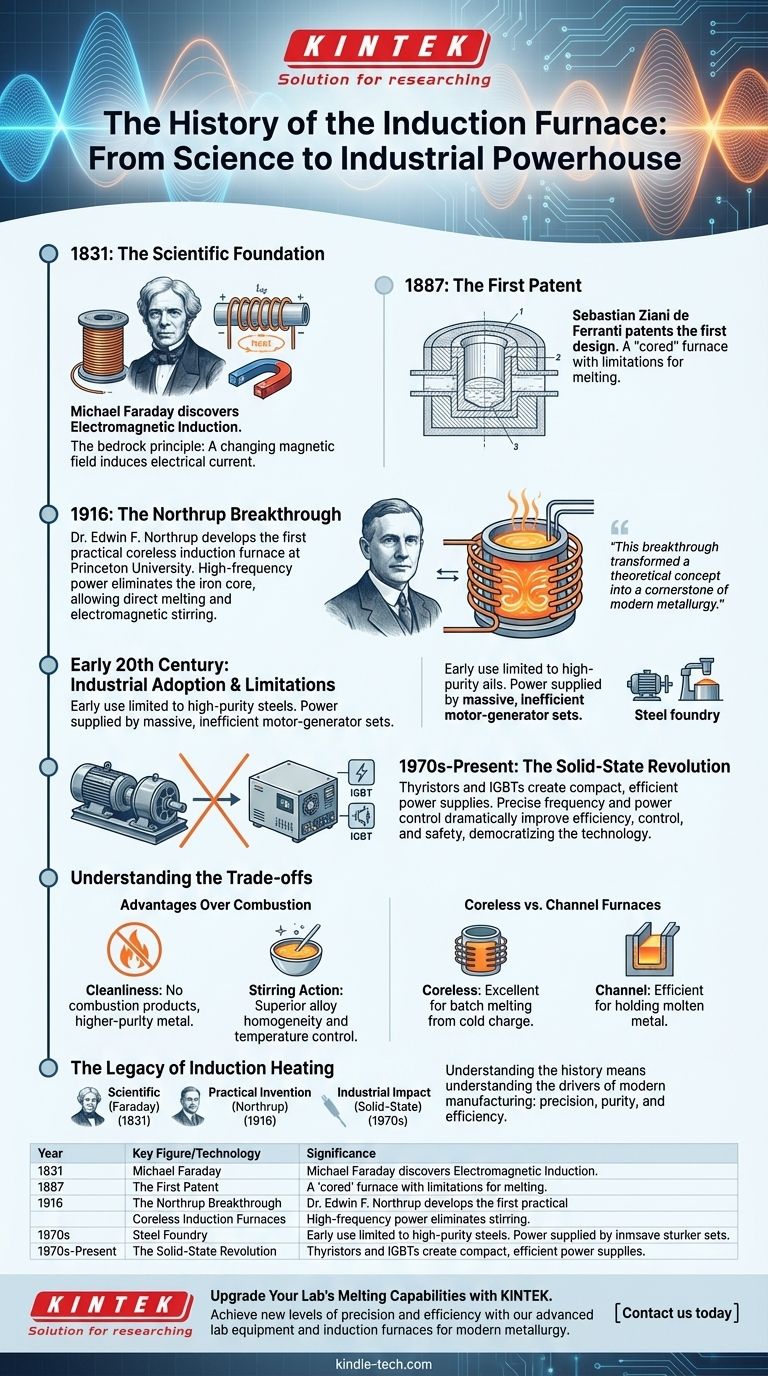
The modern induction furnace was not the product of a single inventor but an evolution built upon a fundamental scientific discovery. Its conceptual origins trace back to the late 19th century with a patent by Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti, but the first truly practical, high-frequency industrial furnace was developed by Dr. Edwin F. Northrup at Princeton University in 1916. This breakthrough transformed a theoretical concept into a cornerstone of modern metallurgy.
The history of the induction furnace is a story of turning a physical principle—electromagnetic induction—into an industrial powerhouse. Its evolution was driven by the relentless pursuit of cleaner, more controllable, and more efficient methods for melting metal, a journey that spans from a university laboratory to the heart of global manufacturing.

The Scientific Foundation: From Theory to Application
To understand the furnace's history, we must first understand the science that makes it possible. The entire concept rests on a discovery made decades before the first furnace was ever conceived.
The Principle of Induction (1831)
In 1831, scientist Michael Faraday discovered the principle of electromagnetic induction. He demonstrated that a changing magnetic field could induce an electrical current in a nearby conductor without any physical contact. This discovery is the absolute bedrock of induction technology.
Linking Induction to Heat
The induced electrical currents, known as eddy currents, are not inherently useful for melting. However, as they flow through a conductive material like metal, they encounter electrical resistance. This resistance generates intense heat, a phenomenon known as Joule heating. The induction furnace masterfully exploits this effect.
The Birth of the Industrial Furnace
With the scientific principles established, the next step was engineering a practical device. This took several decades and the work of multiple pioneers.
The First Patent (1887)
Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti, a British electrical engineer, was the first to patent a design for a furnace based on induction principles. His design featured an iron core surrounded by a primary coil, conceptually similar to a transformer. While a critical first step, this "cored" or "channel" furnace design had limitations and was not widely adopted for melting at the time.
The Northrup Breakthrough (1916)
The true watershed moment came from Dr. Edwin F. Northrup in the United States. He developed the first practical coreless induction furnace. By using a high-frequency power source, he eliminated the need for the iron core, allowing the crucible containing the metal to be placed directly inside the induction coil.
This design was far more versatile and efficient for melting, as it allowed for strong stirring action within the molten metal, ensuring a homogenous mix and temperature. Northrup's work is widely considered the birth of the modern induction furnace.
Evolution and Industrial Adoption
Following Northrup's invention, the induction furnace began its steady integration into industry, a process accelerated by continuous improvements in power supply technology.
Early Industrial Use
In the early 20th century, induction furnaces were expensive and complex. Their use was primarily limited to producing high-purity specialty steels and non-ferrous alloys where the prevention of contamination from combustion byproducts (like carbon) was critical.
The Motor-Generator Era
For decades, the high-frequency power required by coreless furnaces was supplied by large, complex motor-generator sets. These were massive, inefficient, and required significant maintenance, limiting the size and cost-effectiveness of induction melting operations.
The Solid-State Revolution (1970s-Present)
The invention of the thyristor and later the Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT) changed everything. These solid-state devices allowed for the creation of compact, reliable, and highly efficient power supplies.
Engineers could now precisely control the furnace's frequency and power, dramatically improving energy efficiency, melt control, and operational safety. This revolution made induction melting economically viable for a much broader range of foundries and applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The adoption of the induction furnace was driven by its clear advantages over older technologies, though it was not without its own initial challenges.
Advantages Over Combustion Furnaces
The key driver for adoption was the inherent cleanliness of induction heating. Unlike cupola or reverberatory furnaces that burn fuel, induction introduces no products of combustion into the melt. This results in higher-purity metal.
Furthermore, the electromagnetic forces create a natural stirring action, leading to superior alloy homogeneity and precise temperature control, which are difficult to achieve in fuel-fired furnaces.
Early Limitations
The primary barrier to early adoption was cost and complexity. The electrical infrastructure and sophisticated power supplies were far more expensive than a simple cupola furnace. Early furnaces were also limited in their melt capacity compared to traditional bulk melting methods like blast furnaces.
Coreless vs. Channel Furnaces
The two main historical paths, coreless and channel furnaces, serve different purposes. The coreless furnace, perfected by Northrup, excels at batch melting from a cold charge. The channel furnace, closer to Ferranti's original concept, is more efficient for holding large quantities of molten metal at temperature or for continuous duplexing operations.
The Legacy of Induction Heating
Understanding the history of the induction furnace is to understand the drivers of modern manufacturing: precision, purity, and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is scientific principles: The story begins with Faraday's 1831 discovery of electromagnetic induction, the non-contact transfer of energy.
- If your primary focus is the first practical invention: Dr. Edwin Northrup's coreless, high-frequency furnace of 1916 is the definitive starting point for the modern industrial tool.
- If your primary focus is widespread industrial impact: The development of solid-state power supplies from the 1970s onward democratized the technology, making it the efficient and precise standard it is today.
From a 19th-century scientific curiosity, the induction furnace has evolved into an indispensable and highly refined tool for shaping the metallic world around us.
Summary Table:
| Key Milestone | Year | Key Figure/Technology | Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Principle of Electromagnetic Induction | 1831 | Michael Faraday | Scientific foundation for all induction heating |
| First Patent | 1887 | Sebastian Ziani de Ferranti | First conceptual design for an induction furnace |
| First Practical Coreless Furnace | 1916 | Dr. Edwin F. Northrup | Birth of the modern industrial induction furnace |
| Solid-State Revolution | 1970s-Present | Thyristor & IGBT Technology | Enabled compact, efficient, and reliable power supplies |
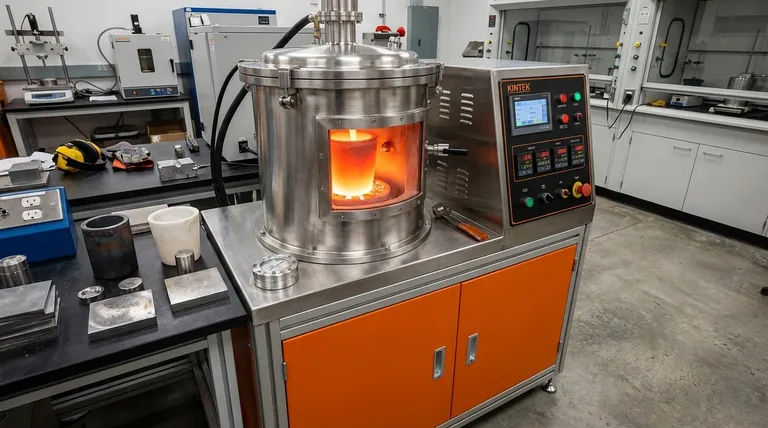
Upgrade Your Lab's Melting Capabilities with KINTEK
Just as the induction furnace evolved from a scientific principle to an industrial powerhouse, your laboratory can achieve new levels of precision and efficiency with the right equipment. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable induction furnaces that deliver the purity, temperature control, and homogeneity essential for modern metallurgy and materials science.
Whether you're melting specialty alloys, conducting research, or optimizing your production process, our solutions are designed to meet your specific laboratory needs. Contact us today to discuss how our induction furnaces can transform your operations and drive your success forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the four types of heat treating processes? Master Annealing, Normalizing, Hardening, and Tempering
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- What are the three main heat treatments? Mastering Annealing, Hardening & Tempering
- Why do you heat treat in a vacuum? Achieve Perfect Surface Finish and Material Integrity



















