In sintering, the heating rate is the speed at which the furnace temperature is increased during the manufacturing cycle, typically measured in degrees per minute (°C/min or °F/min). It is not a single value but a carefully programmed sequence of different rates corresponding to specific stages of the process. This controlled ramp-up is critical for burning off binders without causing damage and for achieving the desired final density and dimensional precision in the part.
The core challenge of sintering is not just reaching a peak temperature, but managing the entire thermal journey. The heating rate is the primary tool for navigating this journey, ensuring binders are removed safely and that the part densifies uniformly without introducing critical defects.

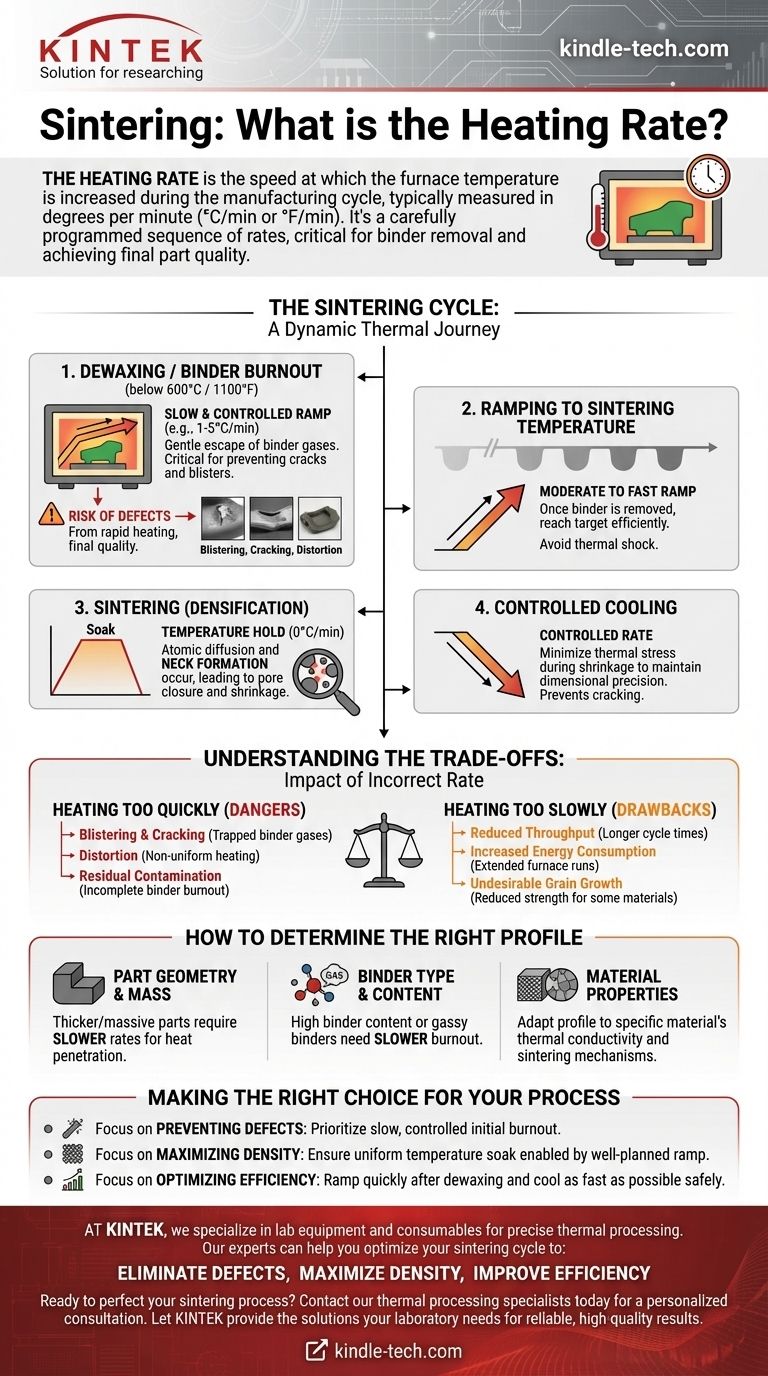
The Sintering Cycle: More Than Just a Peak Temperature
A common misconception is that sintering is simply about baking a part at a high temperature. In reality, it is a dynamic thermal process with distinct phases, each requiring a specific heating rate to succeed. The entire temperature profile—including heating, holding, and cooling—determines the final quality.
Phase 1: Dewaxing / Binder Burnout
Before high-temperature sintering can begin, the "green body" (the pressed powder form) must be heated slowly to burn off the binders and lubricants used during molding.
This initial heating rate is the most critical part of the cycle. If the temperature rises too quickly, the binder vaporizes aggressively, creating high internal pressure that can crack, blister, or distort the part before it has any strength. A slow, controlled rate allows these gases to escape gently through the part's natural porosity.
Phase 2: Ramping to Sintering Temperature
Once the binder is fully removed (typically below 600°C or 1100°F), the heating rate can often be increased more rapidly. With the risk of binder-related defects gone, the goal is to reach the target sintering temperature efficiently without causing thermal shock.
Phase 3: Sintering (Densification)
At the peak temperature, the part is held for a specific duration. During this "soak," the material's atoms diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, a process called neck formation. This process closes the pores between particles, causing the part to shrink and densify. The heating profile leading up to this stage ensures the entire part reaches this temperature uniformly, which is essential for consistent densification.
Phase 4: Controlled Cooling
Just as with heating, the cooling rate is also controlled. Cooling too quickly can induce thermal stress, leading to cracks and compromising the dimensional precision achieved during sintering.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Impact of an Incorrect Heating Rate
Choosing a heating rate is a balancing act between quality and efficiency. An improperly calibrated rate is a primary cause of failed sintering runs.
The Dangers of Heating Too Quickly
A rapid heating rate, especially during the initial burnout phase, is the most common source of defects.
- Blistering and Cracking: Trapped binder gases build pressure and physically damage the fragile green body.
- Distortion: Non-uniform heating causes different areas of the part to shrink at different rates, leading to warping.
- Residual Contamination: If the binder does not have time to burn off completely, carbon residue can remain, inhibiting proper densification and affecting the material's final properties.
The Drawbacks of Heating Too Slowly
While safer, an excessively slow heating rate is not without consequences.
- Reduced Throughput: Longer cycle times directly translate to lower production capacity and higher operational costs.
- Increased Energy Consumption: Running a furnace for extended periods significantly increases energy usage.
- Undesirable Grain Growth: For some materials, spending too much time at elevated temperatures (even below the peak) can cause grains to grow, which can sometimes reduce the final strength of the material.
How to Determine the Right Profile
The ideal heating profile is not universal; it is tailored to the specific application. It depends on several key factors.
Part Geometry and Mass
Thicker and more massive parts require slower heating rates. Heat needs time to penetrate to the core of the part, and a slow rate ensures the temperature difference between the surface and the center remains minimal, preventing internal stress.
Binder Type and Content
The amount and type of binder are critical variables. A part with a high percentage of binder or a binder that releases a large volume of gas requires a much slower and more cautious burnout phase.
Material Properties
Different materials, such as ceramics and powdered metals, possess different thermal conductivities and sintering mechanisms. The heating profile must be adapted to the specific material's behavior to achieve optimal relative density and strength.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Optimizing the heating rate is fundamental to successful sintering. Your specific goal will determine where you focus your attention.
- If your primary focus is preventing defects (cracks, blisters): Prioritize a slow, highly controlled heating rate during the initial binder burnout phase below 600°C.
- If your primary focus is maximizing density and strength: Concentrate on achieving a uniform temperature soak at the peak, which is enabled by a well-planned ramp-up that avoids thermal gradients.
- If your primary focus is optimizing production efficiency: Profile your cycle to ramp up quickly after the critical dewaxing phase is complete and ensure the cooling phase is as fast as possible without introducing thermal shock.
Mastering the heating rate transforms sintering from a simple heating step into a precise and repeatable engineering process.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Phase | Typical Heating Rate | Primary Goal | Risk of Incorrect Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dewaxing / Binder Burnout | Slow (e.g., 1-5°C/min) | Safely remove binders without damage | Cracking, blistering, distortion |
| Ramp to Sintering Temp | Moderate to Fast | Reach target temperature efficiently | Thermal shock, uneven heating |
| Sintering (Soak) | 0°C/min (Hold) | Achieve uniform densification and shrinkage | Low density, inconsistent properties |
| Controlled Cooling | Controlled Rate | Minimize thermal stress during shrinkage | Cracking, warping |
Struggling with sintering defects like cracking or low density? Your heating rate could be the key.
At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Our experts can help you optimize your sintering cycle to:
- Eliminate Defects: Prevent cracking and blistering with a tailored binder burnout profile.
- Maximize Density: Achieve superior part strength and performance.
- Improve Efficiency: Reduce cycle times and energy consumption without sacrificing quality.
Ready to perfect your sintering process? Contact our thermal processing specialists today for a personalized consultation. Let KINTEK provide the solutions your laboratory needs for reliable, high-quality results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the temperature of sintering zirconia? Mastering the Protocol for Perfect Dental Restorations
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the sintering time for zirconia? A Guide to Precise Firing for Optimal Results



















