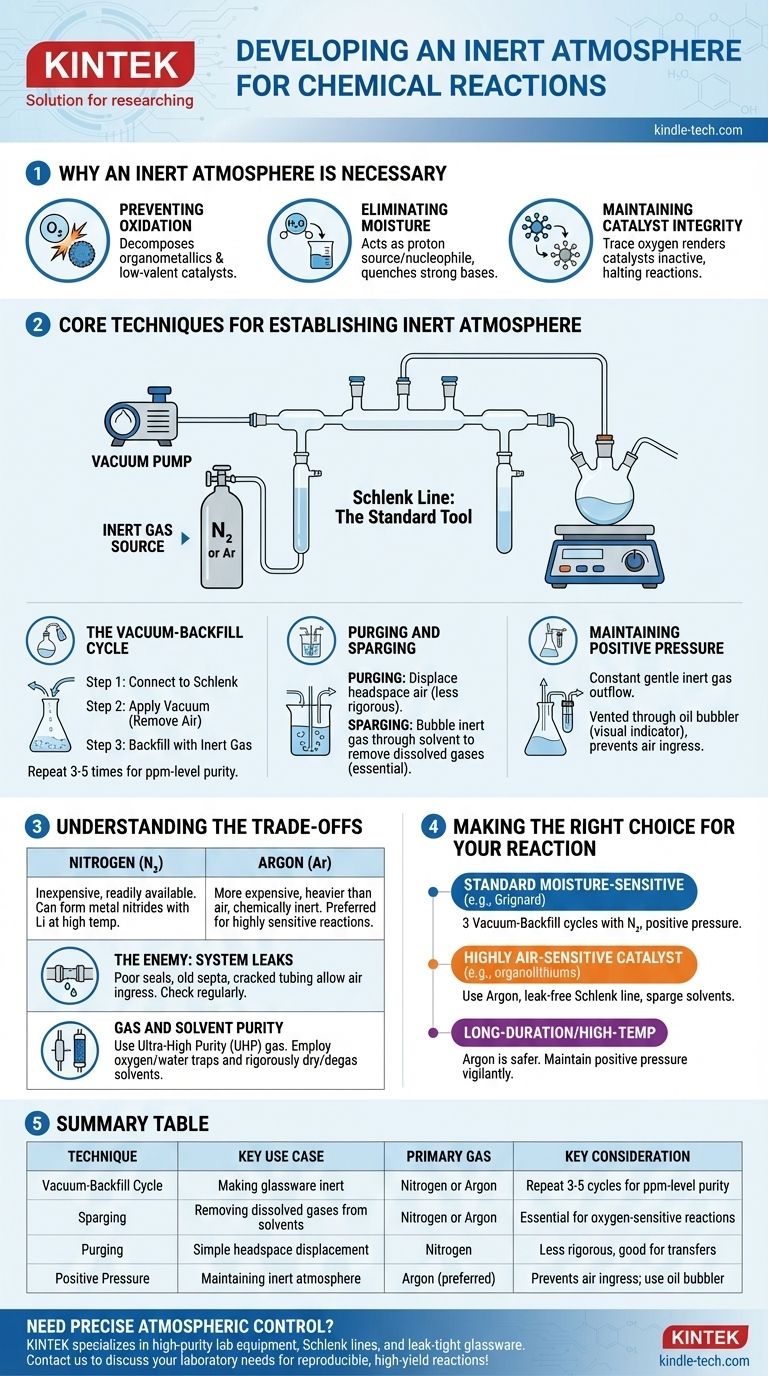
In practice, an inert atmosphere is created by physically removing the reactive air from a reaction vessel and replacing it with a non-reactive gas, most commonly nitrogen or argon. This is typically achieved using a dual-manifold system called a Schlenk line, which allows a chemist to alternate between applying a vacuum to the vessel and backfilling it with the inert gas. This cycle is repeated several times to ensure all oxygen and moisture are removed.
The core objective is not simply to add an inert gas, but to rigorously displace and remove the reactive atmosphere already present. Mastering this control over the reaction environment is fundamental to preventing unwanted side reactions and ensuring the integrity of sensitive materials.

Why an Inert Atmosphere is Necessary
Many chemical reactions involve reagents or produce products that are sensitive to components of ambient air. Failing to control the atmosphere can lead to failed reactions, low yields, or the formation of dangerous byproducts.
Preventing Oxidation
The most common culprit is **molecular oxygen (O₂) **, a powerful oxidizing agent. It can readily react with and decompose many common reagents, especially organometallics, low-valent metal catalysts, and radical intermediates.
Eliminating Moisture
Water vapor (H₂O) is another major concern. It acts as a proton source (a weak acid) and a nucleophile, which can quench strong bases (like Grignard reagents or organolithiums) or react with highly electrophilic compounds (like acid chlorides).
Maintaining Catalyst Integrity
In catalysis, the active state of a metal catalyst is often in a specific, low oxidation state. Exposure to even trace amounts of oxygen can irreversibly oxidize the catalyst, rendering it inactive and halting the reaction.
Core Techniques for Establishing an Inert Atmosphere
The standard tool for this process is a Schlenk line, a glass manifold connected to both a vacuum pump and a source of high-purity inert gas. This setup allows for two primary techniques.
The Vacuum-Backfill Cycle
This is the most common method for making glassware inert.
- The empty, dry reaction flask is connected to the Schlenk line.
- A vacuum is applied, removing the bulk of the air from the flask.
- The vacuum is closed, and the inert gas valve is opened, backfilling the flask with nitrogen or argon to ambient pressure.
This cycle is typically repeated three to five times to reduce the concentration of oxygen and moisture to negligible levels (parts-per-million).
Purging and Sparging
Purging involves simply passing a steady stream of inert gas through the headspace of the flask to displace the air. This is a less rigorous method but can be useful for simple transfers.
Sparging is the process of bubbling the inert gas through a liquid (like a reaction solvent) via a long needle or tube. This is essential for removing dissolved gases, especially oxygen, from the solvent before the reaction begins.
Maintaining Positive Pressure
Once the inert atmosphere is established, a slight positive pressure of the inert gas is maintained throughout the experiment. This ensures a constant, gentle outflow of gas, preventing any air from leaking into the system. This outflow is typically vented through an oil or mercury bubbler, which also serves as a visual indicator of the gas flow rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right gas and being aware of system limitations are critical for success. While these techniques are powerful, they are not foolproof.
Nitrogen vs. Argon
Nitrogen (N₂) is the workhorse for most inert atmosphere chemistry. It is inexpensive and readily available. However, under certain conditions (e.g., reactions with lithium metal at high temperatures), it can be reactive, forming metal nitrides.
Argon (Ar) is significantly more expensive but is heavier than air and chemically inert under virtually all laboratory conditions. It is the gas of choice for highly sensitive reactions or those involving metals that can react with N₂.
The Enemy: System Leaks
The effectiveness of your inert atmosphere is only as good as the weakest seal in your setup. Poorly greased glass joints, old rubber septa, or cracked tubing can allow air to slowly leak back into the system, compromising the reaction. Regularly checking for leaks with a vacuum gauge is standard practice.
Gas and Solvent Purity
Simply using a tank of inert gas is not enough. For extremely sensitive work, ultra-high purity (UHP) gas is required. Additionally, oxygen or water traps may be placed in-line to "scrub" the last traces of contaminants from the gas before it enters the manifold. Likewise, solvents must be rigorously dried and de-gassed (often by sparging) before use.
Making the Right Choice for Your Reaction
Your specific approach should be tailored to the sensitivity of your reagents and the goal of your experiment.
- If your primary focus is a standard, moisture-sensitive reaction (e.g., Grignard): Performing three vacuum-backfill cycles with nitrogen and maintaining positive pressure is typically sufficient.
- If your primary focus is a reaction using a highly air-sensitive catalyst or reagent (e.g., organolithiums, low-valent nickel): Using argon, ensuring a leak-free Schlenk line, and sparging your solvents are critical for success.
- If your primary focus is a long-duration or high-temperature reaction: Argon is the safer choice to avoid potential side reactions with nitrogen, and you must remain vigilant about maintaining positive pressure over the entire reaction time.
Mastering these atmospheric control techniques is what gives you true command over the chemical environment, transforming a reaction from a matter of chance into a predictable, reproducible process.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Key Use Case | Primary Gas | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vacuum-Backfill Cycle | Making glassware inert | Nitrogen or Argon | Repeat 3-5 cycles for ppm-level purity |
| Sparging | Removing dissolved gases from solvents | Nitrogen or Argon | Essential for oxygen-sensitive reactions |
| Purging | Simple headspace displacement | Nitrogen | Less rigorous, good for transfers |
| Positive Pressure | Maintaining inert atmosphere | Argon (preferred) | Prevents air ingress; use oil bubbler |
Need precise atmospheric control for your sensitive reactions? KINTEK specializes in high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including Schlenk lines, gas purification systems, and leak-tight glassware. Our experts can help you select the right setup to prevent oxidation, eliminate moisture, and maintain catalyst integrity. Contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and achieve reproducible, high-yield reactions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the purpose of inert atmosphere? A Guide to Protecting Your Materials and Processes
- What provides an inert atmosphere? Achieve Safety and Purity with Nitrogen, Argon, or CO2
- What is meant by inert atmosphere? A Guide to Preventing Oxidation & Ensuring Safety
- Can nitrogen be used for brazing? Key Conditions and Applications Explained
- Why nitrogen is used in furnace? A Cost-Effective Shield for High-Temperature Processes



















