of using an SPS furnace for LATP? Achieve Higher Ionic Conductivity & Faster Sintering
- What is the annealing temperature of molybdenum? Optimize Your Thermal Processing for Pure Mo & Alloys
- What is the arc melting technique? Master High-Purity Metal Melting for Refractory Alloys
- What does it mean to sinter metals? A Guide to Solid-State Fusion for Strong, Complex Parts
- What is the primary function of a vacuum heating furnace? Optimize High-Purity Li2O Synthesis
- What is the primary purpose of using an electric drying oven for dense refractory bricks? Optimize Raw Material Prep
- What types of steel can be quenched? A Guide to Hardenable Steels for Optimal Performance



















