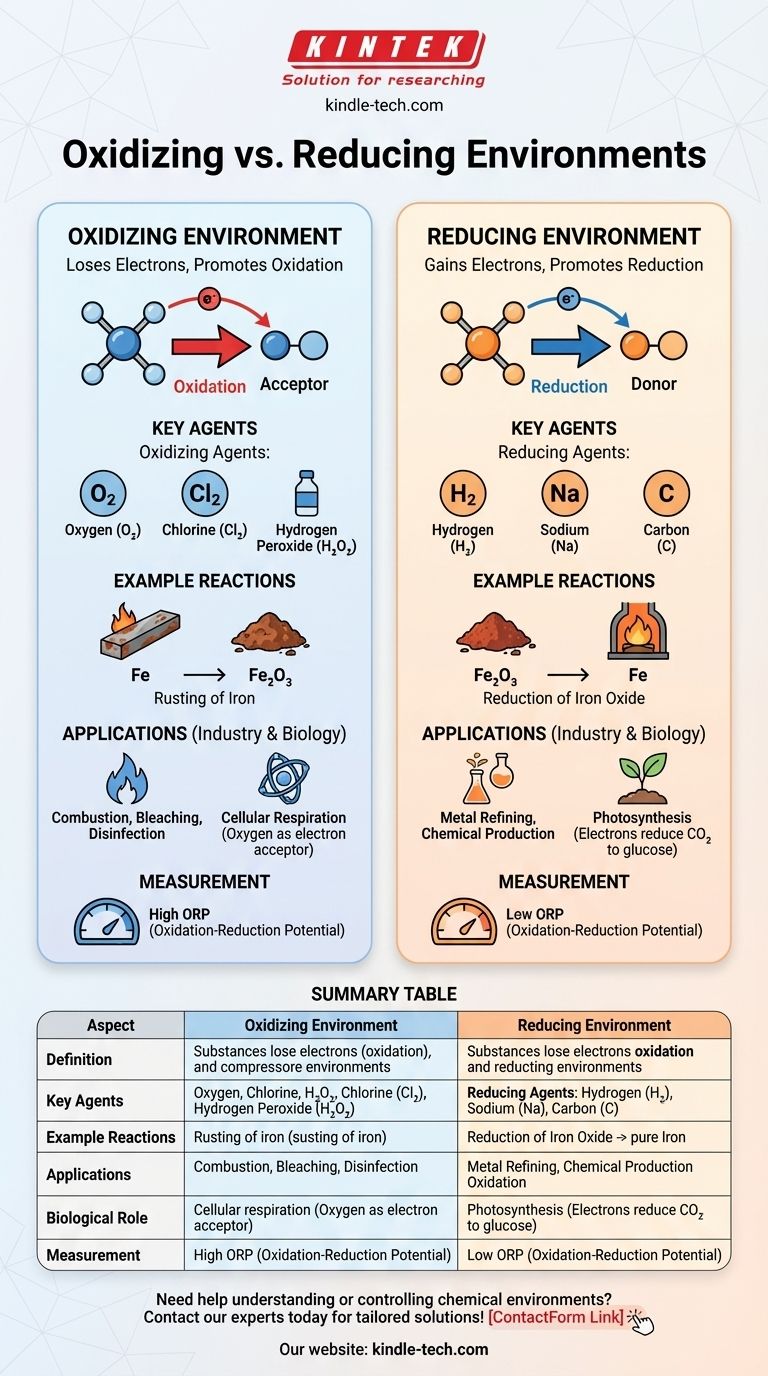
In chemistry, an oxidizing environment is one where substances tend to lose electrons, promoting oxidation reactions, while a reducing environment is one where substances tend to gain electrons, promoting reduction reactions. The key difference lies in the availability of electron acceptors (oxidizing agents) or electron donors (reducing agents). Oxidizing environments are characterized by the presence of oxidizing agents like oxygen or halogens, which facilitate the loss of electrons. In contrast, reducing environments contain reducing agents like hydrogen or metals, which facilitate the gain of electrons. These environments play critical roles in chemical reactions, industrial processes, and biological systems.

Key Points Explained:
-
Definition of Oxidizing and Reducing Environments:
- Oxidizing Environment: A chemical environment where substances are more likely to lose electrons, leading to oxidation. This environment is rich in oxidizing agents, such as oxygen, chlorine, or other electron acceptors.
- Reducing Environment: A chemical environment where substances are more likely to gain electrons, leading to reduction. This environment is rich in reducing agents, such as hydrogen, metals, or other electron donors.
-
Role of Oxidizing and Reducing Agents:
- Oxidizing Agents: These are substances that accept electrons from other substances, thereby oxidizing them. Common examples include oxygen (O₂), chlorine (Cl₂), and hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂).
- Reducing Agents: These are substances that donate electrons to other substances, thereby reducing them. Common examples include hydrogen (H₂), sodium (Na), and carbon (C).
-
Chemical Reactions in Different Environments:
- Oxidizing Environment: In such an environment, oxidation reactions dominate. For example, rusting of iron occurs in an oxidizing environment where iron (Fe) loses electrons to oxygen, forming iron oxide (Fe₂O₃).
- Reducing Environment: In such an environment, reduction reactions dominate. For example, the reduction of metal oxides to pure metals occurs in a reducing environment, such as when carbon is used to reduce iron oxide to iron in a blast furnace.
-
Applications in Industry and Biology:
- Industrial Applications: Oxidizing environments are used in processes like combustion, bleaching, and disinfection. Reducing environments are crucial in processes like metal refining and the production of certain chemicals.
- Biological Systems: In biological systems, oxidizing environments are found in processes like cellular respiration, where oxygen acts as the final electron acceptor. Reducing environments are found in processes like photosynthesis, where electrons are donated to reduce carbon dioxide to glucose.
-
Measurement and Control:
- Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP): The ORP is a measure of the tendency of a chemical environment to either gain or lose electrons. A high ORP indicates an oxidizing environment, while a low ORP indicates a reducing environment.
- Control in Industrial Processes: In industries, controlling the oxidizing or reducing nature of the environment is crucial for optimizing chemical reactions, ensuring product quality, and preventing unwanted side reactions.
-
Examples of Oxidizing and Reducing Environments:
- Oxidizing Environment: The Earth's atmosphere is an oxidizing environment due to the presence of oxygen. This is why metals like iron corrode when exposed to air.
- Reducing Environment: The interior of a blast furnace is a reducing environment where carbon monoxide (CO) acts as a reducing agent to convert iron ore (Fe₂O₃) into metallic iron (Fe).
By understanding the differences between oxidizing and reducing environments, chemists and engineers can better control and optimize chemical reactions in various applications, from industrial processes to biological systems.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Oxidizing Environment | Reducing Environment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Substances lose electrons (oxidation) due to electron acceptors like oxygen or halogens. | Substances gain electrons (reduction) due to electron donors like hydrogen or metals. |
| Key Agents | Oxidizing agents: Oxygen (O₂), chlorine (Cl₂), hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂). | Reducing agents: Hydrogen (H₂), sodium (Na), carbon (C). |
| Example Reactions | Rusting of iron (Fe → Fe₂O₃). | Reduction of iron oxide to iron (Fe₂O₃ → Fe). |
| Applications | Combustion, bleaching, disinfection. | Metal refining, chemical production. |
| Biological Role | Cellular respiration (oxygen as electron acceptor). | Photosynthesis (electrons reduce CO₂ to glucose). |
| Measurement | High Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP). | Low Oxidation-Reduction Potential (ORP). |
Need help understanding or controlling chemical environments? Contact our experts today for tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace Negative Material Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions
- What is hydrogen annealing? Achieve Superior Material Properties with Bright Annealing
- Why is a hydrogen atmosphere furnace necessary for W-Cu composite? Unlock Superior Infiltration and Density
- Why is an industrial furnace with hydrogen atmosphere control necessary for the pre-sintering of Fe-Cr-Al materials?
- What is hydrogen atmosphere heat treatment? Achieve Superior Surface Purity & Brightness












