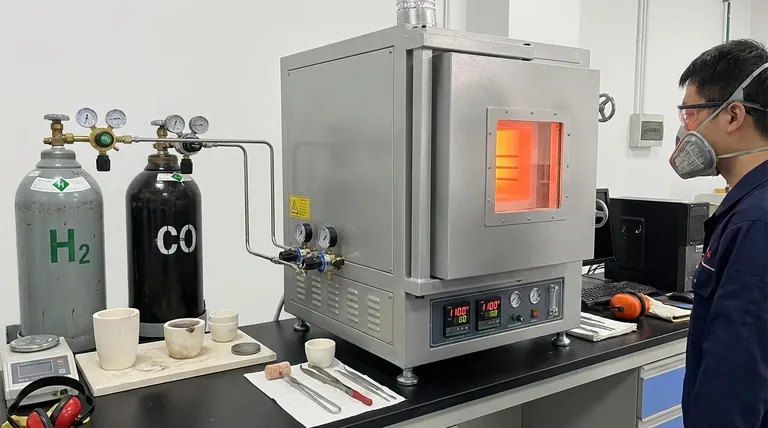
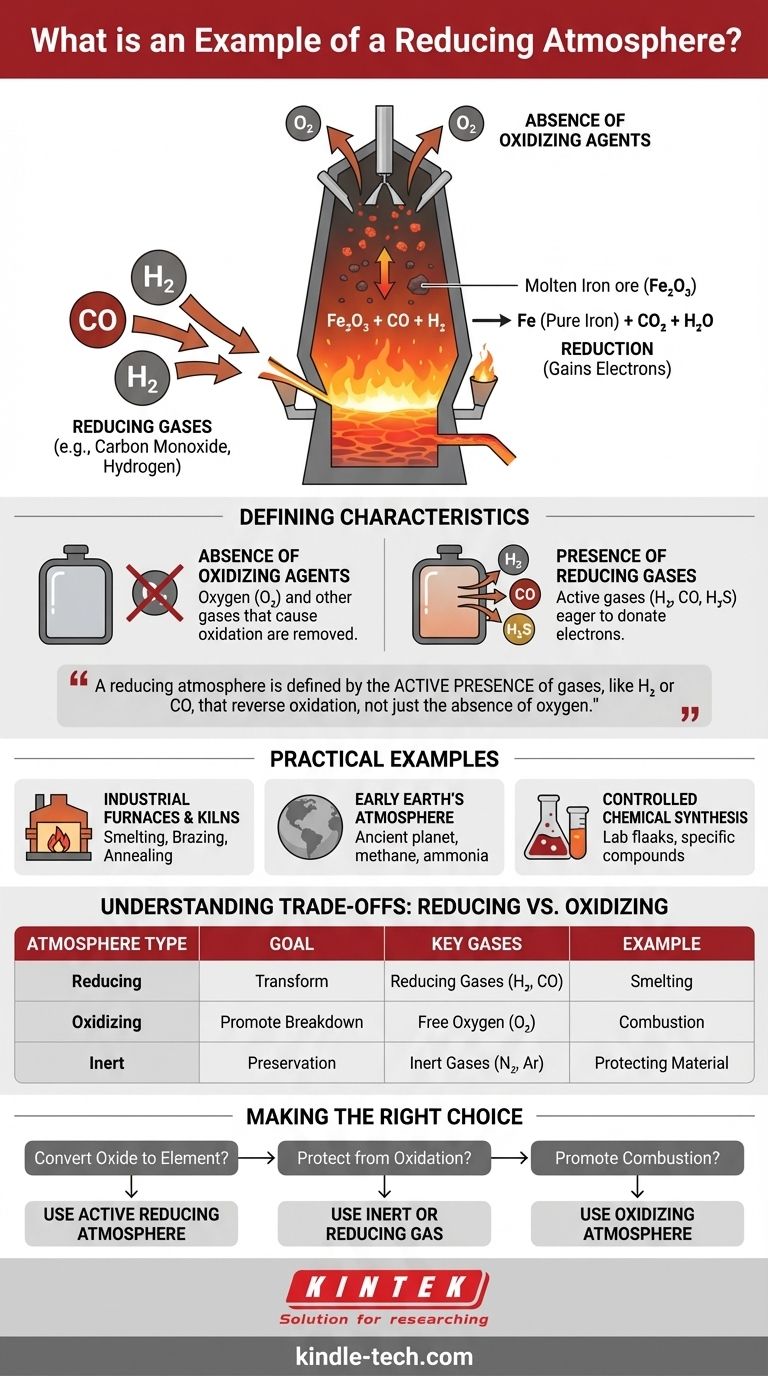
A classic example of a reducing atmosphere is the environment inside a blast furnace used for smelting iron ore. In this high-temperature process, oxygen is deliberately removed and carbon monoxide is introduced, creating a condition that actively strips oxygen atoms from the iron ore, thereby "reducing" it to pure, metallic iron.
The critical takeaway is that a reducing atmosphere is not merely about the absence of oxygen; it is defined by the active presence of gases, like hydrogen or carbon monoxide, that are chemically driven to donate electrons and reverse the process of oxidation.

What Defines a "Reducing" Atmosphere?
To fully grasp the concept, it's essential to understand its two defining characteristics: what is absent and what is present.
The Absence of Oxidizing Agents
The first step in creating a reducing atmosphere is the removal of oxygen and other gases that cause oxidation.
Our everyday atmosphere is an oxidizing atmosphere. It's the reason an apple slice turns brown and iron rusts. These processes are driven by the presence of free oxygen.
The Presence of Reducing Gases
A true reducing atmosphere contains active reducing agents. These are gases that are chemically unstable and eager to donate electrons to other substances.
Common examples include hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), and hydrogen sulfide (H₂S). These gases actively seek out oxygen atoms in other materials and bind with them.
The Chemical Reaction (Reduction)
This environment facilitates a chemical reaction called reduction. In chemistry, reduction occurs when an atom or molecule gains electrons, lowering its oxidation state.
In the blast furnace example, the carbon monoxide (CO) gives electrons to the iron oxide (Fe₂O₃), which gains them. This reduces the iron ore to elemental iron (Fe).
Practical Examples in Nature and Industry
Understanding where these atmospheres occur helps solidify the concept and its importance.
Industrial Furnaces and Kilns
Smelting, brazing, and annealing metals are often performed in a reducing atmosphere. This prevents the formation of oxides (scale or rust) on the metal's surface at high temperatures, ensuring a clean and strong final product.
The Early Earth's Atmosphere
Billions of years ago, before the rise of photosynthetic life, Earth's atmosphere was naturally reducing. It was rich in gases like methane, ammonia, and water vapor but contained virtually no free oxygen.
Controlled Chemical Synthesis
In laboratories and chemical plants, reducing atmospheres are created to produce specific chemical compounds. The controlled environment ensures that only the desired reduction reaction occurs without interference from unwanted oxidation.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Reducing vs. Oxidizing
The choice between creating a reducing, inert, or oxidizing atmosphere is a critical engineering decision driven by the desired outcome. The trade-offs are fundamental.
Goal: Transformation vs. Preservation
An oxidizing atmosphere promotes breakdown (rusting, burning). A reducing atmosphere promotes transformation by removing oxygen from compounds. An inert atmosphere (like pure argon) is used for preservation, preventing any reaction from occurring.
The Challenge of Safety and Control
Reducing atmospheres often involve gases that are either flammable (hydrogen) or toxic (carbon monoxide). Maintaining these conditions, especially at high temperatures, requires sophisticated engineering controls to ensure safety and process efficiency.
Cost and Complexity
Creating and maintaining a specific atmospheric condition is an added layer of complexity and cost. However, for many industrial processes, this control is not optional—it is the only way to produce the desired material.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your understanding of atmospheric conditions should be tied directly to the chemical goal you wish to achieve.
- If your primary focus is converting an oxide to its pure element (e.g., ore to metal): You require an active reducing atmosphere containing a gas like carbon monoxide or hydrogen.
- If your primary focus is protecting a material from surface oxidation during heat treatment: You need to displace oxygen, which can be done with an inert gas (like nitrogen or argon) or a reducing gas.
- If your primary focus is combustion or simulating natural weathering: You require an oxidizing atmosphere, specifically one with a controlled amount of oxygen.
Ultimately, the nature of an atmosphere is defined by which chemical reactions it promotes and which it prevents.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Reducing Atmosphere | Oxidizing Atmosphere |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Transform materials (e.g., ore to metal) | Promote breakdown (e.g., combustion, rusting) |
| Key Absence | Free Oxygen (O₂) | N/A |
| Key Presence | Reducing Gases (H₂, CO) | Free Oxygen (O₂) |
| Example Process | Smelting iron in a blast furnace | Burning fuel, natural weathering |
Need precise atmospheric control for your lab processes? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing the tools and expertise to create and manage the exact reducing, inert, or oxidizing environments your research or production requires. Ensure the purity and quality of your materials—contact our experts today to discuss your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How we can develop inert atmosphere for a chemical reaction? Master Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Lab
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- What is an example of an inert atmosphere? Discover the Best Gas for Your Process



















