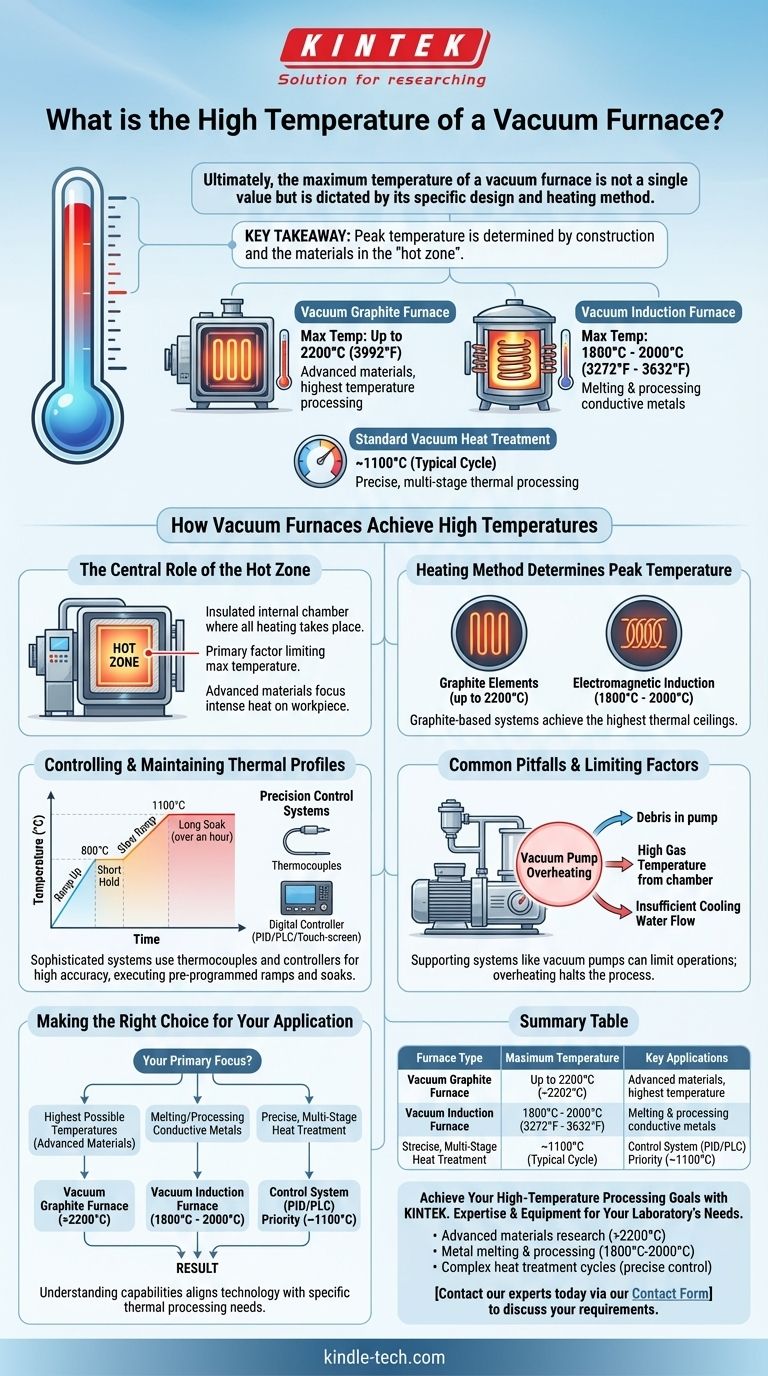
Ultimately, the maximum temperature of a vacuum furnace is not a single value but is dictated by its specific design and heating method. While a typical vacuum heat treatment cycle might operate around 1100°C, specialized vacuum furnaces can reach temperatures well over 2000°C, with graphite-based systems achieving the highest thermal ceilings.
The key takeaway is that a vacuum furnace's peak temperature is determined by its construction, primarily the materials used in its "hot zone." Different designs, like induction or graphite furnaces, are engineered for different temperature ranges and applications.
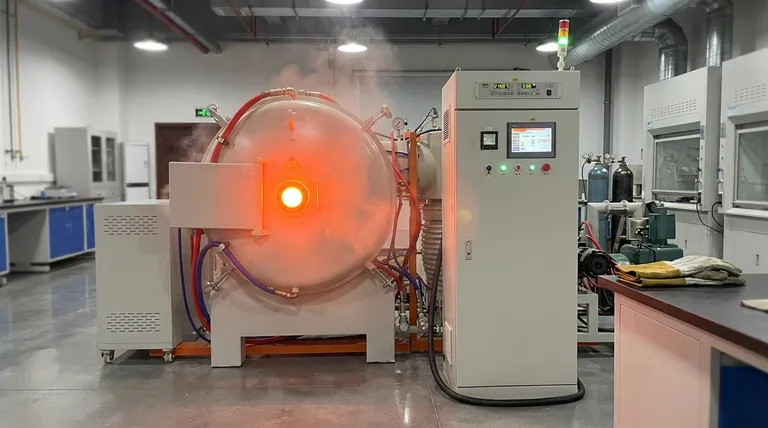

How Vacuum Furnaces Achieve High Temperatures
A vacuum furnace's ability to reach extreme temperatures hinges on the design of its core components. The vacuum environment itself is crucial, as it eliminates heat transfer through convection, allowing for more efficient and controlled heating of the target material.
The Central Role of the Hot Zone
The hot zone is the insulated internal chamber where all heating takes place. Its construction is the primary factor limiting the furnace's maximum temperature.
Engineers use advanced insulating materials and component designs to contain the intense heat, ensuring it is focused on the workpiece while protecting the rest of the furnace.
Heating Method Determines Peak Temperature
The method used to generate heat is directly tied to the furnace's capabilities. Two common high-temperature designs are graphite and induction furnaces.
A vacuum graphite furnace uses graphite heating elements and can achieve maximum temperatures of 2200°C (3992°F).
A vacuum induction melting furnace uses electromagnetic induction to heat conductive materials. These systems can reach temperatures between 1800°C and 2000°C (3272°F - 3632°F).
Controlling and Maintaining Thermal Profiles
Reaching a high temperature is only part of the process. The true utility of a vacuum furnace lies in its ability to precisely control the entire thermal cycle.
Precision Control Systems
Modern vacuum furnaces use sophisticated control systems to manage temperature with high accuracy.
These systems rely on thermocouples to measure temperature and dedicated temperature controllers to regulate it. Control interfaces can range from PID programmable units to fully automatic PLC or touch-screen systems.
Executing a Thermal Program
Furnaces are rarely run at their maximum temperature continuously. Instead, they follow a pre-programmed thermal profile of ramps and soaks.
A typical program might involve heating to 800°C for a short hold, followed by a slow ramp to 1100°C where the temperature is held for over an hour to complete the treatment process.
Common Pitfalls and Limiting Factors
The operational limit of a vacuum furnace is not just about the hot zone. The supporting systems, particularly the vacuum pumps, can introduce their own constraints.
The Challenge of Pump Overheating
The vacuum pump is essential for creating the furnace's environment, but it can be susceptible to overheating, which can halt operations.
High oil temperature in the pump system is a common issue that must be managed to ensure the furnace can run its full cycle reliably.
Causes of Pump Overheating
Several factors can lead to excessive oil temperatures in the vacuum pump.
These include debris being sucked into the pump, excessively high temperatures of the gas being removed from the chamber, or an insufficient flow of cooling water to the pump system. Addressing these issues is critical for stable high-temperature operation.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the material and process requirements of your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures for advanced materials: A vacuum graphite furnace is the most suitable choice, capable of exceeding 2200°C.
- If your primary focus is melting or processing conductive metals: A vacuum induction furnace offers excellent performance, reliably reaching the 1800°C to 2000°C range.
- If your primary focus is precise, multi-stage heat treatment: The control system (PID, PLC) is as important as the peak temperature, ensuring you can execute complex thermal profiles with accuracy.
Understanding these capabilities ensures you align the right technology with your specific thermal processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Maximum Temperature | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Vacuum Graphite Furnace | Up to 2200°C (3992°F) | Advanced materials, highest temperature processing |
| Vacuum Induction Furnace | 1800°C - 2000°C (3272°F - 3632°F) | Melting and processing conductive metals |
| Standard Vacuum Heat Treatment | ~1100°C (Typical Cycle) | Precise, multi-stage thermal processing |
Achieve Your High-Temperature Processing Goals with KINTEK
Whether your application requires the extreme heat of a graphite furnace or the precise control of an induction system, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to meet your laboratory's specific needs. Our vacuum furnaces are engineered for reliability, precision, and performance, ensuring your materials processing is a success.
Let us help you select the perfect furnace for your application:
- For advanced materials research requiring temperatures over 2200°C
- For metal melting and processing in the 1800°C to 2000°C range
- For complex heat treatment cycles demanding precise temperature control
Contact our experts today via our Contact Form to discuss your requirements and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment can enhance your capabilities and drive your research forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is high-temperature vacuum heat treatment critical for Cr-Ni steel? Optimize Strength & Surface Integrity
- Is heat Cannot travel in a vacuum True or false? Discover How Heat Crosses the Void of Space
- What are the most commonly used metals in a vacuum furnace's hot zone? Discover the Key to High-Purity Processing
- What are the applications of vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the temperature of vacuum heat treatment? Achieve Superior Material Properties & Pristine Finishes



















