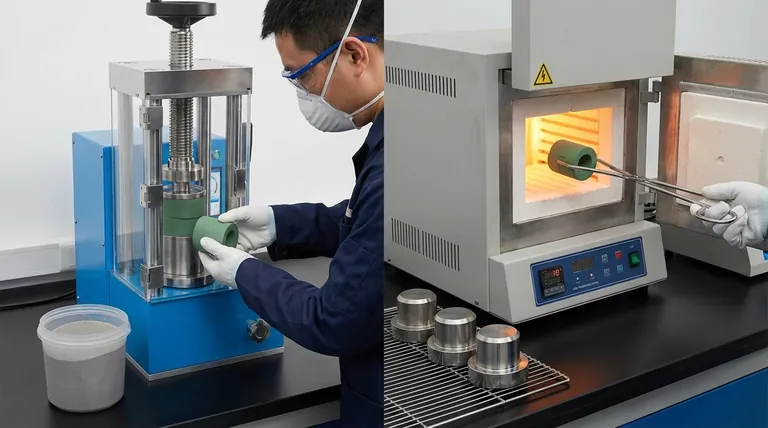
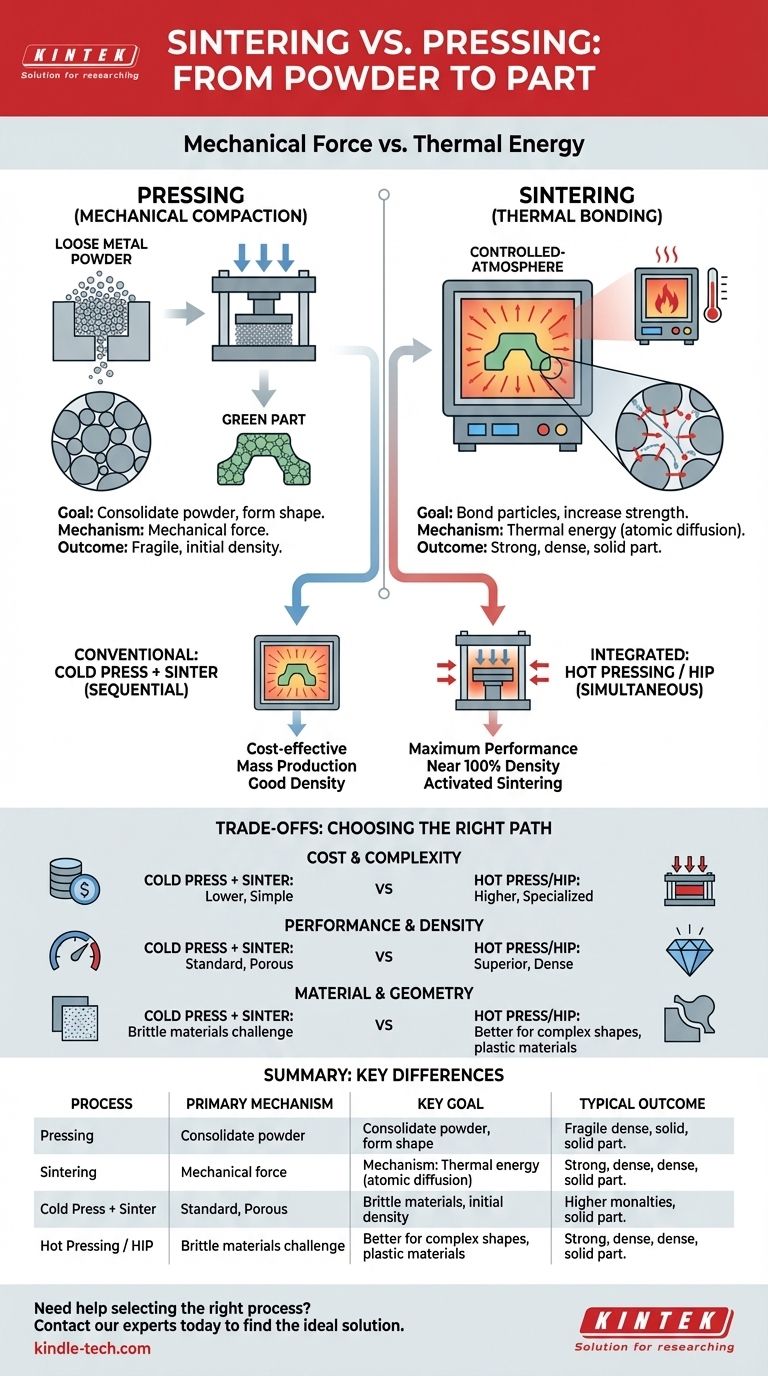
At its core, pressing and sintering are two distinct but complementary processes used to turn powders into solid objects. Pressing is a mechanical process that uses force to compact powder into a desired shape, known as a "green part." Sintering is a subsequent thermal process that heats this part to bond the particles together, increasing its strength and density without melting it.
The fundamental distinction is one of mechanism: pressing uses mechanical force to create shape and initial density, while sintering uses thermal energy to fuse particles together and create a strong, solid mass. They are not alternatives, but rather distinct stages that can be combined in different ways to achieve a final part.

The Fundamental Goal: From Powder to Part
The field of powder metallurgy starts with a simple problem: you have a collection of fine metal or ceramic particles, and you need to create a single, dense, and strong component. Both pressing and sintering are critical tools to solve this problem.
Step 1: Pressing (Mechanical Compaction)
Pressing is the process of applying force to a powder contained within a die. The primary goal is to consolidate the loose powder, increasing its density and forming it into a specific, albeit fragile, shape.
This initial shape is called a green part. It has the desired geometry but lacks significant mechanical strength because the particles are only held together by mechanical interlocking, not true metallurgical bonds.
Step 2: Sintering (Thermal Bonding)
Sintering is what turns the fragile green part into a robust component. The part is placed in a controlled-atmosphere furnace and heated to a high temperature, typically below the material's melting point.
At this elevated temperature, a process of atomic diffusion occurs at the contact points between particles. Atoms migrate across the particle boundaries, causing the individual particles to fuse together, reducing porosity and dramatically increasing the part's strength, density, and integrity.
How the Processes Interact: Cold vs. Hot Methods
The key difference in manufacturing strategy lies in when and how pressing and sintering are combined. This leads to two primary pathways.
The Conventional Path: Cold Pressing + Sintering
This is a sequential, two-step process:
- Cold Pressing: The powder is first pressed into a green part at room temperature.
- Sintering: The green part is then removed from the press and heated in a separate furnace to be sintered.
This is the most common and often most cost-effective method for high-volume production of parts that do not require maximum theoretical density.
The Integrated Path: Hot Pressing (Activated Sintering)
In hot pressing, pressure and heat are applied simultaneously. The powder is placed in a die that can withstand extreme temperatures, and it is heated while under constant mechanical pressure.
This integrated approach is considered an activated sintering process. The pressure helps break down surface oxide films on the powder particles and forces them into intimate contact, accelerating atomic diffusion and alloy formation. The result is a much faster process that can achieve significantly higher final densities compared to conventional sintering.
The High-Pressure Variant: Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP)
Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) is an advanced form of hot pressing. Instead of using a mechanical die, it applies extremely high pressure from all directions via an inert gas. This isostatic pressure is exceptionally effective at eliminating any remaining internal voids, allowing for parts that reach nearly 100% of theoretical density.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right process pathway involves balancing cost, complexity, and the desired performance of the final component.
Cost and Complexity
The conventional Cold Pressing + Sintering method uses simpler, less expensive equipment and is generally the most cost-effective approach for mass production.
Hot Pressing and HIP require highly specialized and expensive presses and furnaces capable of operating under extreme conditions, making them suitable for lower-volume, higher-value components.
Performance and Density
For applications where maximum strength and performance are critical, Hot Pressing and HIP are superior. The simultaneous application of pressure actively closes pores that might otherwise remain after conventional sintering, resulting in a denser and more robust part.
Material and Geometric Constraints
Some brittle ceramic powders can crack under the high stresses of cold pressing. Hot Pressing can be a gentler alternative, as the material is more plastic at elevated temperatures. Furthermore, complex geometries can be difficult to densify uniformly with simple pressing, making the isostatic pressure of HIP a more effective choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by the specific requirements of your component and production environment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume production: The two-step Cold Pressing + Sintering path is the industry standard and the most practical choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum performance, density, and strength: Hot Pressing or Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) are necessary to achieve the superior material properties required for critical applications.
- If you are working with difficult-to-press materials or complex shapes: Hot Pressing or HIP provides the control needed to form a fully dense part without introducing defects.
Ultimately, choosing the right method is about strategically combining mechanical force and thermal energy to achieve your desired outcome efficiently.
Summary Table:
| Process | Primary Mechanism | Key Goal | Typical Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pressing | Mechanical Force | Compact powder into a "green part" shape | Fragile part with initial density |
| Sintering | Thermal Energy | Fuse particles via atomic diffusion | Strong, dense, solid part |
| Cold Press + Sinter | Sequential Force & Heat | Cost-effective mass production | Good density, industry standard |
| Hot Pressing / HIP | Simultaneous Force & Heat | Maximum density & performance | Near 100% theoretical density |
Need help selecting the right powder metallurgy process for your lab's materials?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed for both pressing and sintering applications. Whether you are developing new materials in R&D or optimizing high-volume production, our expertise and product range can help you achieve superior results in density, strength, and efficiency.
Let's discuss your specific requirements. Contact our experts today to find the ideal solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
People Also Ask
- What is cold isostatic pressing mold material? Essential Elastomers for Uniform Density
- What are the applications of cold isostatic pressing? Achieve Uniform Density for Complex Parts
- How big is the isostatic pressing market? A Deep Dive into the $1.2B+ Advanced Manufacturing Enabler
- Why is cold working better than hot working? A Guide to Choosing the Right Metal Forming Process
- How much does an isostatic press cost? A Guide to Lab vs. Industrial Pricing



















