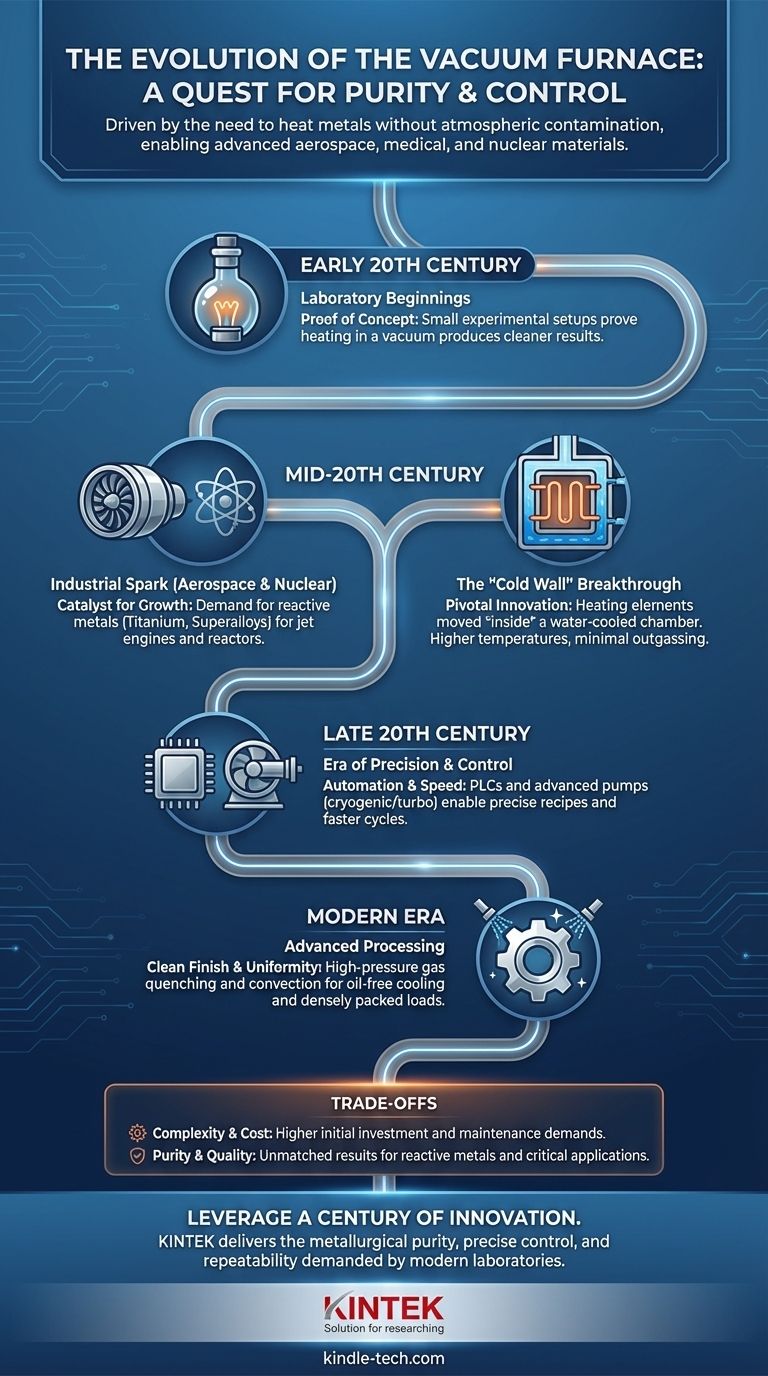
The history of the vacuum furnace is not simply a timeline of machines, but a story of scientific pursuit. It tracks the relentless effort to solve a fundamental problem in metallurgy: how to heat metals to extreme temperatures without letting them be contaminated by the very air that surrounds them. This evolution was driven by the demands of new, high-performance materials required for aerospace, nuclear, and medical advancements.
The development of the vacuum furnace is inseparable from the parallel evolution of vacuum pump technology, advanced control systems, and the creation of exotic alloys. Its history is less about the furnace itself and more about the enabling technologies that allowed engineers to create a perfectly controlled, ultra-clean environment for heat treating.
The Core Problem: Why Heat in a Vacuum?
The entire premise of vacuum heat treating began with the need to overcome the natural limitations of heating metals in the open air or in a standard atmosphere furnace.
The Enemy: Atmospheric Contamination
When metals are heated, they become highly reactive. The oxygen and nitrogen in our atmosphere, normally harmless, aggressively attack the hot metal surface.
This reaction causes oxidation (rusting or scaling) and can introduce impurities that make the metal brittle or change its structural properties. For many high-performance alloys, this contamination is unacceptable.
The Solution: Removing the Atmosphere
The logical solution was to remove the atmosphere entirely. By placing the part inside a sealed chamber and pumping out the air, you create a near-perfect vacuum.
This vacuum environment acts as an invisible shield, protecting the metal part from contamination during the critical heating and cooling phases of treatment.
Early Precursors: Laboratory Beginnings
The concept began in scientific laboratories in the early 20th century. Researchers needed to study the properties of pure materials without the influence of atmospheric gases.
These early devices were small, experimental setups, proving the principle that heating in a vacuum could produce cleaner, more predictable results. They were not yet viable for industrial production.
The Industrial Revolution of Vacuum Technology
The transition from a lab curiosity to an industrial workhorse was ignited by the material demands of the mid-20th century, particularly in the post-war era.
The Catalyst: Aerospace and Nuclear Demands
The dawn of the jet age and the nuclear industry created a sudden need for materials like titanium, zirconium, and superalloys.
These reactive metals were essential for jet engine turbines and nuclear reactor components, but they were impossible to heat treat properly in a conventional furnace. This created the first major commercial driver for vacuum furnace technology.
The "Hot Wall" Furnace
Early industrial vacuum furnaces were of a "hot wall" design. The vacuum chamber itself was heated from the outside.
This design was simple but had significant limitations. The vessel material restricted the maximum operating temperature, and the hot walls of the chamber would release trapped gases (a process called outgassing), compromising the vacuum's purity.
The "Cold Wall" Breakthrough
The pivotal innovation was the "cold wall" furnace. In this design, the heating elements and insulation were moved inside a water-cooled vacuum chamber.
This elegant solution meant the chamber walls stayed cool, preventing outgassing and allowing for much higher processing temperatures. The "cold wall" furnace unlocked the ability to process high-temperature alloys and became the foundation for all modern vacuum furnaces.
The Era of Precision and Control
With the fundamental design established, the focus shifted to making furnaces more precise, efficient, and versatile.
From Manual to Automated
Early furnaces required constant manual supervision. The development of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) revolutionized the process.
Operators could now program a precise, multi-step recipe for heating, soaking, and cooling. This ensured every part received the exact same treatment, delivering unprecedented consistency and quality control essential for industries like medical and aerospace.
The Pumping Revolution
A furnace is only as good as its vacuum pumps. The history of vacuum furnaces mirrors the history of pump technology, moving from slower oil diffusion pumps to cleaner, faster cryogenic and turbomolecular pumps.
Better pumps allowed furnaces to achieve deeper vacuum levels more quickly, resulting in cleaner parts and shorter overall cycle times.
Adding Convection and Gas Quenching
To improve temperature uniformity for densely packed loads, engineers added high-power fans for convection-assisted heating.
Furthermore, high-pressure gas quenching was introduced as an alternative to oil quenching. Injecting inert gas like nitrogen or argon at high pressure cools the parts rapidly and cleanly, eliminating the mess, fire hazard, and environmental concerns of oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While revolutionary, vacuum furnace technology is not a universal solution. Its history reveals a consistent set of trade-offs that persist today.
Complexity and Cost
Vacuum furnaces are inherently more complex and have a higher initial capital cost than their atmospheric counterparts. They involve sophisticated vacuum pumps, seals, and control systems.
Cycle Time Considerations
The process of pumping a chamber down to a deep vacuum level takes time. While modern pumps are fast, the overall cycle time can sometimes be longer than for a continuous atmospheric furnace.
Maintenance Demands
Maintaining a leak-free vacuum system requires specialized knowledge and diligence. Seals, pumps, and internal hot zones all require regular, skilled maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
How This History Informs Modern Choices
Understanding this technological evolution from a simple concept to a sophisticated system allows you to select the right tool for your specific goal.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive metals (like titanium or niobium): The "cold wall" design, born from aerospace needs, is the only viable technology.
- If your primary focus is clean, bright finishing of tool steels: A furnace with high-pressure gas quenching is essential to achieve hardness without post-process cleaning.
- If your primary focus is absolute precision and repeatability (for medical implants or aerospace): Modern PLC controls and advanced vacuum pump systems are non-negotiable features.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, simple parts with low cleanliness requirements: The historical trade-off still holds; a less complex and less expensive atmospheric furnace is likely more cost-effective.
By tracing its origins, you can see the vacuum furnace not as a machine, but as the culmination of a century-long quest for metallurgical purity and control.

Summary Table:
| Era | Key Development | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Early 20th Century | Laboratory-scale vacuum heating | Proved principle of contamination-free processing |
| Mid-20th Century | Industrial "Cold Wall" furnace | Enabled processing of reactive metals (titanium, superalloys) |
| Late 20th Century | PLC controls & advanced pumps | Achieved precision, repeatability, and faster cycle times |
| Modern Era | High-pressure gas quenching & convection | Delivered clean finishes, uniform heating, and oil-free cooling |
Ready to leverage a century of innovation in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in advanced vacuum furnace systems that deliver the metallurgical purity, precise control, and repeatability demanded by modern laboratories. Whether you're processing reactive metals, tool steels, or medical implants, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for your specific needs.
Contact us today to discuss how our lab equipment can enhance your research and production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum heat treatment work? Achieve Superior Material Properties in a Pristine Environment
- What is the leak rate for a vacuum furnace? Ensure Process Purity and Repeatability
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock High-Purity Heat Treatment for Superior Materials
- How does argon and nitrogen cooling compare in vacuum furnaces? A Guide to Faster, Cheaper Quenching
- What is the maximum temperature in a vacuum furnace? It Depends on Your Materials and Process Needs



















