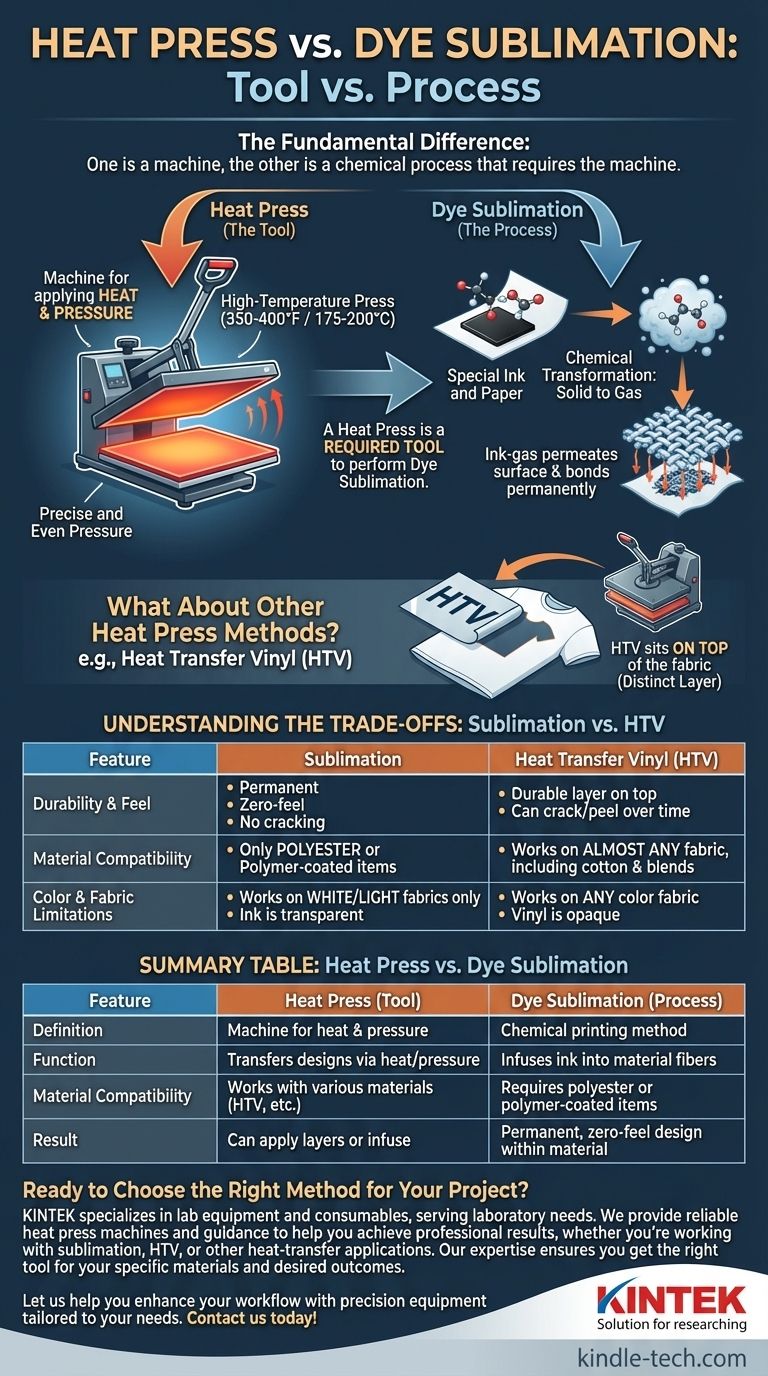
The fundamental difference between a heat press and sublimation is that one is a machine, and the other is a chemical process that often uses that machine. A heat press is a tool that applies heat and pressure, while dye sublimation is a specific printing method where ink turns into a gas and permanently bonds with a material's fibers, a process which requires the heat and pressure from a heat press to work.
The core mistake is thinking in terms of "Heat Press vs. Sublimation." The correct framing is that a heat press is a required tool to perform the process of dye sublimation. You cannot do one without the other.

What is a Heat Press? The Tool
A heat press is a piece of equipment, much like an oven or a laminator. Its sole purpose is to provide a controlled environment of high temperature and consistent, even pressure over a flat surface.
A High-Temperature Press
The machine has a heated plate (the platen) that reaches precise temperatures, often between 350-400°F (175-200°C). This consistent heat is critical for many types of transfers, including sublimation.
Precise and Even Pressure
Unlike a home iron, a heat press applies uniform pressure across the entire design. This ensures there are no cold spots and that the transfer is applied evenly, which is essential for a professional result.
What is Dye Sublimation? The Process
Dye sublimation is a specific chemical printing process that creates a permanent, high-quality image. It is not just a method of sticking something onto a surface; it's a method of infusing color directly into it.
A Special Ink and Paper
The process starts with printing a design onto special transfer paper using specialized sublimation inks. These solid inks are designed to change states under heat.
The Chemical Transformation
When the sublimation paper is placed on a compatible item (like a polyester shirt or a poly-coated mug) and subjected to the heat and pressure of a heat press, the magic happens. The solid ink turns directly into a gas, skipping the liquid phase entirely.
A Permanent Bond
This ink-gas permeates the surface of the polyester or polymer coating, whose pores have opened up from the heat. As it cools, the gas turns back into a solid, becoming a permanent part of the material itself. The design is now in the fabric, not on it.
What About Other Heat Press Methods?
The confusion between the tool and the process arises because a heat press is used for multiple applications, not just sublimation. The most common alternative is Heat Transfer Vinyl (HTV).
Heat Transfer Vinyl (HTV)
HTV is a material with a heat-activated adhesive on one side. A design is cut from a sheet of this vinyl, placed on a garment, and then a heat press is used to melt the adhesive, effectively gluing the vinyl design onto the surface of the fabric.
The "On Top" vs. "In The" Difference
This is the critical distinction. HTV sits on top of the fabric. You can feel it as a distinct layer. Sublimation is infused into the fabric's fibers. It has no feel or texture whatsoever.
Understanding the Trade-offs
When deciding on a printing method, you are not choosing between a heat press and sublimation. You are choosing between sublimation and other methods that also use a heat press, like HTV.
Durability and Feel
Sublimation is permanent. Because the ink is part of the fabric, it will not crack, peel, or fade and has zero feel. HTV is durable but is ultimately a layer on top of the garment. Over time and with many washes, it can eventually crack or peel.
Material Compatibility
This is a major deciding factor. Sublimation only works on polyester or materials with a special polymer coating. It cannot bond with natural fibers like cotton. HTV works on almost any fabric, including cotton, polyester, and blends.
Color and Fabric Limitations
Sublimation ink is transparent, so it must be used on white or very light-colored garments for the colors to appear correctly. It cannot be used on black or dark fabrics. HTV is opaque, like paint, so you can apply a white vinyl design onto a black shirt with no issues.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Your choice depends entirely on your desired outcome and the materials you are using.
- If your primary focus is ultimate durability and a zero-feel finish on light-colored apparel: Your best choice is dye sublimation.
- If your primary focus is working with cotton or dark-colored fabrics: You must use a method like Heat Transfer Vinyl (HTV).
- If your primary focus is vibrant, photorealistic detail on hard surfaces: You should use sublimation, provided the item (mug, tile, etc.) has the necessary polymer coating.
Ultimately, understanding this distinction transforms your question from "which is better" to "which is the right process for my specific job."
Summary Table:
| Feature | Heat Press (Tool) | Dye Sublimation (Process) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Machine for applying heat & pressure | Chemical printing method |
| Function | Transfers designs via heat/pressure | Infuses ink into material fibers |
| Material Compatibility | Works with various materials (HTV, etc.) | Requires polyester or polymer-coated items |
| Result | Can apply layers (e.g., HTV) or infuse (sublimation) | Permanent, zero-feel design within material |
| Common Uses | HTV on cotton/dark fabrics, sublimation | Light-colored apparel, coated hard goods |
Ready to Choose the Right Method for Your Project?
Understanding the difference between a heat press and the sublimation process is just the first step. Whether you're looking to create durable, full-color designs on polyester with sublimation or apply vibrant HTV to cotton fabrics, having the right equipment is crucial.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. We provide reliable heat press machines and guidance to help you achieve professional results, whether you're working with sublimation, HTV, or other heat-transfer applications. Our expertise ensures you get the right tool for your specific materials and desired outcomes.
Let us help you enhance your workflow with precision equipment tailored to your needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your success!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press 25T 30T 50T
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature range for compression molding? Optimize Your Process for Perfect Parts
- What are the pros and cons of hot forging? Unlock Superior Strength for Critical Components
- What is a heated hydraulic press used for? Essential Tool for Curing, Molding, and Laminating
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What is the hot press molding method? A Guide to Shaping Materials with Heat & Pressure

















