In practical terms, there is no functional difference between a retort furnace and a muffle furnace. The two terms describe the same type of equipment, where the distinction is purely semantic and historical. A "retort" is the sealed vessel that holds the material, while the "muffle" is the separate chamber that encloses the retort, shielding it from the direct heat source. Therefore, a muffle furnace is simply a furnace that uses a muffle to heat a retort.
The core principle to understand is not the name, but the function: indirect heating. Both terms describe a furnace designed to heat a sample without it ever touching the heating elements or combustion byproducts, ensuring purity and temperature uniformity.

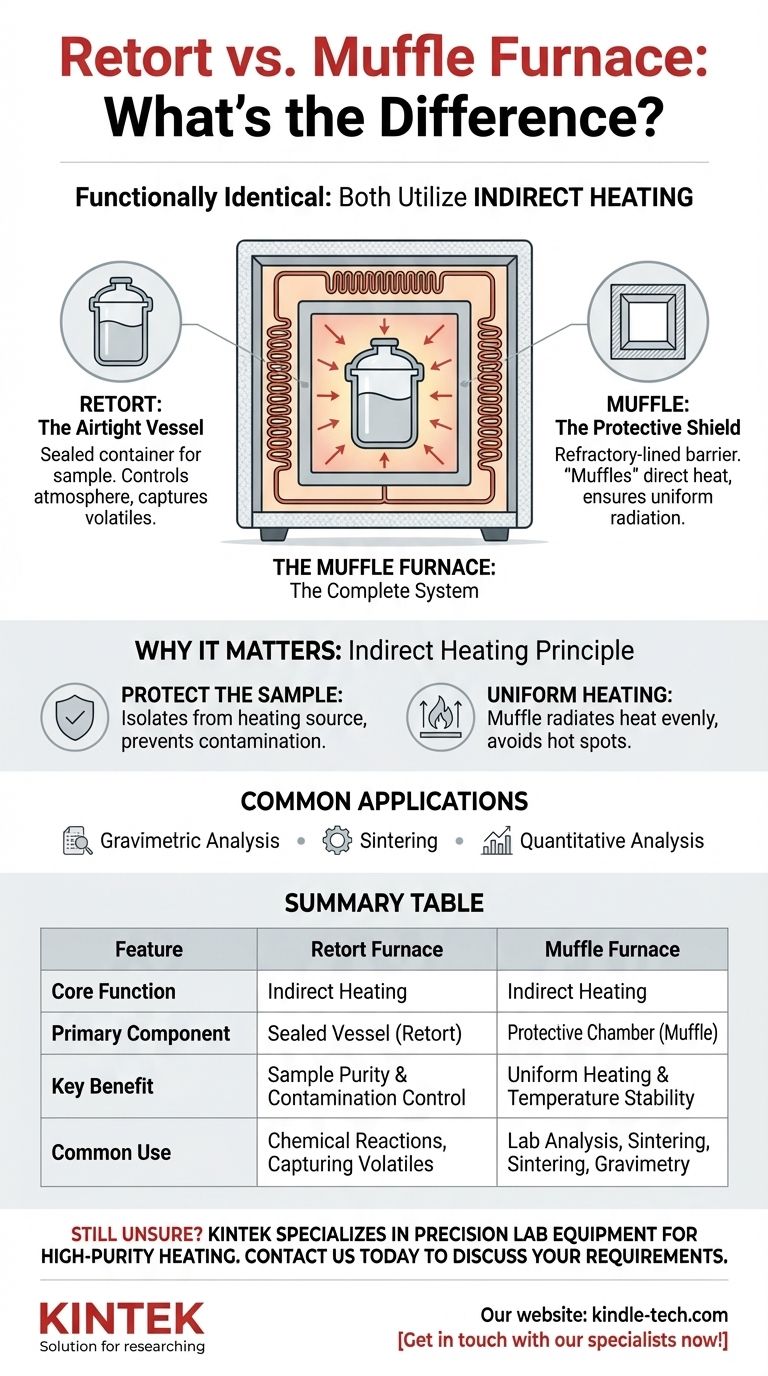
Deconstructing the Terminology: Retort vs. Muffle
The confusion between these terms stems from different industries using different language to describe parts of a whole. A chemist might talk about the retort, while a furnace engineer talks about the muffle.
The Retort: The Airtight Vessel
A retort is the container where you place your sample. Its defining feature is that it's sealed.
This term comes from the chemical industry, where containing a reaction, controlling the atmosphere inside the vessel, or capturing volatile byproducts is critical.
The Muffle: The Protective Shield
A muffle is a refractory-lined chamber that sits between the heating elements and the retort. It acts as a barrier.
The muffle's job is to "muffle" the direct, harsh heat. It absorbs energy from the heating elements and then radiates it evenly onto the retort, preventing hot spots and contamination.
The Muffle Furnace: The Complete System
A muffle furnace is the entire apparatus: the outer insulated cabinet, the heating elements (electric coils or gas burners), and the muffle chamber itself.
By definition, a muffle furnace is designed for indirect heating. In modern usage, "muffle furnace" has become the standard name for this type of equipment, especially for box-shaped lab furnaces.
Why This Distinction Matters: The Principle of Indirect Heating
Focusing on the "why" behind the design is more useful than debating the name. The muffle design exists to solve specific engineering challenges.
The Goal: Protect the Sample
The primary purpose of the muffle design is to isolate the sample from the heating source.
This prevents contamination from flaking electric elements or the byproducts of fuel combustion. It also provides much more uniform heating than exposed elements would.
Common Applications
This design is critical for processes like:
- Gravimetric analysis: Where any added mass from contamination would ruin the results.
- Sintering: Fusing powders where direct contact with heating elements could cause unwanted chemical reactions.
- Quantitative analysis: Any process requiring high purity and repeatable thermal conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
A muffle furnace is a specific tool, and its design comes with trade-offs compared to other furnace types.
Muffle Furnace vs. Tube Furnace
A tube furnace is superior for processes requiring precise atmospheric control. It's designed to have gas passed through a narrow tube, which is difficult to achieve in a large box-style muffle furnace.
However, a muffle furnace offers a much larger chamber, making it ideal for heating multiple samples or larger, bulkier objects in an air atmosphere.
Muffle Furnace vs. Simple Resistance Furnace
A standard box furnace might use exposed resistance elements within the chamber. This is a simpler, often cheaper design.
A muffle furnace, by contrast, uses its ceramic muffle to deliver cleaner, more uniform heat and often allows for faster temperature ramp-up rates. The muffle protects both the sample from the elements and the elements from any sample off-gassing.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
The right choice depends entirely on your material, your process, and your atmospheric requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or sensitive analysis: You need a muffle furnace to prevent sample contamination and ensure uniform heating.
- If your primary focus is processing bulk materials in an air atmosphere: A standard muffle (or box) furnace is an efficient and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is precise atmosphere control (e.g., using inert gas): A tube furnace is specifically designed for this and is the superior choice.
- If you are shopping for equipment: Treat the terms "muffle furnace" and "retort furnace" as functionally identical, but always verify the specifications for temperature range, uniformity, and atmosphere control.
Ultimately, focusing on the principle of indirect heating will serve you better than getting lost in historical terminology.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Retort Furnace | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Core Function | Indirect Heating | Indirect Heating |
| Primary Component | Sealed Vessel (Retort) | Protective Chamber (Muffle) |
| Key Benefit | Sample Purity & Contamination Control | Uniform Heating & Temperature Stability |
| Common Use | Chemical Reactions, Capturing Volatiles | Lab Analysis, Sintering, Gravimetry |
Still unsure which furnace is right for your lab's high-purity heating needs?
KINTEK specializes in precision lab equipment, including muffle furnaces designed for superior temperature control and sample protection. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution for applications like gravimetric analysis, sintering, or quantitative testing.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's reliable lab equipment can enhance your results.
Get in touch with our specialists now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the inside material of a muffle furnace? Choose the Right Lining for Your Application
- What temperature do you fire alumina? Achieve Optimal Density and Strength
- Do you need to heat the clean crucible before using it? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Process Accuracy
- What is the critical point of heat treatment? Master the Key to Steel Transformation
- What precautions should be taken while heating and cooling the crucible? Prevent Thermal Shock and Ensure Safety



















