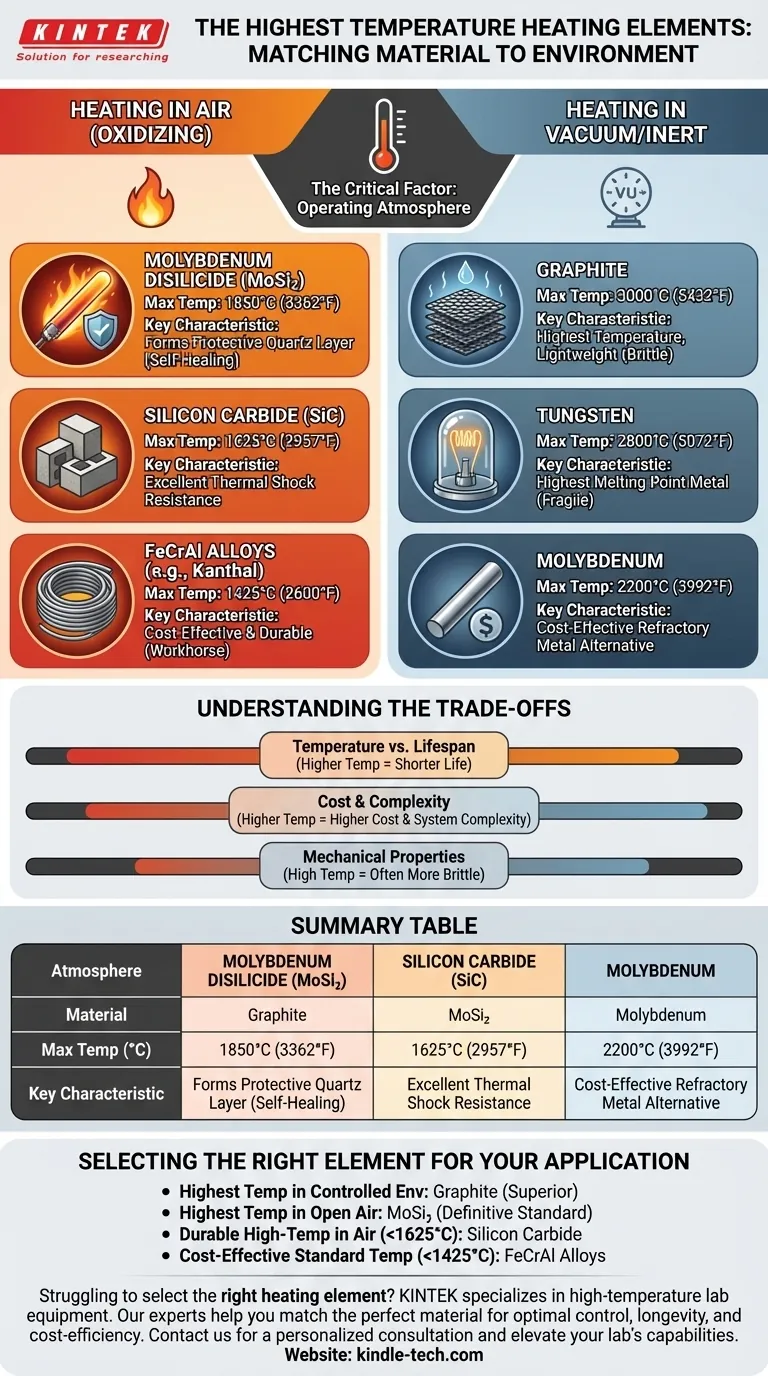
The highest temperature heating element available is graphite, which can operate at temperatures up to 3000°C (5432°F). However, this is only possible in a vacuum or a controlled, inert atmosphere. For applications in normal air, the highest temperature elements are made from Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂), which can reliably reach 1850°C (3362°F).
The selection of a heating element is not about finding a single "hottest" material, but about matching a material's properties to its operating environment. The presence of oxygen is the single most important factor that dictates which element you can use.

The Critical Factor: Operating Atmosphere
Nearly all high-temperature heating challenges are defined by one question: will the element be exposed to air (an oxidizing atmosphere) or will it be in a vacuum or inert gas (a non-oxidizing atmosphere)?
Heating in Air (Oxidizing Environments)
When heated in air, most materials rapidly react with oxygen and are destroyed. The most successful elements form a stable, protective oxide layer on their surface.
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂)
Molybdenum Disilicide is the undisputed champion for high-temperature heating in air, capable of reaching 1850°C (3362°F).
When heated, it forms a thin, self-healing layer of pure quartz (silica glass) on its surface that prevents further oxidation of the underlying material.
Silicon Carbide (SiC)
Silicon Carbide is another exceptional ceramic-based element, widely used for temperatures up to 1625°C (2957°F).
Like MoSi₂, it forms a protective silica layer. SiC is known for its structural strength at high temperatures and its ability to withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Iron-Chrome-Aluminum (FeCrAl) Alloys
Commonly known by the trade name Kanthal, these metallic alloys are the workhorses of industrial heating up to 1425°C (2600°F).
They are relatively inexpensive, easy to form, and durable, making them the standard for most kilns and furnaces that don't require extreme temperatures.
Heating in Vacuum or Inert Atmospheres
By removing oxygen, we can use materials with exceptionally high melting points that would otherwise burn up instantly in air.
Graphite
With a sublimation point over 3600°C, graphite is the highest-temperature heating element for non-oxidizing environments, with a practical operating limit of 3000°C (5432°F).
It is lightweight and has excellent thermal shock resistance. However, it is brittle and must be protected from oxygen at all times when hot.
Tungsten
Tungsten has the highest melting point of any pure metal at 3422°C (6192°F). It is commonly used for heating elements in vacuum furnaces up to 2800°C (5072°F).
While incredibly effective, tungsten is dense, expensive, and becomes very brittle after being heated, making it fragile.
Molybdenum
Molybdenum is a refractory metal often used as a more cost-effective alternative to tungsten. It performs exceptionally well in vacuum environments up to 2200°C (3992°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs
The maximum temperature is only one part of the equation. Practical and financial constraints often guide the final selection.
Temperature vs. Lifespan
Operating any heating element near its maximum rated temperature will dramatically shorten its lifespan. Aggressive temperature cycling also introduces thermal stress, which can lead to mechanical failure, especially in brittle ceramic or refractory metal elements.
Cost and Complexity
As a rule, higher temperature capabilities come with higher costs. Graphite and Tungsten elements not only use expensive materials but also require complex vacuum or controlled-atmosphere furnace systems, which are far more expensive to build and operate.
Mechanical Properties
The ideal heating element is easy to form and resistant to shock. Materials like FeCrAl are ductile and simple to work with. In contrast, MoSi₂, SiC, and especially Tungsten and Graphite are brittle and require careful handling and support within the furnace structure.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Your final choice depends entirely on your specific goal and operating conditions.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest possible temperature in a controlled environment: Graphite is the superior choice, followed by Tungsten for applications requiring a pure metallic element.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible temperature in open air: Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) is the definitive industry standard.
- If you need a durable, reliable element for high-temperature work in air (below 1625°C): Silicon Carbide (SiC) offers an excellent balance of performance and longevity.
- If you require a cost-effective solution for standard furnace temperatures (below 1425°C): FeCrAl alloys provide the best combination of price, durability, and ease of use.
Ultimately, choosing the correct heating element is a matter of precisely matching the material's properties to its specific operating environment and your performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Atmosphere | Material | Max Temperature (°C) | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air (Oxidizing) | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | 1850°C | Forms protective quartz layer |
| Air (Oxidizing) | Silicon Carbide (SiC) | 1625°C | Excellent thermal shock resistance |
| Air (Oxidizing) | FeCrAl Alloys (e.g., Kanthal) | 1425°C | Cost-effective & durable |
| Vacuum/Inert | Graphite | 3000°C | Highest temperature, lightweight |
| Vacuum/Inert | Tungsten | 2800°C | Highest melting point metal |
| Vacuum/Inert | Molybdenum | 2200°C | Cost-effective refractory metal |
Struggling to select the right heating element for your lab furnace or kiln? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratories worldwide. Our experts can help you match the perfect heating element material to your specific operating environment and performance goals—ensuring optimal temperature control, longevity, and cost-efficiency. Contact us today for a personalized consultation and elevate your lab's capabilities with KINTEK's reliable solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) Thermal Elements Electric Furnace Heating Element
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Cylindrical Lab Electric Heating Press Mold for Laboratory Applications
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Is molybdenum disulfide a heating element? Discover the best material for high-temperature applications.
- What is molybdenum disilicide used for? Powering High-Temperature Furnaces Up to 1800°C
- What are the properties of molybdenum heating element? Choose the Right Type for Your Furnace Atmosphere
- Which high temperature furnace elements to be used in oxidizing atmosphere? MoSi2 or SiC for Superior Performance
- What is the temperature range of a MoSi2 heating element? Unlock 1900°C Performance for Your Lab



















