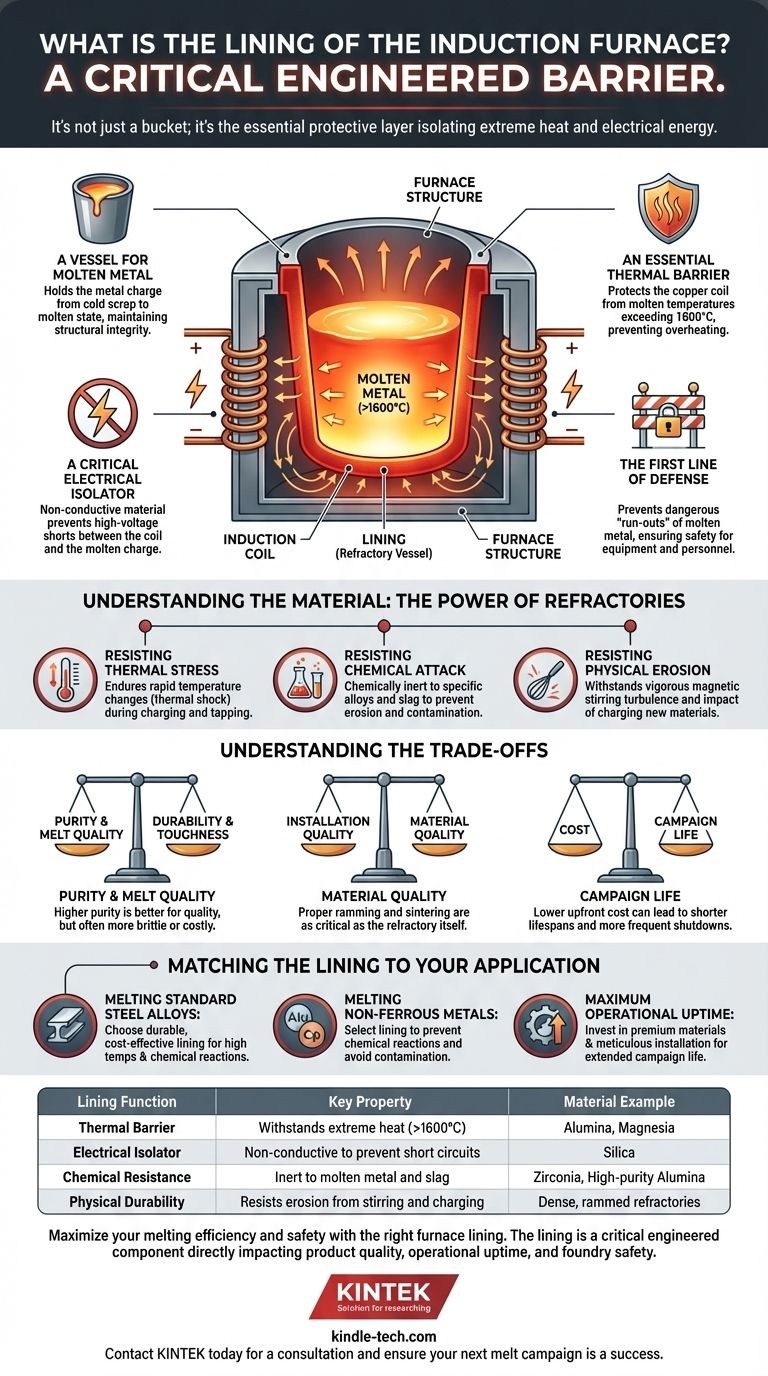
In an induction furnace, the lining is the critical inner layer made from specialized refractory materials that forms the crucible. This lining is the component that directly contains the molten metal, but its function is far more complex than being a simple bucket. It serves as the essential barrier that isolates the extreme heat and electrical energy of the melt from the furnace's vital components, most importantly the induction coil.
The furnace lining is not merely a container; it is an engineered barrier that must withstand intense thermal, chemical, and physical stresses to ensure the safety, efficiency, and operational integrity of the entire induction furnace system.

The Lining's Role in Furnace Operation
The lining sits at the heart of the furnace, separating the molten charge from the rest of the structure. Its performance dictates the safety and efficiency of every melt cycle.
A Vessel for Molten Metal
The most apparent function of the lining is to act as the refractory vessel, or crucible, that holds the metal charge. It must maintain its structural integrity from the initial loading of cold, solid scrap through the entire high-temperature melting process.
An Essential Thermal Barrier
Induction furnaces generate immense heat. The lining provides critical thermal insulation, protecting the copper induction coil from the molten metal, which can exceed temperatures of 1600°C (2900°F). Without this barrier, the coil would quickly overheat and fail.
A Critical Electrical Isolator
The induction coil creates a powerful magnetic field to heat the metal. The lining is made of non-conductive material, preventing the high electrical energy from shorting out between the coil and the molten metal charge. This electrical isolation is fundamental to the induction principle.
The First Line of Defense
A breach in the lining is one of the most dangerous failures in a foundry, potentially leading to a "run-out" where molten metal escapes. A properly installed and maintained lining is the primary safety measure against this catastrophic event, protecting both equipment and personnel.
Understanding the Material: The Power of Refractories
The lining's ability to perform its duties comes from the unique properties of refractory materials. These are non-metallic materials engineered to withstand extreme conditions.
What is a Refractory?
Simply put, a refractory is a material that retains its strength and chemical properties at very high temperatures. The choice of refractory (e.g., silica, alumina, magnesia) depends on the type of metal being melted and the specific operating conditions of the furnace.
Resisting Thermal Stress
The lining must endure severe and rapid temperature changes, a phenomenon known as thermal shock. It experiences this when cold scrap is charged into a hot furnace and again when the molten metal is tapped out.
Resisting Chemical Attack
Different metals and the byproducts of melting (slag) can be chemically aggressive. The lining material must be chosen to be chemically inert to the specific alloy being melted to prevent both erosion of the lining and contamination of the final product.
Resisting Physical Erosion
The strong magnetic fields in an induction furnace create a vigorous stirring action within the molten bath. This turbulence, along with the impact of charging new material, causes constant physical wear that the lining must be strong enough to resist.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The performance of a furnace lining is not absolute; it is a balance of competing factors. Recognizing these trade-offs is crucial for effective furnace management.
Purity vs. Durability
Higher-purity refractory materials typically have a higher melting point and are less reactive, which is good for melt quality. However, they can sometimes be more brittle or significantly more expensive than materials that prioritize physical toughness and erosion resistance.
Installation vs. Material Quality
Even the highest-quality refractory material will fail prematurely if installed incorrectly. The process of ramming (compacting) the dry material to the correct density and then properly heating it for the initial sinter (curing) is as critical as the material itself.
Cost vs. Campaign Life
A lower-cost lining might seem economical upfront, but it will likely have a shorter lifespan. This results in more frequent furnace shutdowns for relining, leading to lost production time and increased labor costs that can outweigh the initial savings.
Matching the Lining to Your Application
Selecting the correct lining is a strategic decision that directly impacts operational outcomes. It must be aligned with your specific production goals.
- If your primary focus is melting standard steel alloys: You will need a durable, cost-effective lining that can withstand high temperatures and the chemical reactions of carbon and alloy steels.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or copper: The lining must be chosen specifically to prevent chemical reactions with these metals and avoid contaminating the pure melt.
- If your primary focus is maximum operational uptime: Invest in premium, high-purity refractory materials and a meticulous installation process to extend the lining's campaign life and reduce furnace downtime.
Ultimately, viewing the furnace lining as a consumable but highly engineered component is the key to safe and efficient melting operations.
Summary Table:
| Lining Function | Key Property | Material Example |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Barrier | Withstands extreme heat (>1600°C) | Alumina, Magnesia |
| Electrical Isolator | Non-conductive to prevent short circuits | Silica |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to molten metal and slag | Zirconia, High-purity Alumina |
| Physical Durability | Resists erosion from stirring and charging | Dense, rammed refractories |
Maximize your melting efficiency and safety with the right furnace lining. The lining is not just a consumable; it's a critical engineered component that directly impacts your product quality, operational uptime, and foundry safety. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory and foundry needs. Our experts can help you select the optimal refractory material for your specific metal and operational goals. Contact KINTEL today for a consultation and ensure your next melt campaign is a success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is VIM in metallurgy? A Guide to Vacuum Induction Melting for High-Performance Alloys
- What are the advantages of induction melting? Achieve Faster, Cleaner, and More Controlled Metal Melting
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity



















