In short, some of the hardest commercially available PVD coatings are advanced nanocomposites, such as Aluminum Titanium Silicon Nitride (AlTiSiN). These specialized coatings can achieve hardness values exceeding 40 Gigapascals (GPa), significantly harder than traditional options like Titanium Nitride (TiN). However, the "hardest" coating is not always the best choice for performance.
Focusing solely on hardness is a common but critical mistake. The true key to performance is selecting a coating that balances hardness with other essential properties—like toughness, thermal stability, and lubricity—that match the specific demands of your application.
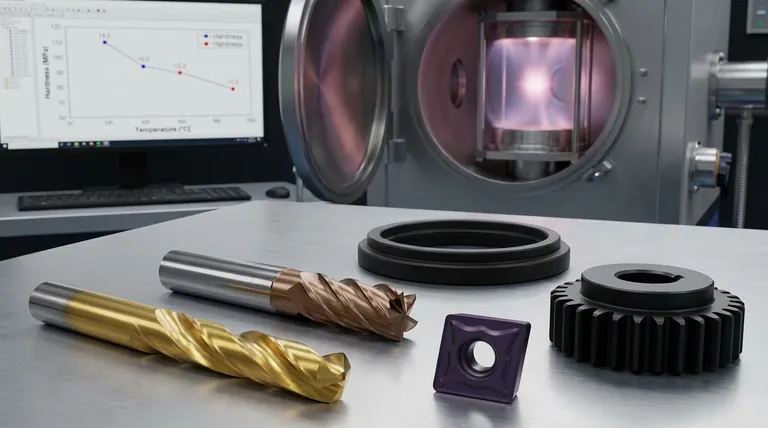

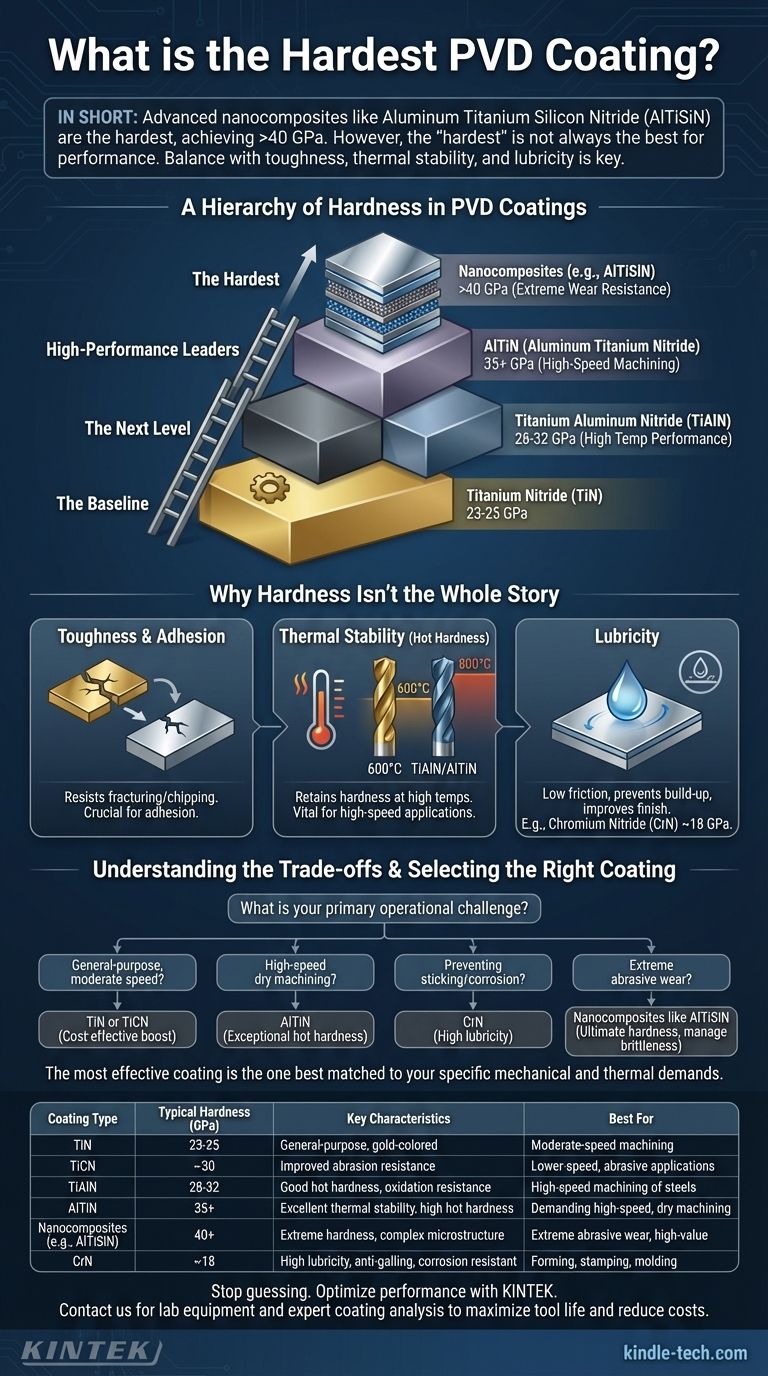
A Hierarchy of Hardness in PVD Coatings
When we discuss coating hardness, we are measuring its resistance to localized plastic deformation, such as a scratch or indentation. While values vary based on the specific deposition process and composition, PVD coatings fall into a clear hierarchy.
The Baseline: Titanium Nitride (TiN)
Titanium Nitride is the iconic, gold-colored general-purpose PVD coating. It serves as the benchmark against which most other coatings are measured. Its hardness typically falls in the range of 23-25 GPa.
The Next Level: TiCN and TiAlN
By introducing other elements, we can significantly increase hardness. Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN) adds carbon to the structure, boosting hardness to around 30 GPa and improving abrasion resistance at lower speeds.
Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiAlN) incorporates aluminum, which not only increases room-temperature hardness to the 28-32 GPa range but critically improves performance at high temperatures.
High-Performance Leaders: AlTiN and Nanocomposites
Coatings with a high aluminum-to-titanium ratio, known as AlTiN, are a step above TiAlN. They are specifically engineered for high-speed machining and can reach hardness values of 35 GPa or more.
The hardest coatings belong to the class of nanocomposite or nanolayered structures. Formulations like Aluminum Chromium Nitride (AlCrN) or Aluminum Titanium Silicon Nitride (AlTiSiN) create complex microstructures that resist deformation, pushing hardness values above 40 GPa.
Why Hardness Isn't the Whole Story
Choosing a coating based on a single hardness number is like choosing a car based only on its top speed; it ignores the factors that actually determine performance in the real world. A tool's success or failure depends on a combination of properties.
The Role of Toughness and Adhesion
Toughness is a material's ability to absorb energy and resist fracturing or chipping. An extremely hard coating can be brittle, like glass. If it chips at the cutting edge under pressure or impact, its high hardness becomes irrelevant.
Furthermore, a coating is useless if it doesn't stick to the substrate. Adhesion is critical, and the internal stresses of some super-hard coatings can compromise their ability to bond with the tool.
Thermal Stability (Hot Hardness)
This is arguably the most important factor in high-speed applications like machining. Hot hardness is a coating's ability to retain its hardness at elevated temperatures. Heat is the enemy of a cutting edge.
A coating like TiN begins to oxidize and soften around 600°C (1100°F). In contrast, aluminum-bearing coatings like TiAlN and AlTiN form a stable, protective layer of aluminum oxide at high temperatures. This allows them to maintain their hardness well past 800°C (1470°F), enabling much higher cutting speeds.
The Impact of Lubricity
Lubricity, or a low coefficient of friction, determines how easily chips slide off the tool face. A "slippery" coating prevents built-up edge (BUE), reduces heat generation, and improves surface finish.
Coatings like Chromium Nitride (CrN), while softer than TiAlN at around 18 GPa, are prized for their excellent lubricity and anti-stick properties, making them ideal for forming, stamping, and molding applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every coating choice involves a compromise. There is no single "best" coating, only the best one for a specific job.
The Hardness vs. Brittleness Compromise
As a general rule, as a coating's hardness increases, its toughness decreases and its internal stress increases. Applying the absolute hardest coating possible to an application with intermittent cuts (milling) can lead to micro-chipping and premature failure.
Application Temperature is Crucial
The operating temperature dictates your choice. A TiN-coated drill bit used on wood will last a long time. That same bit used for high-speed dry machining of hardened steel will fail almost instantly, whereas an AlTiN-coated bit would excel.
Cost and Complexity
Advanced nanocomposite coatings are more expensive and complex to deposit correctly. Their superior properties are only worth the investment if the application is demanding enough to benefit from them. For many general-purpose tasks, a simpler coating like TiN is a more economical solution.
Selecting the Right Coating for Your Application
To make an effective choice, stop asking "which is hardest?" and start defining your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose machining at moderate speeds: A cost-effective choice like TiN or the slightly harder TiCN provides a significant performance boost over an uncoated tool.
- If your primary focus is high-speed dry machining of steels or hard alloys: An aluminum-based coating like AlTiN is the clear choice for its exceptional hot hardness.
- If your primary focus is preventing material sticking, galling, or corrosion: A coating with high lubricity like CrN is superior, even though it is not as hard as others.
- If your primary focus is extreme abrasive wear in a demanding, high-value application: A specialized nanocomposite coating like AlTiSiN offers the ultimate in hardness, provided the process is controlled to manage brittleness.
Ultimately, the most effective coating is not the hardest, but the one best matched to the specific mechanical and thermal demands of your task.
Summary Table:
| Coating Type | Typical Hardness (GPa) | Key Characteristics | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiN (Titanium Nitride) | 23-25 | General-purpose, gold-colored | Moderate-speed machining, general wear resistance |
| TiCN (Titanium Carbonitride) | ~30 | Improved abrasion resistance | Lower-speed, abrasive applications |
| TiAlN (Titanium Aluminum Nitride) | 28-32 | Good hot hardness, oxidation resistance | High-speed machining of steels |
| AlTiN (Aluminum Titanium Nitride) | 35+ | Excellent thermal stability, high hot hardness | Demanding high-speed, dry machining |
| Nanocomposites (e.g., AlTiSiN) | 40+ | Extreme hardness, complex microstructure | Extreme abrasive wear, high-value applications |
| CrN (Chromium Nitride) | ~18 | High lubricity, anti-galling, corrosion resistant | Forming, stamping, molding applications |
Stop guessing and start optimizing your tool performance. The right PVD coating is a balance of hardness, toughness, and thermal stability tailored to your specific application. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced materials testing and coating analysis. Our experts can help you select or develop the ideal coating solution to maximize tool life, increase productivity, and reduce costs. Contact us today to discuss your needs and let us demonstrate the value we bring to your laboratory or production process.
Get a Custom Coating Recommendation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer



















