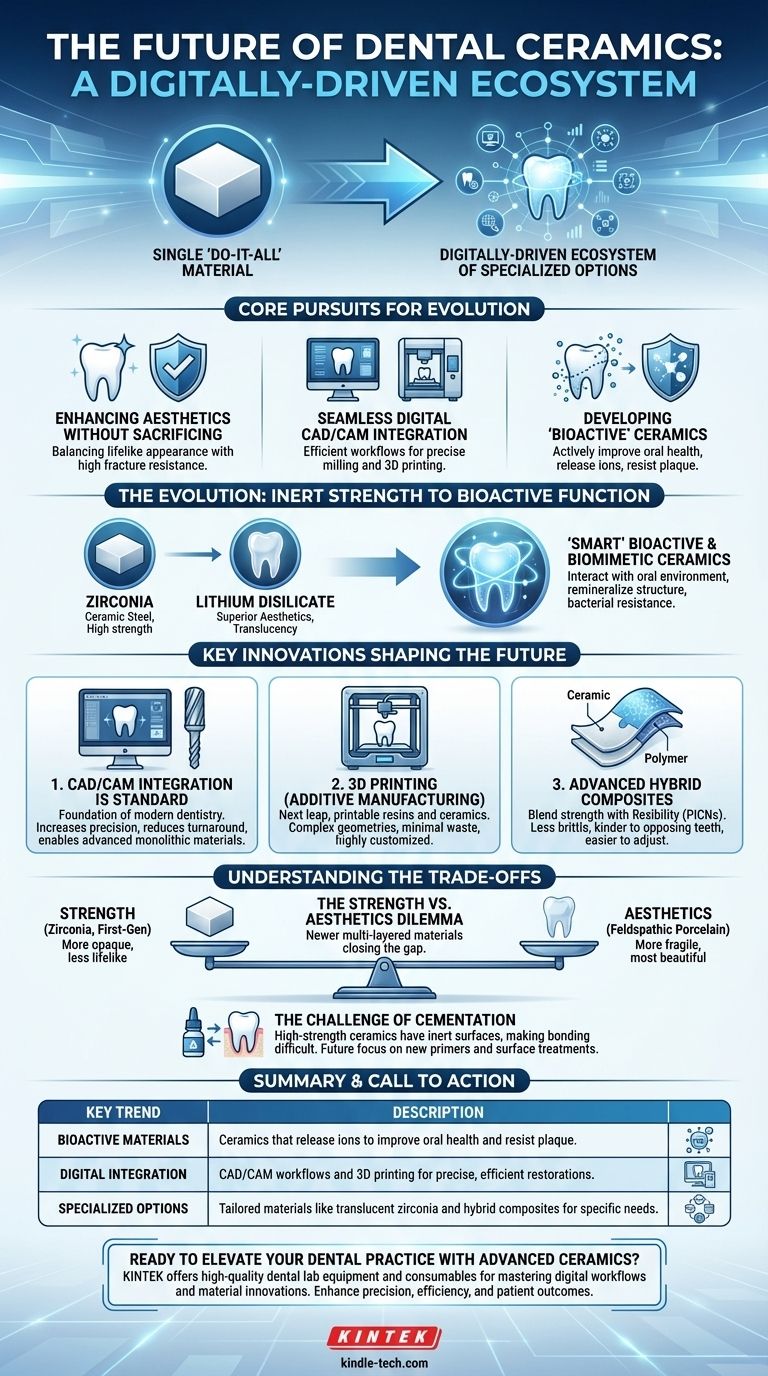
The future of dental ceramics is a trajectory moving away from a single "do-it-all" material and toward a digitally-driven ecosystem of specialized options. This evolution is defined by three core pursuits: enhancing aesthetics without sacrificing strength, integrating materials with seamless digital CAD/CAM workflows, and developing "bioactive" ceramics that actively improve oral health.
The central shift in dental ceramics is from passive, inert materials to a sophisticated, digitally-integrated toolkit. The future lies not in finding one perfect material, but in mastering the selection of highly specialized ceramics—from ultra-translucent zirconias to 3D-printable resins—that are tailored to specific clinical needs and manufactured with digital precision.

The Evolution from Inert Strength to Bioactive Function
For decades, the goal in dental ceramics was simple: find a material that was strong enough to survive in the mouth and looked reasonably like a tooth. This led to the dominance of materials prized for their mechanical properties.
The Era of High-Strength Materials
The two titans of modern ceramics have been zirconia and lithium disilicate. Zirconia became the gold standard for posterior crowns and bridges due to its immense fracture resistance, often called "ceramic steel."
Lithium disilicate, on the other hand, offered superior aesthetics and translucency, making it the preferred choice for anterior restorations where appearance is paramount. The market was largely a choice between these two options.
The Push for "Smart" Ceramics
The next frontier is the development of materials that do more than just fill a space. The focus is shifting to bioactive and biomimetic ceramics.
These materials are designed to interact favorably with the surrounding oral environment. This includes ceramics that can release ions like fluoride, calcium, and phosphate to help remineralize adjacent tooth structure or materials with surfaces that resist plaque and bacterial accumulation.
Key Innovations Shaping the Future
Three technological shifts are fundamentally changing how ceramic restorations are designed, manufactured, and implemented.
1. CAD/CAM Integration is Now Standard
Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAD/CAM) is no longer a niche technology; it is the foundation of modern restorative dentistry. The future of ceramics is inextricably linked to materials that can be efficiently milled or printed.
This digital workflow increases precision, reduces turnaround times for patients, and allows for the use of advanced, monolithic materials that are difficult to process using traditional lab techniques.
2. 3D Printing (Additive Manufacturing)
While milling (subtractive manufacturing) is the current standard, 3D printing represents the next leap. Printable ceramic-filled resins and, eventually, pure ceramics will allow for the creation of complex geometries with minimal material waste.
This technology will enable highly customized, intricate restorations and has the potential to dramatically reduce the cost and time associated with manufacturing crowns, veneers, and implants.
3. Advanced Hybrid Composites
A rapidly growing category is hybrid ceramics, also known as polymer-infiltrated ceramic networks (PICNs). These materials blend the strength and wear-resistance of ceramics with the flexibility and shock-absorption of polymers.
They are less brittle than traditional ceramics, making them kinder to the opposing teeth. They are also easier to mill and adjust in the clinic, offering a compelling combination of durability and practicality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single material solves every problem. The core challenge in dental materials science remains balancing a series of competing properties.
The Strength vs. Aesthetics Dilemma
This is the classic trade-off. The strongest materials, like first-generation zirconia, are often the most opaque and least lifelike. The most beautiful materials, like traditional feldspathic porcelains, are the most fragile.
While newer materials like multi-layered, high-translucency zirconia are closing this gap, clinicians must still carefully select a material based on the specific location in the mouth and the functional load it will endure.
The Challenge of Cementation and Bonding
The clinical success of a ceramic restoration depends heavily on how well it is bonded to the tooth. High-strength ceramics like zirconia have notoriously inert surfaces that make achieving a durable, long-term chemical bond more challenging than with glass-ceramics.
Future developments will focus on new ceramic primers, cements, and surface treatments to make the bonding process more predictable and reliable across all material types.
How to Prepare for the Future of Dental Ceramics
Navigating these advancements requires a focus on principles rather than specific brand names, as the materials themselves will continue to evolve rapidly.
- If your primary focus is aesthetic anterior restorations: Master the use of modern high-translucency zirconias and advanced lithium disilicates, paying close attention to material selection based on patient needs.
- If your primary focus is durable, long-term posterior restorations: Deepen your understanding of monolithic zirconia and the emerging category of hybrid ceramics, which offer excellent wear characteristics.
- If your primary focus is practice efficiency and growth: Invest your educational efforts in mastering digital workflows, from intraoral scanning to CAD/CAM design and in-office milling or printing.
The future belongs to the clinician who can leverage a diverse material portfolio with the power of digital technology to deliver truly personalized and durable patient care.
Summary Table:
| Key Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Bioactive Materials | Ceramics that release ions to improve oral health and resist plaque. |
| Digital Integration | CAD/CAM workflows and 3D printing for precise, efficient restorations. |
| Specialized Options | Tailored materials like translucent zirconia and hybrid composites for specific needs. |
Ready to Elevate Your Dental Practice with Advanced Ceramics?
As the future of dental ceramics evolves, having the right lab equipment and consumables is crucial for mastering digital workflows and material innovations. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality dental lab equipment and consumables that support the latest in CAD/CAM technology, milling, and material testing. Whether you're integrating 3D printing or optimizing your ceramic processes, our solutions are designed to enhance precision, efficiency, and patient outcomes.
Contact us today to discover how KINTEK can help you stay ahead in the rapidly changing world of dental ceramics!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results
- What is the sintering temperature of zirconium? A Guide to the 1400°C-1600°C Range for Dental Labs



















