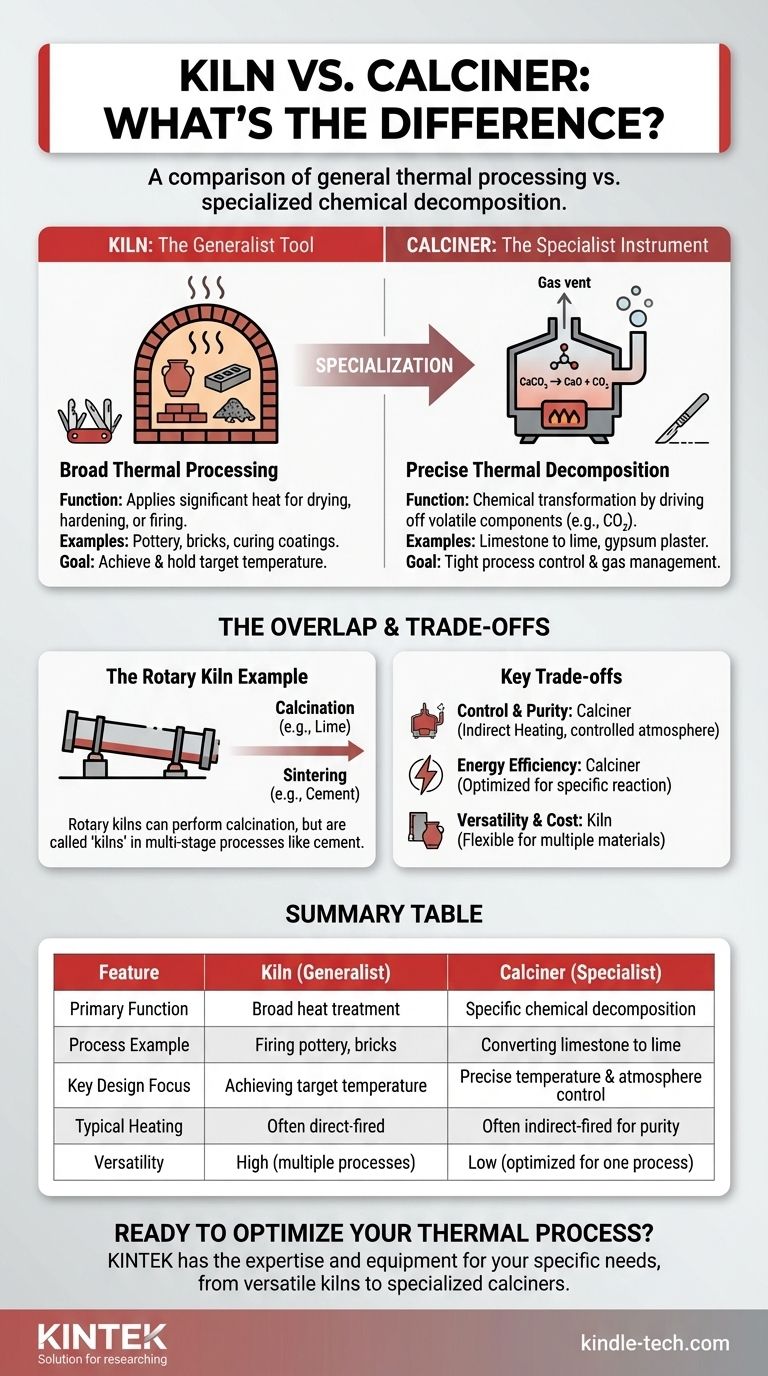
In essence, the primary difference is one of specialization. A kiln is a broad term for any high-temperature furnace used for processes like drying, hardening, or firing materials. A calciner, on the other hand, is a specific type of furnace designed and optimized for calcination—a precise thermal treatment that causes chemical decomposition, typically by removing volatile components like carbon dioxide or water from a solid.
While many calciners are technically a type of kiln, the key distinction lies in the intended process. A kiln is a generalist's tool for applying heat, whereas a calciner is a specialist's instrument engineered specifically for the chemical process of calcination.

What is a Kiln? The Generalist Tool
A kiln is best understood as a thermally insulated chamber, or an oven, that produces temperatures sufficient to complete a desired process, such as hardening, drying, or inducing chemical changes.
Broad Thermal Processing
The function of a kiln is simply to apply a significant amount of heat. This can be for a vast range of applications, from firing pottery and bricks to curing coatings or producing cement.
Common Examples
The most recognizable examples are pottery kilns, which harden clay, and brick kilns, which fire bricks to achieve structural integrity. Large industrial rotary kilns used in cement manufacturing are also a primary example.
Key Functionality
The main goal in a general kiln is to achieve and hold a target temperature. While the atmosphere may be controlled (e.g., for oxidation or reduction in pottery), the design is not necessarily optimized for managing the off-gassing of specific volatile compounds as a primary chemical objective.
What is a Calciner? The Specialist Instrument
A calciner is engineered for one core process: calcination. This specificity deeply influences its design and operation.
The Process of Calcination
Calcination is a precise thermal decomposition process. A solid material is heated to a high temperature in a controlled atmosphere, driving off a specific volatile fraction. It is not simply drying; it is a chemical transformation.
A classic example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) to produce lime (calcium oxide, CaO) by driving off carbon dioxide (CO₂). Another is producing gypsum plaster by heating gypsum rock to remove bound water molecules.
Designed for Process Control
Because calcination is a specific chemical reaction, calciners are designed for tight process control. This often includes precise temperature management and efficient systems to handle and remove the large volumes of gas released during the reaction.
Indirect vs. Direct Firing
Many calciners use indirect heating, where the material is heated through the walls of a chamber, keeping it separate from the combustion flame and flue gases. This prevents contamination and allows for precise control of the atmosphere around the material—something often critical for the desired chemical outcome. Kilns, especially large rotary kilns, are frequently directly fired.
The Overlap: When a Kiln Functions as a Calciner
The confusion between the terms often arises because the most common piece of industrial hardware for both processes can be the same: the rotary kiln.
The Rotary Kiln Example
A rotary kiln is a large, rotating industrial furnace. When this device is used to heat limestone to produce lime, it is performing calcination and can rightly be called a calciner.
However, in cement production, that same rotary kiln first performs calcination (driving CO₂ from limestone) and then continues to heat the material to an even higher temperature to cause sintering. Because its function extends beyond just calcination, it is almost always referred to as a cement kiln.
Function Defines the Name
Ultimately, the most accurate term depends on the primary, intended function of the equipment. If a furnace is designed, built, and operated specifically to perform calcination, it is a calciner. If it is used for a broader range of heat treatment tasks, it is a kiln.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a general-purpose kiln and a specialized calciner involves clear engineering and financial trade-offs.
Process Control and Purity
A dedicated calciner, especially an indirect-fired model, offers superior control over the material's processing atmosphere. This is essential for high-purity applications where contamination from combustion gases would be unacceptable.
Energy Efficiency
A system engineered specifically for a single calcination reaction can be optimized for heat transfer and gas removal for that exact process. This often results in higher energy efficiency compared to using a more versatile, less-specialized kiln for the same task.
Versatility and Cost
A general-purpose kiln offers far more flexibility. It can be used for multiple materials and processes, making it a more versatile asset. A highly specialized calciner is an expert at one task but may be unsuitable for others.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of terminology and equipment depends entirely on the specific industrial process you are evaluating.
- If your primary focus is firing ceramics, hardening bricks, or general heat treating: You are dealing with a kiln.
- If your primary focus is the chemical decomposition of a mineral to produce a new solid (e.g., lime from limestone): You require the process of calcination, which is best done in a calciner.
- If you are analyzing a multi-stage thermal process like cement manufacturing: Recognize that the equipment (a rotary kiln) is performing multiple functions, one of which is calcination.
Understanding this distinction between a general process and a specific one is the key to describing and designing thermal systems accurately.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Kiln (Generalist) | Calciner (Specialist) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Broad heat treatment (drying, firing, hardening) | Specific chemical decomposition (calcination) |
| Process Example | Firing pottery, curing bricks | Converting limestone to lime (CaCO₃ to CaO) |
| Key Design Focus | Achieving and holding target temperature | Precise temperature & atmosphere control for gas removal |
| Typical Heating | Often direct-fired | Often indirect-fired for purity |
| Versatility | High (multiple materials/processes) | Low (optimized for one process) |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Process?
Whether your project requires the versatile heat treatment of a kiln or the precise chemical decomposition of a calciner, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's needs. Our specialized lab equipment and consumables are designed for accuracy, efficiency, and purity.
Let us help you achieve superior results. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect thermal solution for your research or production goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















