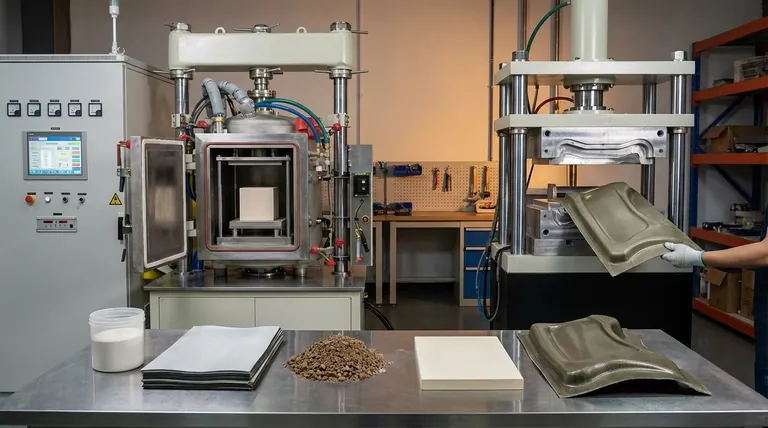
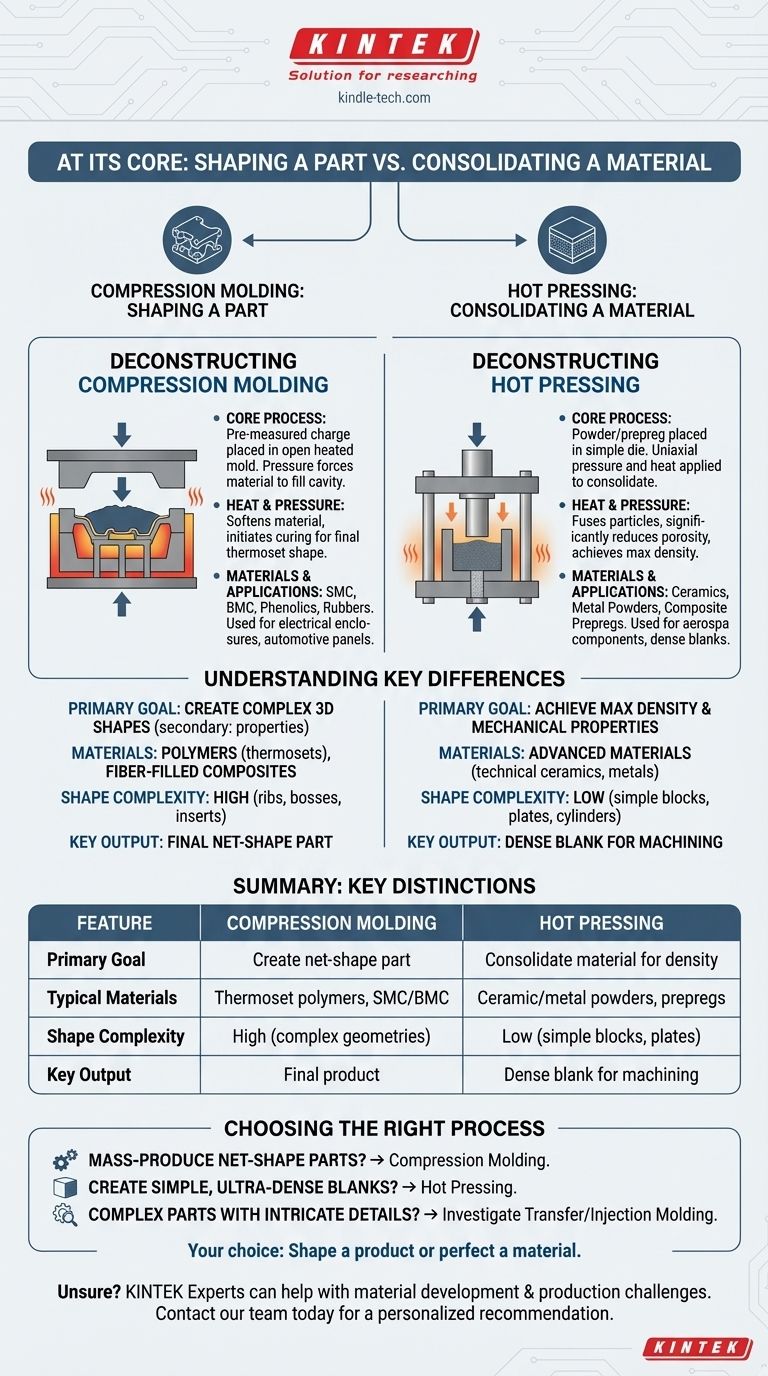
At its core, the distinction between hot pressing and compression molding lies in their primary objective and the materials they process. Compression molding primarily uses a mold to shape polymers and composites into a final net-shape part. In contrast, hot pressing uses a simple die to consolidate powders or composite prepregs into a dense, simple form like a block or plate, focusing on material properties rather than complex geometry.
While both processes apply heat and pressure, the fundamental difference is their goal: compression molding is for shaping a part, while hot pressing is for consolidating a material.

Deconstructing Compression Molding
Compression molding is a high-pressure forming process used extensively for thermosetting polymers and fiber-reinforced composites. The process is defined by its straightforward approach to creating shaped parts.
The Core Process
A pre-measured amount of molding material, known as the "charge," is placed directly into the open, heated lower half of a mold cavity. The top half of the mold is then closed, applying pressure to force the material to fill the entire cavity.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
The combination of heat and pressure is critical. Heat softens the material to allow it to flow and, for thermoset polymers, initiates the chemical cross-linking reaction (curing) that permanently hardens it into its final shape.
Typical Materials and Applications
This method is ideal for materials like Bulk Molding Compound (BMC), Sheet Molding Compound (SMC), phenolics, and rubbers. It is commonly used to produce larger, fairly intricate parts such as electrical enclosures, automotive body panels, and appliance housings.
Deconstructing Hot Pressing
Hot pressing is fundamentally a materials science process used to increase the density and improve the mechanical properties of a material. It is less about creating a final shape and more about consolidating the material itself.
The Core Process
In a typical uniaxial hot press, a powder (like a ceramic or metal) or a stack of composite prepreg is placed into a simple die cavity. Pressure is then applied from one direction (uniaxially) by a plunger or ram while the entire assembly is heated.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
The simultaneous application of high temperature and pressure forces the material particles to fuse and compact, significantly reducing porosity. The main goal is to achieve a theoretical maximum density, which directly enhances strength, hardness, and other physical properties.
Typical Materials and Applications
Hot pressing is the go-to process for fabricating high-performance ceramics, metal powders, and flat composite laminates for aerospace or defense. The output is typically a simple geometric form—such as a disc, puck, or plate—that is then machined to its final dimensions.
Understanding the Key Differences
While both processes seem similar, their goals and applications are distinct. Mistaking one for the other can lead to significant design and manufacturing errors.
Primary Goal: Shaping vs. Densification
This is the most critical distinction. Compression molding's goal is to create a specific, often complex, three-dimensional shape. The properties of the resulting part are important, but secondary to achieving the desired geometry.
Hot pressing's goal is to achieve maximum material density and superior mechanical properties. The shape is simple and often just a precursor to further machining.
Materials Used: Polymers vs. Powders
Compression molding is predominantly used for polymers, especially thermosets, and fiber-filled polymer composites.
Hot pressing is used for advanced materials where density is paramount, such as technical ceramics (e.g., silicon carbide), metal powders, and high-performance composite laminates.
Complexity of Shape: High vs. Low
Compression molding can produce parts with relatively complex geometries, including ribs, bosses, and inserts.
Hot pressing is almost exclusively limited to simple, regular shapes like blocks, cylinders, and plates, dictated by the simple die used.
Choosing the Right Process for Your Application
Selecting the correct process depends entirely on your end goal: the material you are using and the part you need to create.
- If your primary focus is to mass-produce net-shape parts from thermoset polymers or composites: Compression molding is your most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is to create simple, ultra-dense blanks from ceramic powders, metal powders, or advanced composites: Hot pressing is the correct choice to maximize material performance.
- If your primary focus is to create complex parts where material must flow into intricate details: You should investigate other methods like Transfer Molding or Injection Molding.
Your choice ultimately comes down to deciding whether your priority is to shape a product or to perfect a material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Compression Molding | Hot Pressing |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Create a net-shape part | Consolidate material for density |
| Typical Materials | Thermoset polymers, SMC/BMC | Ceramic/metal powders, composite prepregs |
| Shape Complexity | High (complex geometries) | Low (simple blocks, plates) |
| Key Output | Final product (e.g., automotive panel) | Dense blank for machining |
Unsure which process is right for your material or part? The experts at KINTEK can help. We specialize in lab equipment and consumables, providing the right solutions for your material development and production challenges.
Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Vacuum Box Laboratory Hot Press
- Automatic Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
People Also Ask
- What conditions does a Vacuum Hot Pressing Furnace provide for Copper-MoS2-Mo composites? Achieve Peak Densification
- Why is precise temperature control necessary for SiC/Cu Vacuum Hot Pressing? Mastering the Cu9Si Interface Phase
- What are the primary advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Maximize Density in B4C-CeB6 Ceramics
- What advantages does hot pressing sintering equipment provide for NASICON? Achieve 100% Dense Solid Electrolyte Plates
- How does the uniaxial pressing function of a vacuum hot press furnace influence the microstructure of ZrC-SiC ceramics?



















