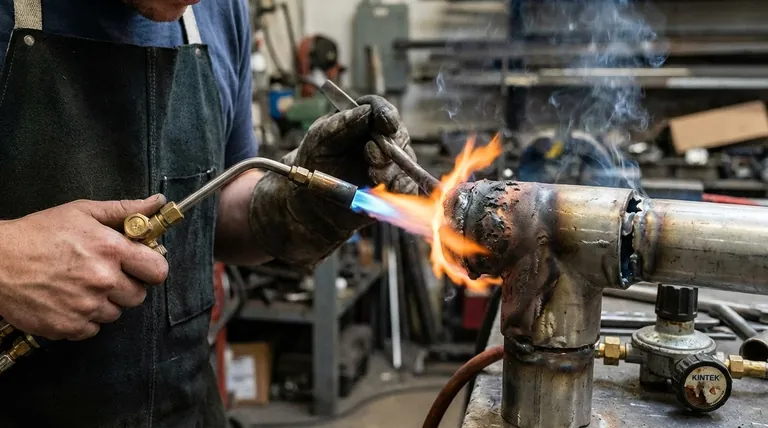
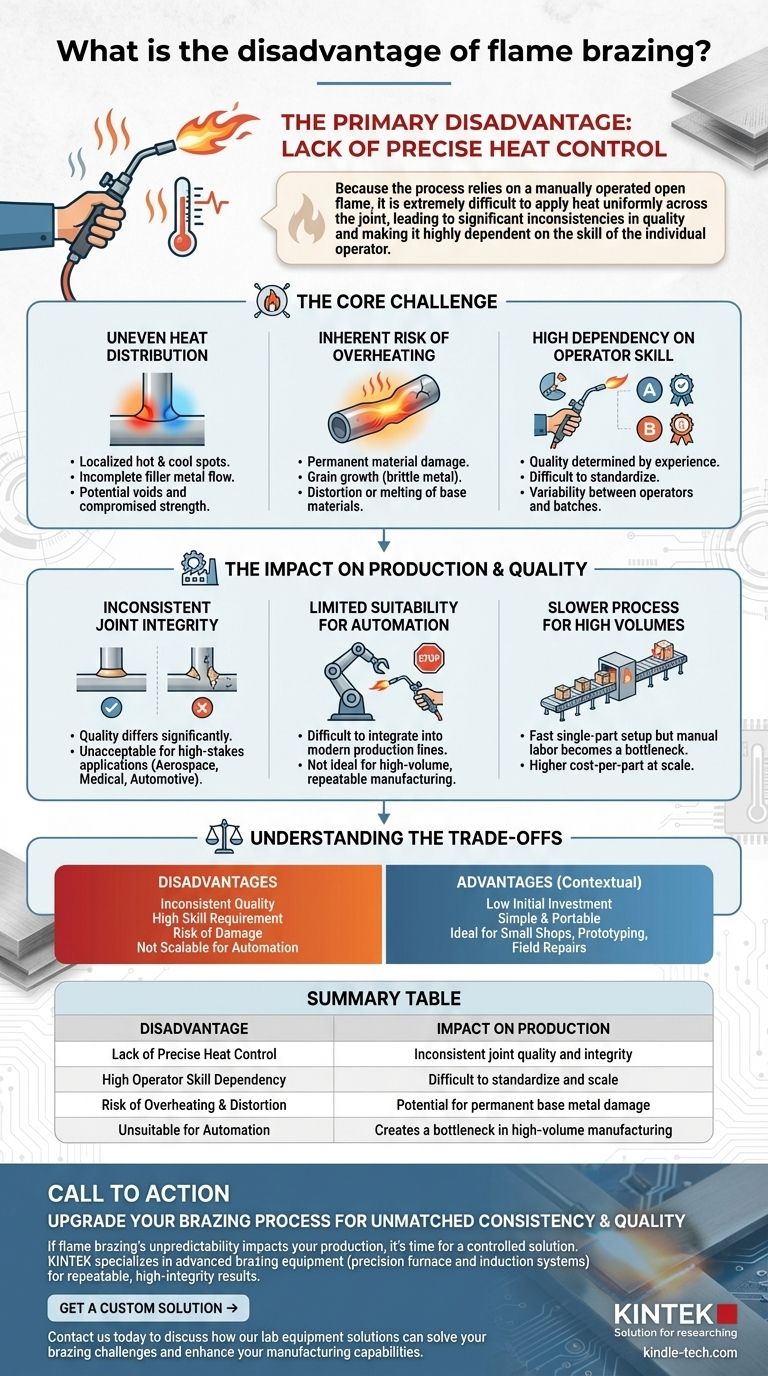
The primary disadvantage of flame brazing is its inherent lack of precise heat control. Because the process relies on a manually operated open flame, it is extremely difficult to apply heat uniformly across the joint, leading to significant inconsistencies in quality and making it highly dependent on the skill of the individual operator.
The core issue with flame brazing is its manual nature. This introduces a level of variability that is often unacceptable for high-precision or automated manufacturing, making alternatives like furnace or induction brazing superior when consistency and repeatability are critical.

The Core Challenge: Lack of Precise Control
The fundamental weakness of flame brazing is the difficulty of managing the thermal energy from a torch. This single issue is the source of several cascading problems that impact joint quality and process reliability.
Uneven Heat Distribution
A handheld flame almost never heats a part uniformly. This creates localized hot spots and cool spots across the joint area.
Incomplete filler metal flow is a common result. The brazing alloy will be drawn toward the hottest areas, potentially starving other parts of the joint and creating voids that compromise its strength.
The Inherent Risk of Overheating
An unskilled operator, or even a skilled one working on a complex part, can easily overheat the base metals.
Overheating can cause permanent material damage, grain growth that makes the metal brittle, or distortion of the parent materials. In extreme cases, it can melt the base metal, resulting in a failed component.
High Dependency on Operator Skill
The quality of a flame-brazed joint is almost entirely determined by the technician's experience and technique.
This reliance on a "master craftsman" makes the process difficult to standardize and scale. Two different operators will almost certainly produce joints with different metallurgical properties, even when following the same procedure.
The Impact on Production and Quality
The lack of control directly affects the efficiency of a production environment and the reliability of the final product, especially when compared to more automated methods.
Inconsistent Joint Integrity
Because of uneven heating and operator variability, joint quality can differ significantly from one part to the next.
This inconsistency is unacceptable in applications where failure is not an option, such as in the aerospace, medical, or automotive industries.
Limited Suitability for Automation
The manual nature of flame brazing makes it exceptionally difficult to integrate into a modern, automated production line.
Processes like induction brazing (using electromagnetic fields) or furnace brazing (using controlled-atmosphere ovens) are far better suited for high-volume, repeatable manufacturing.
Slower Process for High Volumes
While flame brazing has a fast setup time for a single part, the manual labor involved makes it a bottleneck in mass production.
Automated methods can process hundreds or thousands of parts with minimal human intervention, delivering a much lower cost-per-part at scale.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite its disadvantages, flame brazing remains a widely used process. Its weaknesses in one context are its strengths in another. Recognizing these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
The Advantage of Simplicity and Cost
The primary reason for its popularity is its low initial investment. The equipment—torches, regulators, and gas cylinders—is inexpensive and widely available.
This makes it the ideal choice for small shops, prototyping, and one-off repair jobs where the cost of a furnace or induction coil would be prohibitive.
When Precision is Overkill
For many applications, such as general plumbing or HVAC repairs, the high precision of furnace brazing is unnecessary.
In these cases, the portability and flexibility of a torch are far more valuable than absolute temperature control. The joint requirements are simply not demanding enough to justify a more advanced process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct brazing method requires you to match the process capabilities to your project's specific demands for quality, volume, and cost.
- If your primary focus is low-cost, low-volume work or field repairs: Flame brazing is often the best choice due to its portability, flexibility, and minimal setup cost.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with consistent, verifiable quality: Induction or furnace brazing offers the superior control and automation capabilities required.
- If your primary focus is joining complex assemblies or thin materials prone to distortion: The precise, uniform heating of furnace brazing is necessary to ensure joint integrity without damaging the components.
Understanding these fundamental trade-offs empowers you to select the joining process that aligns perfectly with your project's demands for cost, quality, and scale.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact on Production |
|---|---|
| Lack of Precise Heat Control | Inconsistent joint quality and integrity |
| High Operator Skill Dependency | Difficult to standardize and scale |
| Risk of Overheating & Distortion | Potential for permanent base metal damage |
| Unsuitable for Automation | Creates a bottleneck in high-volume manufacturing |
Upgrade your brazing process for unmatched consistency and quality.
If the unpredictable nature of flame brazing is impacting your production quality and efficiency, it's time for a controlled solution. KINTEK specializes in advanced brazing equipment, including precision furnace and induction systems, designed for laboratories and manufacturing facilities that demand repeatable, high-integrity results.
We provide the reliable equipment and consumables you need to eliminate operator variability, protect your base materials, and seamlessly integrate into automated lines.
Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment solutions can solve your brazing challenges and enhance your manufacturing capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Benchtop Laboratory Freeze Dryer for Lab Use
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- Why is freeze drying a good method for preserving fruits and vegetables? Unlock Superior Food Preservation
- What occurs during the secondary drying phase? Master the Final Step for Product Stability
- Why is freeze drying important for certain chemical products? Preserve Integrity & Extend Shelf Life
- What are the key steps in the freeze drying process? A Guide to Mastering Sublimation
- What are the applications of vacuum freeze-drying technology? Unlock Superior Preservation Across Industries



















