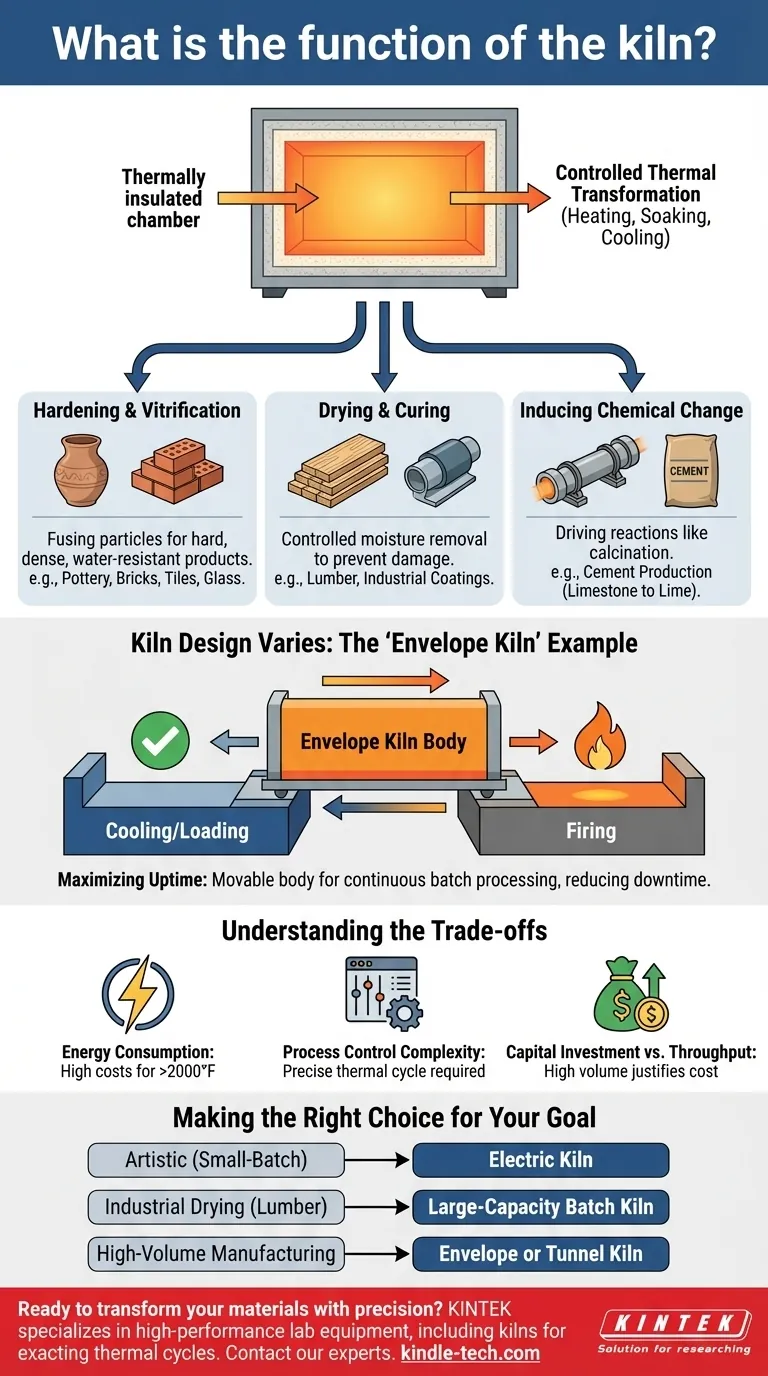
At its core, a kiln is a thermally insulated chamber—a type of specialized oven capable of reaching and maintaining extremely high temperatures. Its primary function is to heat materials to a sufficient temperature to effect a permanent change, such as hardening clay into ceramic, drying lumber, or inducing a specific chemical reaction.
A kiln's function is not simply to generate heat, but to precisely control a high-temperature environment. This control is what transforms materials, and the specific design of the kiln is dictated by the scale, speed, and fragility of the items being processed.
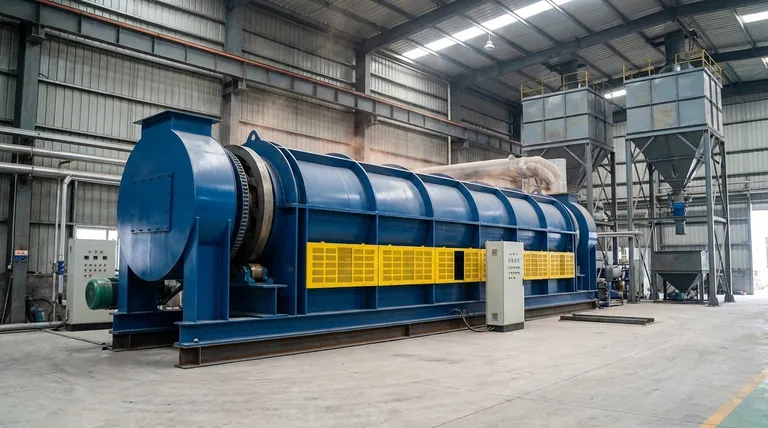

The Fundamental Principle: Controlled Thermal Transformation
A kiln's purpose extends far beyond simple heating. It facilitates a fundamental change in a material's physical or chemical state through the precise application of a thermal cycle (heating, soaking, and cooling).
Hardening and Vitrification
For materials like clay and glass, the kiln's heat causes particles to fuse together in a process called vitrification. This transforms a soft, fragile object into a hard, dense, and water-resistant final product, such as pottery, bricks, or tiles.
Drying and Curing
In other applications, like drying lumber or curing industrial coatings, the kiln provides a controlled environment to remove moisture. This must be done at a specific rate to prevent the material from cracking, warping, or becoming damaged.
Inducing Chemical Change
In heavy industry, kilns are used to drive chemical reactions. For example, a rotary kiln heats limestone to produce lime and carbon dioxide, a critical step in manufacturing cement. This process is known as calcination.
Why Kiln Design Varies: The 'Envelope Kiln' Example
The specific design of a kiln is engineered to solve a particular operational problem. The "envelope kiln" described in your reference material is a perfect example of a design optimized for industrial efficiency.
The Problem: Downtime in Batch Processing
A traditional kiln must be loaded, heated, cooled, and unloaded in sequence. The cooling and reloading periods represent significant downtime, where the expensive equipment is not actively producing.
The Envelope Kiln Solution
This design features a movable kiln body (the "envelope") and two or more stationary bases. While one base is being fired, the other can be safely cooled, unloaded, and re-loaded with a new batch.
The Benefit: Maximizing Uptime
Once the first batch is finished, the hot kiln envelope is simply moved over to the second, pre-loaded base, and the firing process begins again almost immediately. This nearly eliminates downtime, making it ideal for large-volume batch processing of heavy or fragile products where continuous operation is key.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, kilns present significant operational challenges that influence their design and use.
Energy Consumption
Reaching and maintaining temperatures of over 2000°F (1100°C) requires a tremendous amount of energy. Modern kiln designs focus heavily on insulation, heat recovery systems, and efficient fuel sources to manage high operational costs.
Process Control Complexity
The success of a firing depends entirely on following a precise temperature profile. Heating too quickly can cause items to explode from thermal shock, while improper cooling can cause cracks. This requires sophisticated control systems.
Capital Investment vs. Throughput
A simple hobbyist kiln may cost a few thousand dollars. An industrial envelope or tunnel kiln represents a massive capital investment, justified only by the need for high throughput and the operational efficiency it provides.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The right kiln is determined entirely by the material you are processing and your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is artistic creation or small-batch pottery: A simple top-loading or front-loading electric kiln offers the best balance of precise control and affordability.
- If your primary focus is industrial drying, like for lumber: A large-capacity, low-temperature batch kiln with integrated humidity control is essential to prevent product damage.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: An envelope or tunnel kiln is required to maximize throughput and minimize costly downtime between batches.
Ultimately, a kiln is a powerful tool for material transformation, and understanding its function allows you to select the right design for your specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Kiln Function | Key Process | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Hardening & Vitrification | Fusing particles to create a hard, dense material | Pottery, bricks, tiles, glass |
| Drying & Curing | Controlled moisture removal to prevent damage | Lumber, industrial coatings |
| Chemical Change | Driving reactions like calcination | Cement production (limestone to lime) |
Ready to transform your materials with precision? Whether you're in research, manufacturing, or processing, the right kiln is critical to your success. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-performance lab equipment, including kilns designed for exacting thermal cycles. Our experts will help you select the ideal solution for hardening, drying, or chemical processing—ensuring efficiency, control, and reliability. Contact our team today to discuss your specific kiln requirements and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste



















