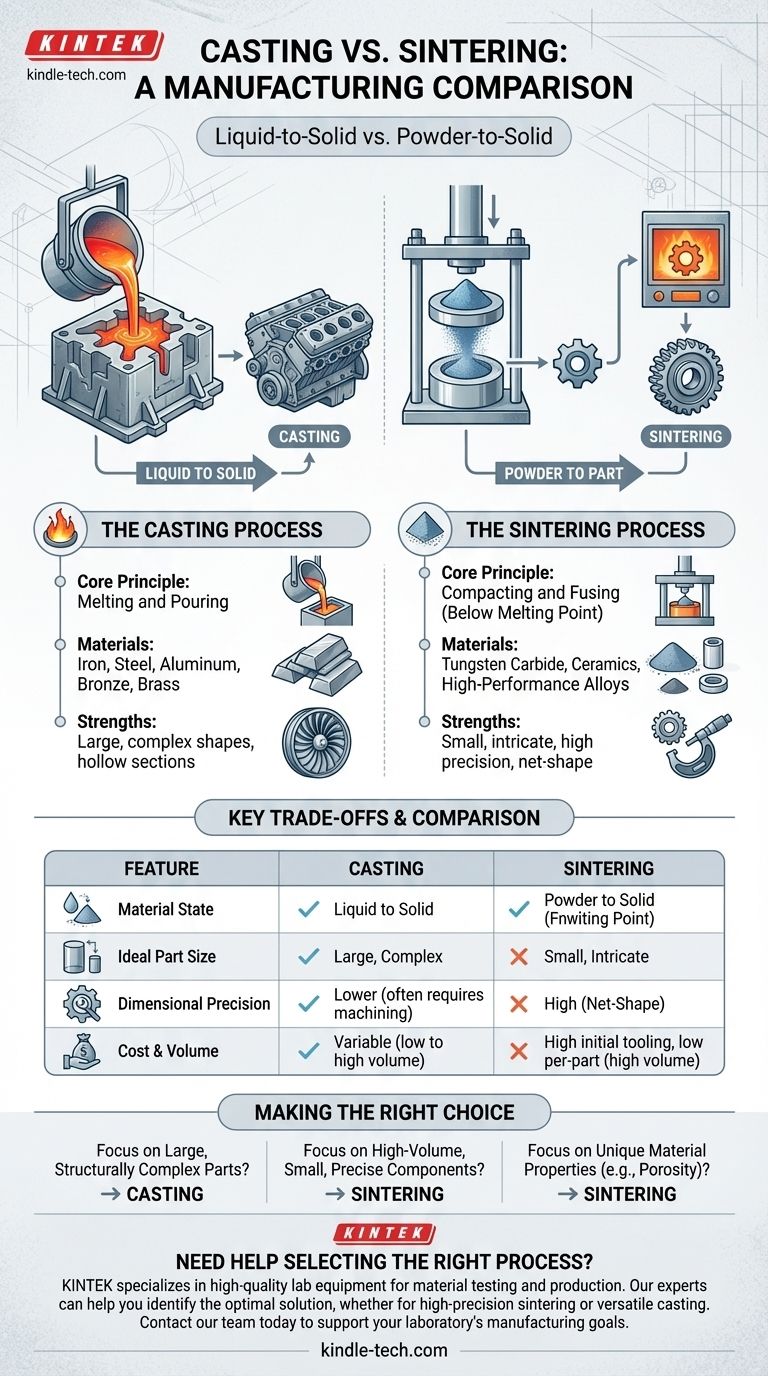
At a fundamental level, the difference between casting and sintering lies in the state of the material during manufacturing. Casting involves completely melting a material into a liquid state and pouring it into a mold to solidify. In contrast, sintering starts with a material in its powdered form, compresses it, and then heats it below its melting point until the particles fuse together into a solid object.
The core distinction is one of transformation: casting is a liquid-to-solid process ideal for large, complex shapes, while sintering is a powder-to-solid process that excels at creating small, high-precision parts with unique material properties.
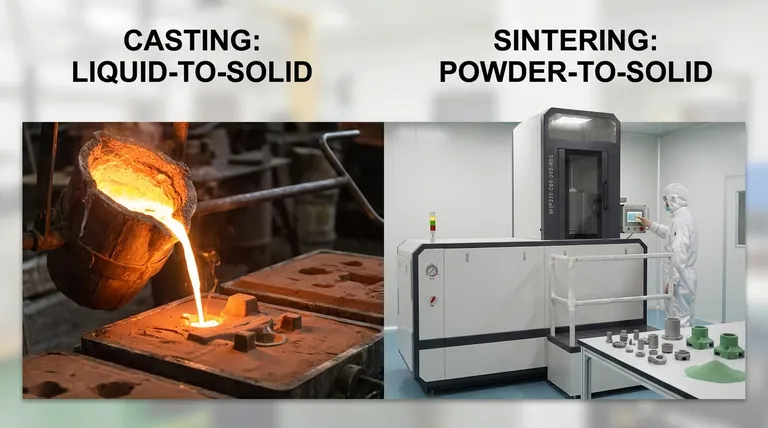
The Casting Process: From Liquid to Solid
Casting is one of the oldest and most versatile manufacturing methods. It relies on the simple principle of changing a material's phase from solid to liquid and back to solid within a shaped container.
The Core Principle: Melting and Pouring
The process begins by heating a metal or other material well above its melting point until it becomes a fully molten liquid. This liquid is then poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape. As the material cools, it solidifies, taking on the shape of the mold before being ejected or broken out.
Common Materials and Applications
Casting is compatible with a vast range of metals, including iron, steel, aluminum, bronze, and brass. This versatility makes it suitable for producing everything from massive engine blocks and industrial machine frames to intricate jewelry and pipe fittings.
Strengths of Casting
The primary advantage of casting is its ability to create very large and geometrically complex parts, including those with hollow sections or intricate internal passageways. Certain casting methods, like sand casting, have relatively low tooling costs, making them economical for prototypes and low-volume production runs.
The Sintering Process: From Powder to Part
Sintering, a key process in powder metallurgy, creates solid objects from powders without ever melting the primary material. It uses a combination of pressure and heat to bond particles together.
The Core Principle: Compacting and Fusing
First, a fine powder of a specific material (or a blend of materials) is placed into a die and compacted under immense pressure to form a "green part." This part is fragile but holds its shape. It is then placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated to a high temperature, but crucially, one that remains below the material's melting point. At this temperature, atomic diffusion occurs, welding the particles together and creating a strong, solid component.
Common Materials and Applications
Sintering is used for materials that are difficult to melt or machine, such as tungsten carbide, ceramics, and certain high-performance alloys. It's also used to create unique components like porous bronze bearings (which can be impregnated with oil) and high-volume automotive parts like transmission gears and camshaft lobes.
Strengths of Sintering
Sintering excels at producing small, intricate parts with very high dimensional accuracy. Because the parts often come out of the furnace in their final (or "net-shape") form, it eliminates the need for costly secondary machining. This process also minimizes material waste and allows for the creation of unique composites and alloys impossible to form through melting.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing between casting and sintering requires a clear understanding of the project's goals regarding size, precision, material, and cost.
Size and Complexity
Casting is the go-to method for large components. There is virtually no upper limit to the size of a cast part. It can also produce complex internal geometries that are impossible to achieve by compacting powder.
Sintering, on the other hand, is limited to smaller parts. The pressure required to compact the powder uniformly restricts the feasible size and thickness of the final component.
Precision and Finishing
Sintered parts are renowned for their high precision and excellent surface finish, often requiring no post-processing. They are considered a net-shape manufacturing process.
Cast parts typically have rougher surfaces and lower dimensional accuracy. They almost always require secondary machining operations to meet tight tolerances, adding time and cost to the production cycle.
Material Properties
Casting produces fully dense, isotropic parts, meaning their mechanical properties are the same in all directions.
Sintered parts almost always retain some level of porosity. While this can be a disadvantage for applications requiring maximum strength, it can also be a key design feature, as seen in self-lubricating bearings or filters.
Cost and Volume
Sintering involves high initial tooling costs for the dies, but the automated process leads to very low per-part costs at high production volumes.
Casting methods vary. Sand casting can be very cheap for one-off parts, while investment casting and die casting have higher tooling costs but are suitable for medium to high volumes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the component you need to produce.
- If your primary focus is large, structurally complex parts like an engine manifold: Casting is almost always the more viable and cost-effective method.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of small, precise components like transmission gears: Sintering offers superior dimensional accuracy and lower per-part costs once tooling is established.
- If your primary focus is unique material properties, such as controlled porosity or combining materials that don't alloy: Sintering provides capabilities that are simply impossible with traditional casting.
Understanding these foundational differences empowers you to select the manufacturing path that best aligns with your design intent, budget, and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Casting | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Material State | Liquid to Solid | Powder to Solid |
| Ideal Part Size | Large, Complex | Small, Intricate |
| Dimensional Precision | Lower (often requires machining) | High (Net-Shape) |
| Key Strength | Complex geometries, large parts | High precision, minimal waste, unique materials |
| Typical Materials | Iron, Steel, Aluminum, Brass | Tungsten Carbide, Ceramics, Alloys |
Need help selecting the right process for your components?
KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables for material testing and production. Whether your project requires the high-precision capabilities of sintering or the versatility of casting, our experts can help you identify the optimal solution.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's manufacturing and R&D goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- What are some of the attractive properties of hot isostatic pressed products? Achieve Perfect Density and Superior Performance
- What pressure is hot isostatic press? Achieve Full Density & Superior Material Performance
- What is the HIP material process? Achieve Near-Perfect Density and Reliability
- What is HIP in material processing? Achieve Near-Perfect Density for Critical Components
- What is the historical background of the Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) process? From Nuclear Roots to Industry Standard



















