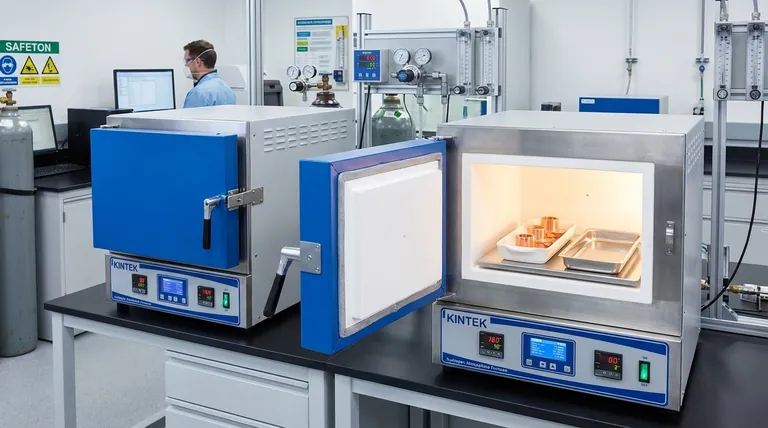
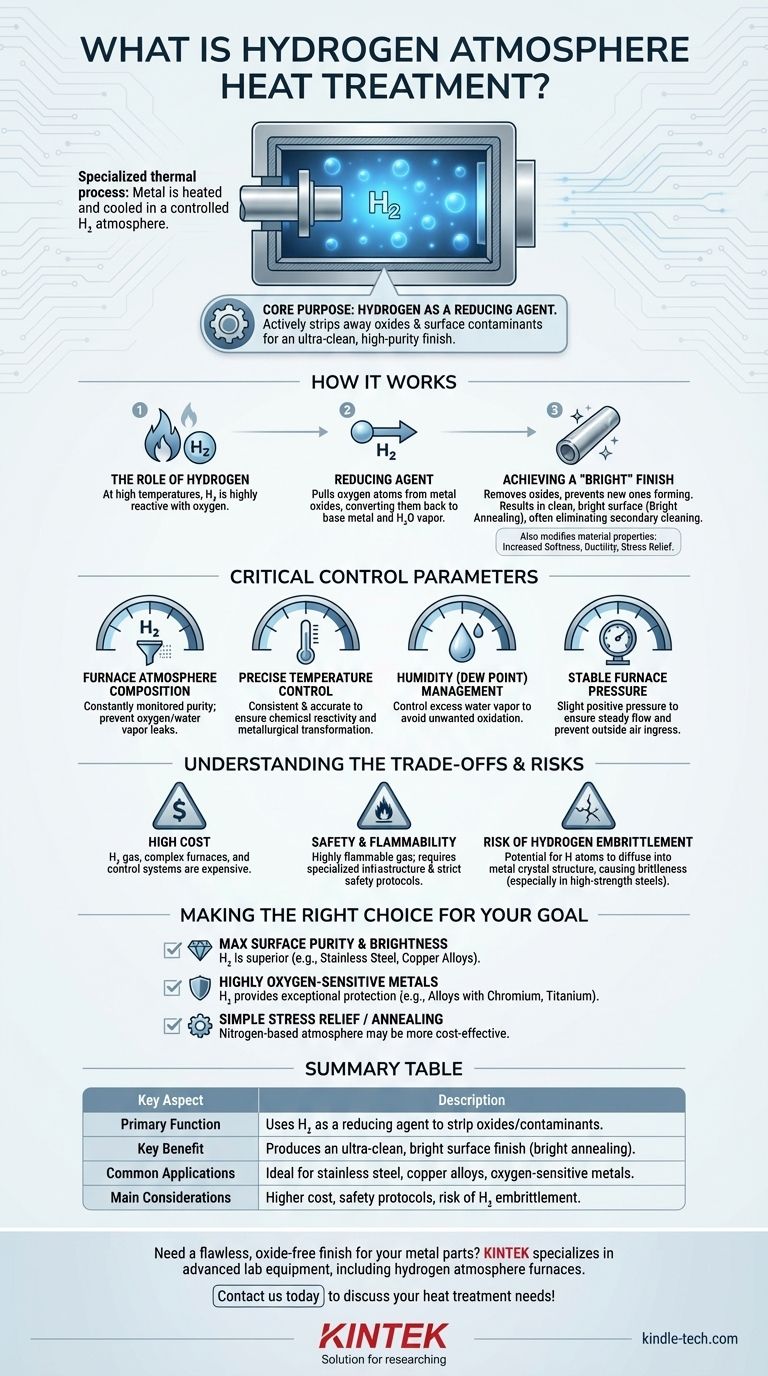
Hydrogen atmosphere heat treatment is a highly specialized thermal process where a metal is heated and cooled within a furnace chamber filled with a controlled hydrogen gas atmosphere. This process leverages the unique chemical properties of hydrogen to alter a material's physical and mechanical characteristics, often to create an exceptionally clean, bright surface finish without oxidation.
The fundamental purpose of using hydrogen is not simply to prevent reactions, but to actively promote desirable ones. Hydrogen acts as a powerful reducing agent, chemically stripping away oxides and surface contaminants to produce an ultra-clean, high-purity finish that is difficult to achieve with other methods.

How Hydrogen Atmosphere Treatment Works
To understand why this process is chosen, we must look at the specific chemical role hydrogen plays at high temperatures. It is an active participant in refining the material.
The Role of Hydrogen as a Reducing Agent
At elevated temperatures, hydrogen gas becomes highly reactive with oxygen. It effectively pulls oxygen atoms away from metal oxides that may be present on the material's surface.
This chemical reaction converts metal oxides (like iron or copper oxides) back into their base metal, producing water vapor (H₂O) as a byproduct, which is then flushed from the furnace.
Achieving a "Bright" Finish
The term bright annealing is frequently associated with this process. Because the hydrogen atmosphere removes existing oxides and prevents any new ones from forming, the metal part exits the furnace with a clean, shiny, and bright surface.
This often eliminates the need for secondary cleaning operations like acid pickling or abrasive blasting, which saves time and reduces costs.
Modifying Material Properties
Like all heat treatments, the controlled heating and cooling cycle alters the metal's internal grain structure. This can be used to increase softness and ductility, relieve internal stresses from prior manufacturing steps, and improve the overall workability of the material.
The Critical Control Parameters
The effectiveness of hydrogen heat treatment is entirely dependent on maintaining a meticulously controlled environment. Failure to manage these variables will compromise the final product quality.
Furnace Atmosphere Composition
The purity of the hydrogen atmosphere must be constantly monitored and maintained. Any contamination, particularly from oxygen or water vapor leaking into the furnace, will negate the benefits of the process.
Precise Temperature Control
Consistent and accurate temperature is crucial. The chemical reactivity of hydrogen and the metallurgical transformation of the part are both highly dependent on reaching and holding specific temperatures throughout the cycle.
Humidity (Dew Point) Management
Controlling the humidity, or dew point, inside the furnace is critical. Excess water vapor can itself become a source of oxygen at high temperatures, leading to unwanted oxidation or decarburization of the metal surface.
Stable Furnace Pressure
The furnace is kept at a slight positive pressure. This ensures a steady, controlled flow of hydrogen gas and, more importantly, prevents outside air from leaking into the chamber and contaminating the pure atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, hydrogen heat treatment is not a universal solution. It involves significant trade-offs that must be considered.
High Cost
Hydrogen gas is significantly more expensive than more common industrial atmosphere gases like nitrogen or argon. The furnaces and control systems required are also more complex and costly.
Safety and Flammability
Hydrogen is a highly flammable gas. Facilities using this process require specialized infrastructure, stringent safety protocols, and advanced leak detection systems to mitigate the inherent risk of explosion.
Risk of Hydrogen Embrittlement
For certain materials, particularly high-strength steels, there is a risk of hydrogen embrittlement. This occurs when individual hydrogen atoms diffuse into the metal's crystal structure, causing a loss of ductility and making it brittle. This potential negative side effect must be carefully managed for susceptible alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heat treatment atmosphere depends entirely on the material and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is maximum surface purity and brightness: Hydrogen is the superior choice, especially for materials like stainless steel or copper alloys, as it actively cleans the surface.
- If you are processing highly oxygen-sensitive metals: For alloys containing elements like chromium or titanium, hydrogen's ability to scavenge trace oxygen provides an exceptional level of protection.
- If your goal is simple stress relief or annealing with no strict surface requirements: A less expensive nitrogen-based atmosphere is often a more practical and cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, choosing a hydrogen atmosphere is a strategic decision for applications where surface chemistry and a flawless finish are paramount.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Uses hydrogen gas as a reducing agent to strip oxides and contaminants. |
| Key Benefit | Produces an ultra-clean, bright surface finish (bright annealing). |
| Common Applications | Ideal for stainless steel, copper alloys, and oxygen-sensitive metals. |
| Main Considerations | Higher cost, safety protocols for flammability, and risk of hydrogen embrittlement. |
Need a flawless, oxide-free finish for your metal parts? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including hydrogen atmosphere furnaces, to help you achieve superior surface purity and material properties. Our experts can help you select the right solution for your specific application. Contact us today to discuss your heat treatment needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are hydrogen furnaces used for? Achieve Purity and Speed in High-Temperature Processing
- What is hydrogen annealing? Achieve Superior Material Properties with Bright Annealing
- What is the use of hydrogen in furnace? A Key to Oxygen-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What are the primary benefits of using hydrogen firing for sintering parts? Achieve Peak Density & Corrosion Resistance
- When would you need to use a controlled atmosphere? Prevent Contamination and Control Reactions



















