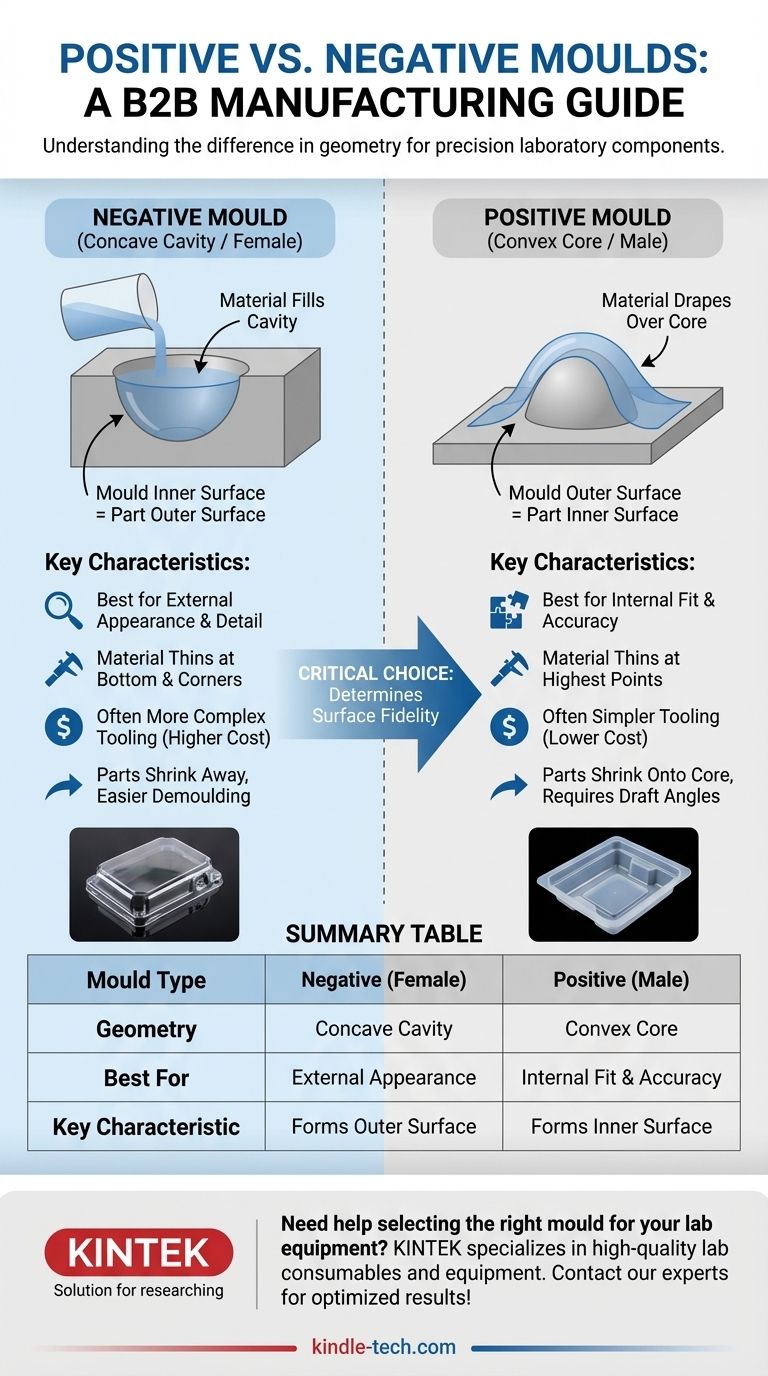
In manufacturing, the fundamental difference lies in the mould's geometry. A negative mould is a concave cavity that you fill or form a material into, much like pouring jello into a jello mould. Conversely, a positive mould is a convex shape that you drape or form a material over, similar to creating a papier-mâché mask over a balloon. The choice between them dictates which surface of the final part will have the highest fidelity.
The decision to use a positive or negative mould is not a matter of preference, but a critical engineering choice. It directly determines whether the inner or the outer surface of your component will be the most dimensionally accurate and have the best surface finish.

Understanding the Core Concepts
To grasp the implications of this choice, we must first clearly define each mould type and how it interacts with the raw material. These are often referred to as "male" and "female" tools.
Negative Moulds: The Cavity (Female)
A negative mould features a concave cavity. The raw material, such as a heated plastic sheet in thermoforming, is forced into this cavity.
The defining characteristic is that the mould's inner surface forms the part's outer surface. This means any detail, texture, or lettering engraved into the mould will be perfectly replicated on the exterior of the finished product.
Positive Moulds: The Core (Male)
A positive mould is a convex shape, or a "core," that rises from a base plate. The raw material is stretched and draped over this shape.
Here, the opposite is true: the mould's outer surface forms the part's inner surface. The critical dimensions and finish are therefore transferred to the inside of the final component.
Practical Implications in Manufacturing
The geometric difference has significant consequences for the final part, especially in processes like thermoforming, vacuum forming, and composites manufacturing.
Which Surface Gets the Detail?
This is the most critical distinction. The surface of the material that is in direct contact with the mould will receive the highest-quality finish and dimensional accuracy.
- Negative Moulds are used when the exterior appearance is paramount. Think of product enclosures, automotive body panels, or retail packaging where the outer look and feel are crucial.
- Positive Moulds are chosen when the interior fit is the priority. This is common for packaging trays that must hold specific items, or internal liners that need to fit precisely inside another assembly.
How Material Thins and Stretches
As a material like a plastic sheet is stretched to form a shape, it thins. The location of maximum thinning differs between the two mould types.
- In a negative mould, the material stretches the most as it is drawn into the deep corners and the bottom of the cavity. The last part of the sheet to touch the mould, typically the base, will be the thinnest.
- In a positive mould, the material thins most at the highest points and sharpest upper edges of the mould, as these are the first areas to make contact and stretch.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a mould type involves balancing design requirements with manufacturing constraints. There is no universally "better" option, only the one that is right for the job.
Tooling Cost and Simplicity
In many cases, creating a convex positive mould can be simpler and therefore less expensive than machining a complex, multi-part concave cavity. This is especially true for simpler geometric forms.
Demoulding and Draft Angles
Ejecting the finished part from the mould is a critical step. Parts tend to shrink onto a positive core, which can make them difficult to remove without adequate draft angles (slight tapering). Conversely, parts shrink away from a negative cavity, which can make ejection easier, but deep, straight-walled cavities can still trap parts.
Process Control
The type of mould can affect secondary process steps. For example, in vacuum forming, a negative mould allows vacuum holes to be placed discreetly on surfaces that will form the part's exterior. In a positive mould, these holes are on the tool surface that forms the part's interior.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be driven by the end-use requirements of your component. Ask yourself which surface is the most critical for function and aesthetics.
- If your primary focus is external appearance and finish: Use a negative (female) mould to ensure the highest fidelity on the outside of the part.
- If your primary focus is internal fit and dimensional accuracy: Use a positive (male) mould to precisely define the inside of the part.
- If you are creating a simple prototype and need to minimize tooling cost: A positive mould is often the faster and more economical path for basic shapes.
Ultimately, the choice is determined by which surface of your part matters most.
Summary Table:
| Mould Type | Geometry | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Negative (Female) | Concave Cavity | External Appearance | Mould surface forms the part's outer surface |
| Positive (Male) | Convex Core | Internal Fit & Accuracy | Mould surface forms the part's inner surface |
Need help selecting the right mould for your lab equipment or consumables?
Choosing the correct mould type is critical for the performance and longevity of your laboratory components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables, ensuring your manufacturing processes yield parts with the precise surface finish and dimensional accuracy your research demands.
Our experts can guide you through the selection process to optimize your results. Contact our team today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
- XRF & KBR steel ring lab Powder Pellet Pressing Mold for FTIR
- No Demolding Lab Infrared Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Culture Dish and Evaporation Dish
People Also Ask
- How do graphite molds function within the vacuum hot pressing process for ZnS? Optimize Densification & Optical Clarity
- What are the primary functions of high-density graphite molds in FAST/SPS? Optimizing Thermal and Mechanical Performance
- What is the role of high-strength graphite molds in vacuum hot pressing Beryllium? Enhance Densification & Precision
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What role do graphite mold components play in the vacuum hot pressing of Ti-3Al-2.5V? Optimize Alloy Densification









