While your question mentions two electrolytic cells, the core distinction in electrochemistry is between an electrolytic cell and a galvanic cell (also known as a voltaic cell). A galvanic cell generates electrical energy from a spontaneous chemical reaction, like a common battery. In contrast, an electrolytic cell uses an external source of electrical energy to force a non-spontaneous chemical reaction to occur.
The fundamental difference comes down to energy conversion. A galvanic cell converts stored chemical energy into electrical energy, while an electrolytic cell does the exact opposite, converting electrical energy into chemical energy to produce desired substances.

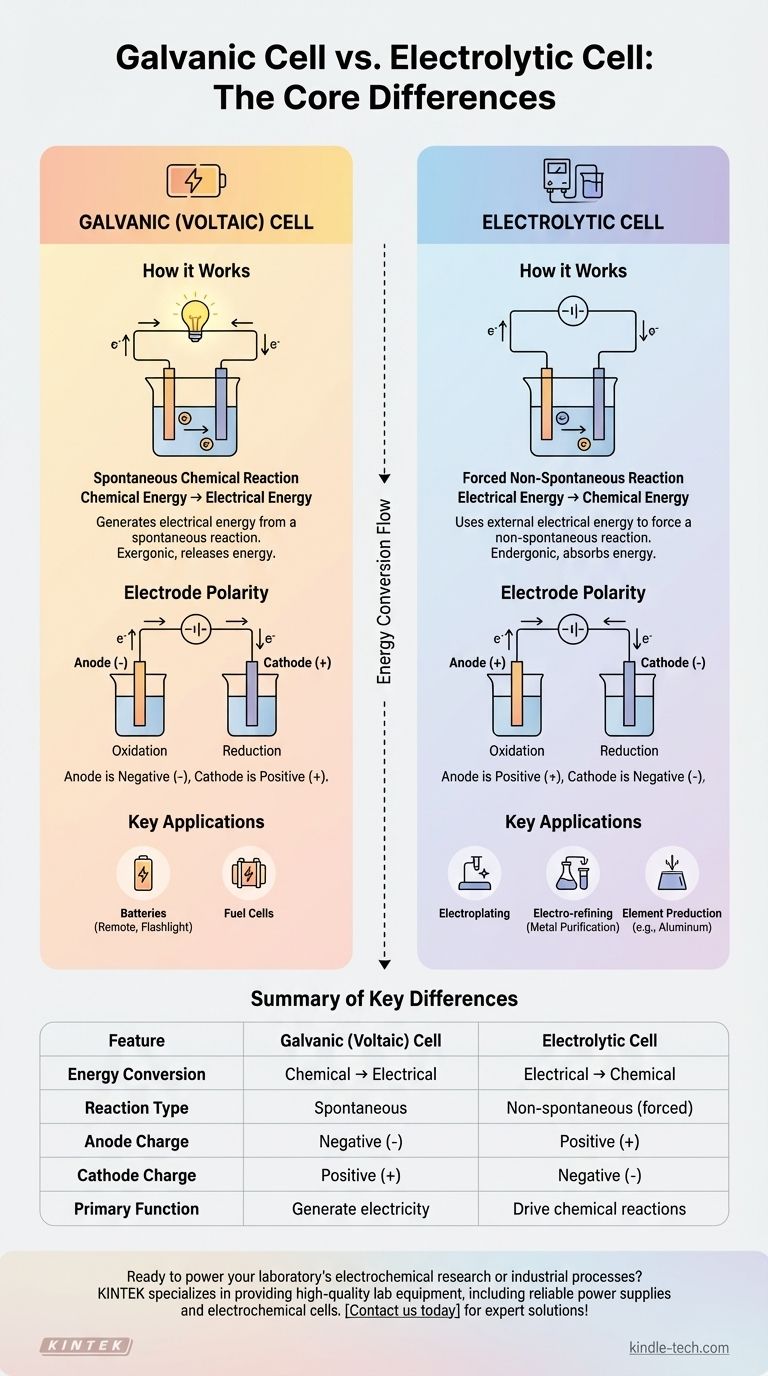
How Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells Work
A galvanic cell is a self-contained system that produces electricity. Think of any standard battery you use in a remote control or flashlight.
Spontaneous Chemical Reactions
The engine of a galvanic cell is a spontaneous redox (reduction-oxidation) reaction. This means the chemical reaction occurs naturally without any external energy input, releasing energy in the process.
Energy Conversion: Chemical to Electrical
The energy released by the spontaneous reaction pushes electrons through an external circuit, creating an electric current. It effectively transforms stored chemical potential energy into usable electrical energy.
Electrode Polarity
In a galvanic cell, the anode is the negative electrode where oxidation occurs, and the cathode is the positive electrode where reduction occurs. Electrons flow from the negative anode to the positive cathode.
How Electrolytic Cells Work
An electrolytic cell is used to drive chemical changes that would not happen on their own. This process is known as electrolysis.
Forcing Non-Spontaneous Reactions
These cells are designed to force a non-spontaneous reaction to proceed. For example, water does not spontaneously break down into hydrogen and oxygen; it requires energy to be forced apart.
The Role of an External Power Source
To drive this reaction, an electrolytic cell must be connected to an external power source, like a battery or a DC power supply. This source provides the energy needed to overcome the reaction's natural resistance.
The Function of the Electrolyte
The cell contains an electrolyte, which is typically a molten salt or a salt solution. This substance contains mobile ions that are attracted to the electrodes, allowing the chemical reactions to take place and completing the electrical circuit.
Applications in Industry
This process is critical for many industrial applications, including electroplating (coating an object with a thin layer of metal), electro-refining to purify metals like copper, and producing pure elements like aluminum from bauxite ore.
Understanding the Core Differences
Comparing these two cells side-by-side reveals their opposite nature. They are two sides of the same electrochemical coin.
Energy Flow and Spontaneity
A galvanic cell is exergonic, meaning it releases energy from a spontaneous reaction. An electrolytic cell is endergonic, meaning it absorbs energy to drive a non-spontaneous reaction.
Electrode Polarity Reversal
This is a critical point of distinction. While oxidation always occurs at the anode and reduction at the cathode, their charges are reversed.
- In a galvanic cell: Anode is negative (-), Cathode is positive (+).
- In an electrolytic cell: Anode is positive (+), Cathode is negative (-).
This reversal happens because the external power source in an electrolytic cell dictates the flow of electrons, overriding the natural tendency of the chemical system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding which cell to use depends entirely on whether your goal is to generate power or create a chemical product.
- If your primary focus is generating power from a chemical process: You are describing a galvanic (voltaic) cell, which is the principle behind all batteries.
- If your primary focus is using power to create a substance: You need an electrolytic cell, which is the basis for industrial electroplating, refining, and element production.
- If your primary focus is understanding basic electrochemistry: Remember that galvanic cells release energy spontaneously, while electrolytic cells require energy to force a reaction.
Ultimately, the direction of energy conversion is the single most important factor that defines and separates these two fundamental electrochemical cells.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Galvanic (Voltaic) Cell | Electrolytic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Conversion | Chemical → Electrical | Electrical → Chemical |
| Reaction Type | Spontaneous | Non-spontaneous (forced) |
| Anode Charge | Negative (-) | Positive (+) |
| Cathode Charge | Positive (+) | Negative (-) |
| Primary Function | Generate electricity (e.g., batteries) | Drive chemical reactions (e.g., electroplating, refining) |
Ready to power your laboratory's electrochemical research or industrial processes? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including reliable power supplies and electrochemical cells tailored for your specific needs. Whether you're developing new battery technologies or optimizing electroplating systems, our expertise ensures you have the right tools for success. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects with precision equipment and expert solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
People Also Ask
- What are the proper storage procedures for the multifunctional electrolytic cell? Protect Your Investment and Ensure Data Accuracy
- What material is the five-port water bath electrolytic cell made of? High Borosilicate Glass & PTFE Explained
- What are the standard components of the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the Precision Instrument for Electrochemical Analysis
- How can contamination be avoided during experiments with the five-port water bath electrolytic cell? Master the 3-Pillar Protocol
- What general precaution should be taken when handling the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Lab Results



















