In simple terms, a heat treatment furnace is a specialized industrial heating chamber designed to perform a critical function: altering the physical and sometimes chemical properties of a material. Unlike a simple oven, its primary role is to execute highly controlled and repeatable temperature cycles to impart specific, useful characteristics to components, particularly steel.
The crucial takeaway is that a heat treatment furnace is not just a device for heating things up. It is a precision tool that engineers a material's final properties by meticulously controlling two fundamental variables: temperature and the chemical makeup of the atmosphere inside the chamber.

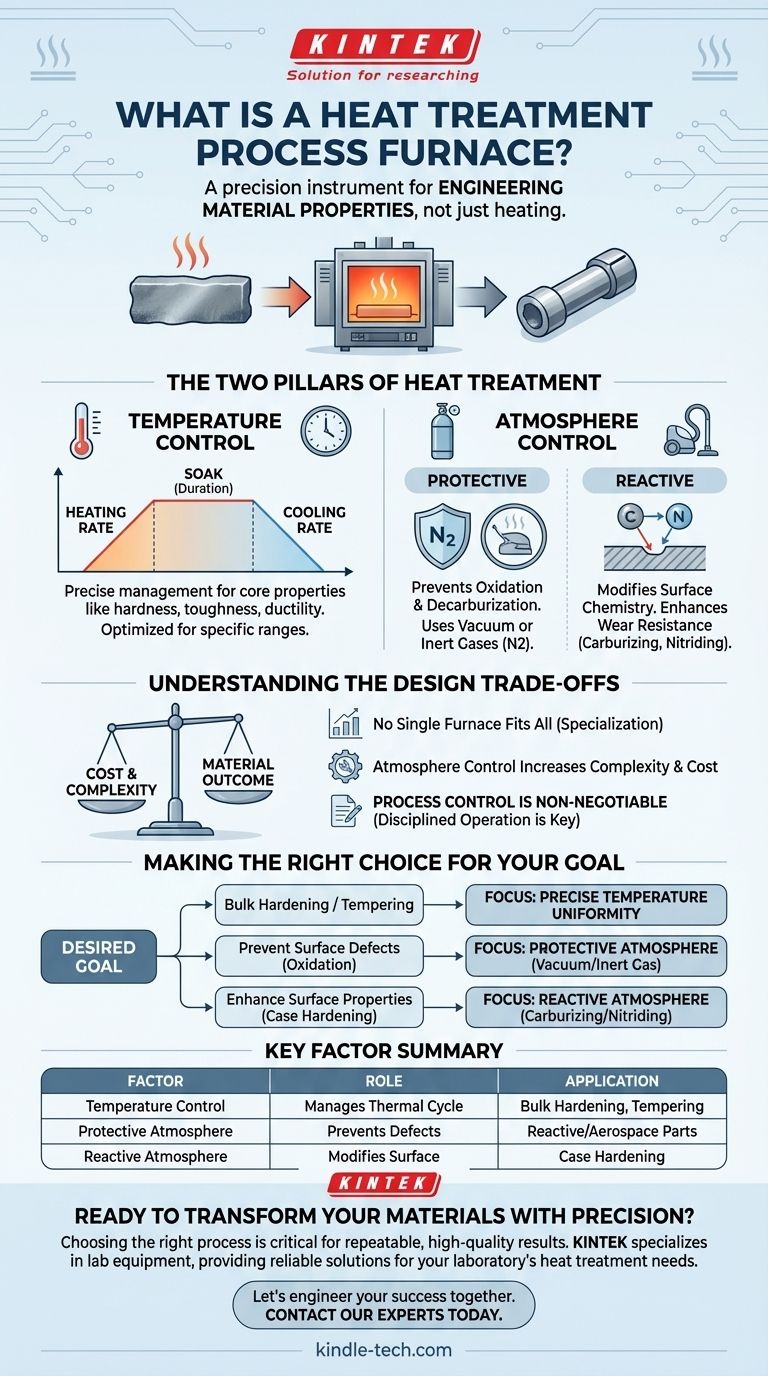
The Two Pillars of Heat Treatment: Temperature and Atmosphere
Understanding a heat treatment furnace requires looking beyond its ability to generate heat and focusing on how it manipulates the environment to achieve a desired result. This control is based on two independent but interconnected factors.
Achieving Precise Temperature Control
A furnace's most basic function is to regulate temperature, but the process is far more complex than simply reaching a set point. It involves managing the entire thermal cycle.
This includes the rate of heating, the duration the material is held at a specific temperature (the "soak"), and the rate of cooling. Each stage is critical for achieving properties like hardness, toughness, or ductility.
Furthermore, furnaces are often designed for specific temperature ranges. A furnace optimized for high-temperature processes like hardening at 1300°C may be inefficient or lack the fine control needed for a low-temperature tempering process at 300°C.
The Critical Role of the Furnace Atmosphere
The gases surrounding the material inside the furnace are known as the furnace atmosphere. This atmosphere can be either a passive protector or an active participant in the treatment process.
The right atmosphere is essential for ensuring the treatment produces the intended results without introducing defects.
Protective Atmospheres
At high temperatures, materials like steel are highly reactive with oxygen in the air. A key function of a furnace's atmosphere is to prevent these unwanted reactions.
The goal is to eliminate or minimize effects like oxidation (scaling or rust) and decarburization (the loss of carbon from the surface of steel, which makes it softer). This is often achieved using a vacuum or by filling the chamber with inert gases.
Reactive Atmospheres
In some processes, the atmosphere is intentionally designed to react with the material's surface to enhance its properties.
This is a form of surface chemistry modification. For example, in carburizing, a carbon-rich atmosphere is used to diffuse carbon into the surface of a steel part, creating a hard, wear-resistant outer layer while keeping the core tough. Similarly, nitriding uses a nitrogen-rich atmosphere to achieve surface hardening.
Understanding the Design Trade-offs
The choice and design of a heat treatment furnace involve significant trade-offs that balance cost, complexity, and the desired material outcome.
No Single Furnace Fits All Needs
The specialization required for precise control means there is no universal heat treatment furnace. A furnace designed for bulk hardening in the open air is fundamentally different and less complex than a vacuum furnace designed for treating sensitive aerospace components.
Using the wrong type of furnace for a job—such as a high-temperature unit for a low-temperature process—can lead to poor results and inefficiency.
The Complexity of Atmosphere Control
Introducing atmosphere control significantly increases the cost and operational complexity of a furnace. A simple air-fired furnace is far less expensive than a vacuum furnace or one requiring a constant supply of purified nitrogen.
The decision to invest in atmosphere control is driven entirely by the need to prevent surface defects or to actively change the surface chemistry of the part being treated.
Process Control is Non-Negotiable
Even the most advanced furnace is only as good as its operating procedure. Mastering the correct process is essential to achieve the desired outcome, reduce failure rates, and extend the service life of the equipment.
Minor deviations in temperature or atmospheric composition can lead to scrapped parts, making disciplined operational control a critical factor for success.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal heat treatment furnace and process are dictated entirely by the desired final properties of the material.
- If your primary focus is bulk hardening or tempering: Your main concern is a furnace with extremely precise and uniform temperature control over a specific range.
- If your primary focus is preventing surface defects like oxidation: You need a furnace with a protective atmosphere, such as a vacuum or inert gas (e.g., nitrogen) system.
- If your primary focus is enhancing surface properties (case hardening): You require a furnace designed for reactive atmospheres that can introduce elements like carbon (carburizing) or nitrogen (nitriding).
Ultimately, a heat treatment furnace is a precision instrument where the controlled environment is deliberately engineered to transform a standard material into a high-performance component.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Role in Heat Treatment | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Manages heating rate, soak time, and cooling rate to achieve core properties (hardness, ductility). | Bulk hardening, tempering. |
| Protective Atmosphere | Prevents surface defects like oxidation and decarburization using vacuum or inert gases. | Treating reactive materials, aerospace components. |
| Reactive Atmosphere | Actively modifies surface chemistry (e.g., adding carbon or nitrogen) for enhanced wear resistance. | Carburizing, nitriding for case hardening. |
Ready to transform your materials with precision?
Choosing the right heat treatment process is critical to achieving the desired properties in your components, whether it's superior hardness, toughness, or a specific surface chemistry. The wrong furnace can lead to scrapped parts and lost productivity.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable solutions for your laboratory's heat treatment needs. Our expertise ensures you get the precise temperature and atmosphere control required for repeatable, high-quality results.
Let's engineer your success together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect furnace solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- What is the standard thickness of plating? Optimize Durability, Corrosion & Cost
- What is a vertical tube furnace? Leverage Gravity for Superior Uniformity and Process Control
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- How do you clean a quartz tube furnace? Prevent Contamination & Extend Tube Lifespan



















