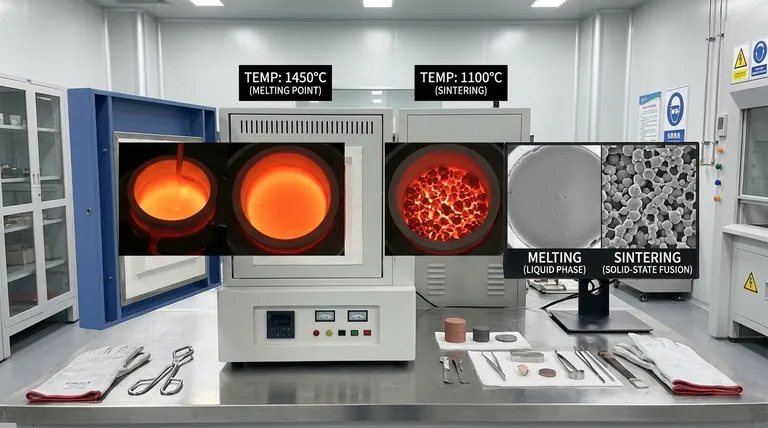
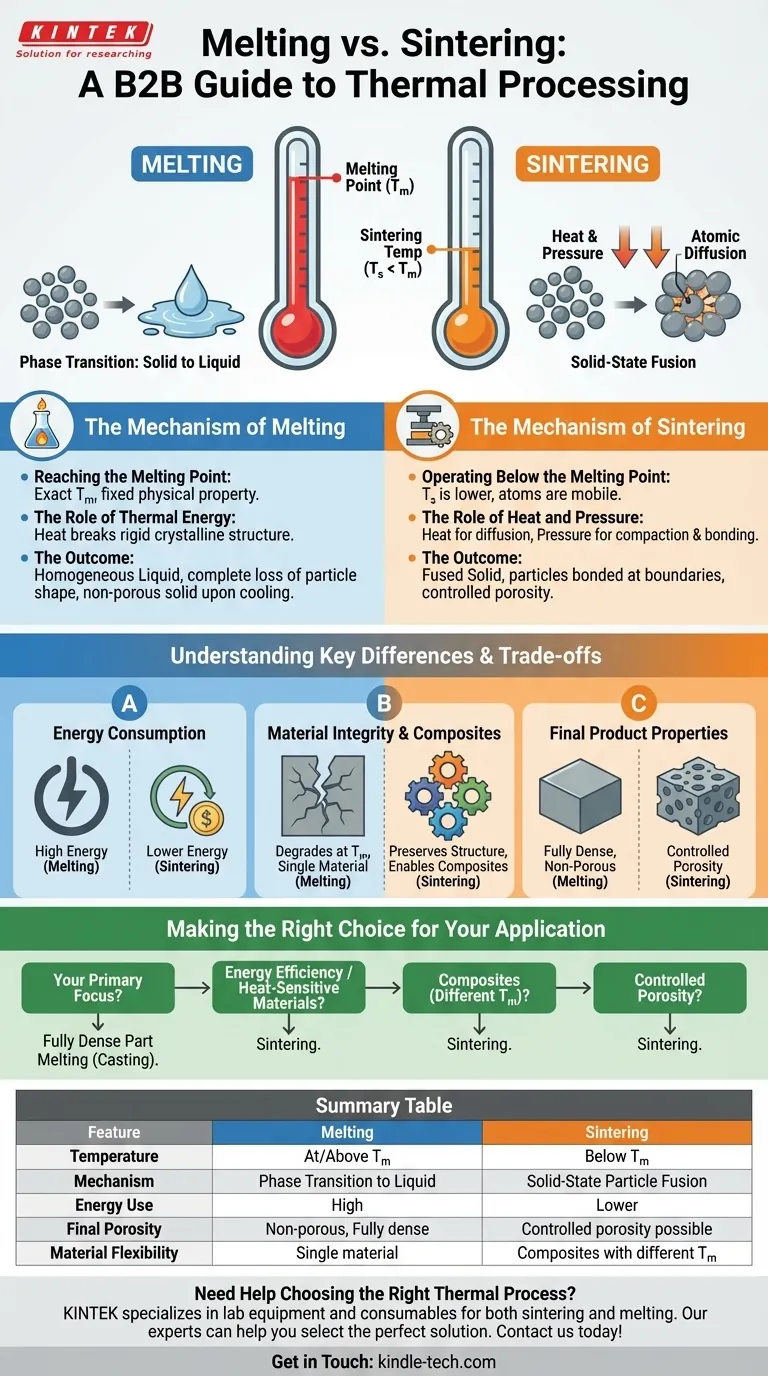
The fundamental difference is that sintering temperature is always lower than a material's melting temperature. Sintering is a process that fuses particles together in a solid state using heat and pressure, whereas melting is a phase transition that turns a solid into a complete liquid using heat alone.
The choice between sintering and melting is not just about temperature; it's a strategic decision. You are choosing between fusing particles while preserving their core structure (sintering) versus completely liquefying the material to form a new solid (melting).

The Mechanism of Melting
Melting is a straightforward thermal process that represents a fundamental change in the state of matter. It is governed by a specific, intrinsic property of a material.
Reaching the Melting Point
The melting point is the exact temperature at which a substance transitions from a solid to a liquid. This temperature is a fixed physical property for a given material under standard pressure.
The Role of Thermal Energy
Melting relies solely on thermal energy. As heat is applied, the atoms or molecules in the solid gain enough energy to break free from their rigid crystalline structure, allowing them to move past one another as a liquid.
The Outcome: A Homogeneous Liquid
The end result of melting is a complete loss of the original particle shape. The material becomes a uniform, homogeneous liquid that, upon cooling, will solidify into a dense, non-porous mass.
The Mechanism of Sintering
Sintering is a more complex manufacturing technique that leverages atomic diffusion to create solid objects without reaching the melting point.
Operating Below the Melting Point
Sintering occurs at a temperature that is typically high enough to make atoms mobile but remains well below the material's melting point. This is the core principle of the process.
The Role of Heat and Pressure
Sintering uses a combination of heat and pressure. Heat provides the energy for atoms at the surfaces of particles to diffuse, while pressure compacts the particles, increasing the contact points where they can bond and fuse.
The Outcome: A Fused Solid
The final product of sintering is a solid object where the individual particles have been fused together at their boundaries. This process can be controlled to create components with specific levels of porosity.
Understanding the Key Differences and Trade-offs
Choosing between these processes has significant implications for energy consumption, material selection, and the properties of the final product.
Energy Consumption
Sintering requires significantly less energy than melting. Operating at a lower temperature directly translates to lower energy costs and faster processing times.
Material Integrity and Composites
Sintering is the only viable option for materials that might degrade or decompose at their melting point. It also allows for the creation of composites by fusing materials with vastly different melting points, such as metals and ceramics, which could never be combined through melting.
Final Product Properties
Melting produces a fully dense, non-porous object. Sintering, by contrast, can create products with controlled porosity, a critical feature for applications like filters, self-lubricating bearings, and some biomedical implants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final goal dictates which thermal process is appropriate for your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is creating a fully dense, non-porous part from a single metal: Melting (casting) is the most direct and effective method.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency or working with heat-sensitive materials: Sintering is the superior choice due to its lower temperature requirements.
- If your primary focus is creating a composite from multiple materials with different melting points: Sintering is the only feasible manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is producing a component with controlled porosity: Sintering provides the necessary control over the final microstructure that melting cannot.
Ultimately, understanding the distinction between these temperatures allows you to select the precise manufacturing tool needed to achieve your specific engineering goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Melting | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | At or above melting point | Below melting point |
| Mechanism | Phase transition to liquid | Solid-state particle fusion |
| Energy Use | High | Lower |
| Final Porosity | Non-porous, fully dense | Controlled porosity possible |
| Material Flexibility | Single material | Composites with different melting points |
Need Help Choosing the Right Thermal Process for Your Materials?
Understanding the critical difference between sintering and melting is key to manufacturing success. Whether your goal is energy efficiency, creating complex composites, or achieving specific porosity, the right equipment is essential.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise furnaces and tools you need for both sintering and melting applications. Our experts can help you select the perfect solution to enhance your lab's capabilities and achieve your specific engineering goals.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how KINTEK can support your material processing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of the muffle oven? Find the Right Heat for Your Lab Process
- Which type of material is used for overheating protection in muffle furnace? A Dual-Layer Safety System Explained
- What is the muffle furnace used for in metallurgy? Achieve Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment
- What is the significance of the muffle furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the use of muffle oven in laboratory? For Clean, High-Temperature Material Processing



















