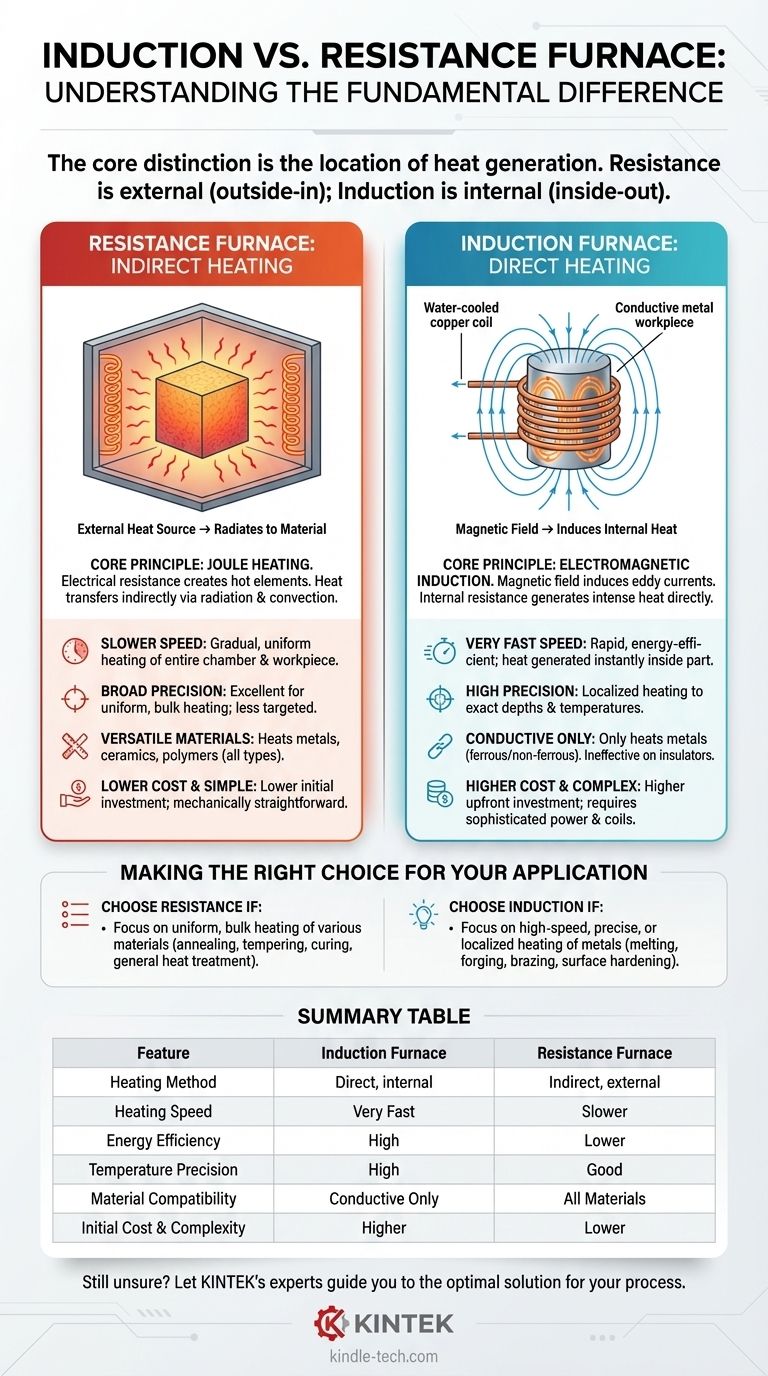
The fundamental difference between induction and resistance furnaces lies in how they generate heat. A resistance furnace uses heating elements that get hot and transfer heat to the material indirectly through radiation and convection, much like a conventional oven. In contrast, an induction furnace uses a magnetic field to generate heat directly inside the material itself, without any physical contact.
The core distinction is the location of heat generation. Resistance heating is external, warming the material from the outside-in. Induction heating is internal, using the material's own properties to generate heat from the inside-out. This single difference dictates their speed, efficiency, and ideal applications.

How Resistance Furnaces Work: The Indirect Heating Method
Resistance furnaces are a foundational technology in thermal processing, valued for their simplicity and versatility. They operate on a straightforward and reliable principle.
The Core Principle: Joule Heating
A resistance furnace works by passing a strong electrical current through a high-resistance material, known as a heating element.
According to Joule's first law, this resistance to electrical flow causes the element to become extremely hot. This is the same principle that makes a toaster or an electric stove top work.
Heat Transfer Mechanism
The hot elements, typically arranged along the walls of the furnace chamber, heat the target material indirectly.
Heat is transferred to the workpiece through a combination of thermal radiation from the hot elements and convection as the air or atmosphere inside the furnace heats up and circulates.
Key Characteristics
This indirect method results in a slower, more gradual heating process. The entire furnace chamber and the full workpiece must be brought up to the target temperature together, ensuring a thorough and uniform soak.
How Induction Furnaces Work: The Direct Heating Method
Induction heating is a more advanced, high-speed process that leverages the principles of electromagnetism to deliver energy with remarkable precision and efficiency.
The Core Principle: Electromagnetic Induction
An induction furnace uses a water-cooled copper coil through which a high-frequency alternating current (AC) is passed.
This current generates a powerful and rapidly changing magnetic field around the coil. When an electrically conductive workpiece (like a piece of steel) is placed within this field, the field induces powerful electrical currents, called eddy currents, to flow within the metal.
Direct and Contactless Heating
The metal's own internal resistance to the flow of these eddy currents generates intense and rapid heat.
Crucially, the heat is generated inside the workpiece itself. There are no external heating elements, and the coil remains cool. It is a clean, contactless method of energy transfer.
Understanding the Trade-offs: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Choosing between these two technologies requires understanding their inherent advantages and limitations, which all stem from their different heating mechanisms.
Heating Speed and Efficiency
Induction is significantly faster and more energy-efficient. Because heat is generated directly where it's needed—inside the part—very little energy is wasted heating the furnace walls or surrounding atmosphere.
Resistance is slower and less efficient. A great deal of energy is first used to heat the massive refractory walls and the entire chamber volume before the workpiece reaches its target temperature.
Temperature Control and Precision
Induction offers unparalleled precision. By designing the shape of the coil and controlling the frequency, you can heat very specific areas of a part to exact depths and temperatures. This is ideal for applications like surface hardening a gear tooth while leaving the core soft.
Resistance provides broad, uniform heating. It is excellent for heating an entire component evenly, but it cannot easily target a specific section. The control is less precise and applies to the entire furnace environment.
Material Compatibility
Resistance furnaces are highly versatile. They can heat virtually any material, including metals, ceramics, polymers, and composites, as the heating process does not depend on the material's electrical properties.
Induction furnaces are highly specialized. They can only heat electrically conductive materials, primarily ferrous and non-ferrous metals. They are completely ineffective on insulators like ceramics or plastics.
Cost and Complexity
Resistance furnaces generally have a lower initial cost and are mechanically simpler. Their maintenance is straightforward, often involving the replacement of heating elements.
Induction systems are more complex and expensive upfront. They require sophisticated power supplies to generate high-frequency currents and often need custom-designed coils for specific parts, adding to the cost and engineering effort.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on your material, your process requirements, and your production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, precise, or localized heating of metals: Induction is the superior choice for applications like melting, forging, brazing, and surface hardening.
- If your primary focus is uniform, bulk heating of various materials (including non-conductors): A resistance furnace is the most versatile and cost-effective solution for processes like annealing, tempering, and curing.
- If your primary focus is maximum energy efficiency and process speed for conductive parts: The direct energy transfer of induction offers unmatched performance.
- If your primary focus is operational simplicity and lower capital investment for general heat treatment: The robust and proven technology of a resistance furnace is the standard.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace is about matching the heating principle to the specific demands of your material and process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Induction Furnace | Resistance Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct, internal (via magnetic field) | Indirect, external (via heating elements) |
| Heating Speed | Very Fast | Slower |
| Energy Efficiency | High (direct energy transfer) | Lower (heats entire chamber) |
| Temperature Precision | High (localized heating possible) | Good (broad, uniform heating) |
| Material Compatibility | Electrically conductive materials only (metals) | All materials (metals, ceramics, plastics, etc.) |
| Initial Cost & Complexity | Higher | Lower |
Still Unsure Which Furnace is Right for Your Process?
Choosing between an induction and resistance furnace is critical for achieving optimal results in your lab or production line. The right equipment directly impacts your efficiency, product quality, and bottom line.
Let KINTEK's experts guide you. We specialize in laboratory equipment and consumables, providing tailored solutions for your specific thermal processing challenges. We can help you:
- Analyze your application to determine the most efficient and cost-effective furnace type.
- Select the perfect model from our range of high-performance equipment.
- Optimize your process for maximum throughput and quality.
Don't leave your results to chance. Contact our technical team today for a personalized consultation and discover the KINTEK advantage in precision heating solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















