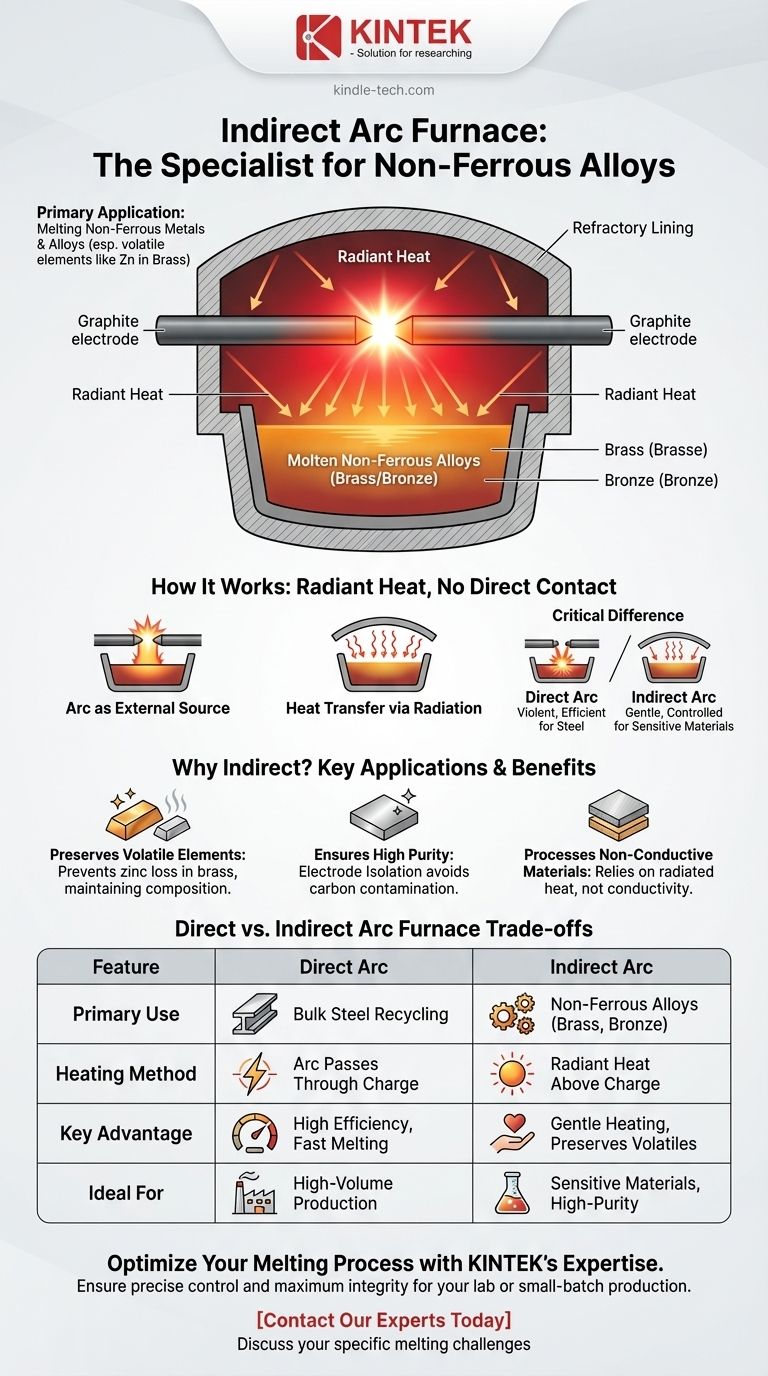
The primary application of an indirect arc furnace is to melt non-ferrous metals and alloys, particularly those containing volatile elements like brass and bronze. Unlike its direct-arc counterpart used for bulk steel, the indirect furnace provides a more controlled, gentle heat that prevents valuable elements from being burned off and lost during the melting process.
The core principle is simple: An indirect arc furnace heats materials without direct contact from the electric arc. This makes it the specialized tool for melting materials that are sensitive, non-conductive, or require high purity, where direct, intense heating would be detrimental.

How an Indirect Arc Furnace Works
An indirect arc furnace operates on a fundamentally different principle than the more common direct arc furnace. Understanding this distinction is key to grasping its specific applications.
The Arc as an External Heat Source
In this furnace, a powerful electric arc is struck between two graphite electrodes positioned above the material being melted (the "charge").
The arc does not pass through the charge itself. It acts purely as a high-temperature radiant heater, similar to a heating element in an oven, but operating at thousands of degrees.
Heat Transfer via Radiation
The immense heat generated by the arc radiates outwards. It heats the furnace's refractory lining and the roof, which in turn radiate that heat down onto the charge.
This process ensures a more uniform and less aggressive transfer of energy to the material, melting it evenly through radiation and conduction.
The Critical Difference from Direct Arc Furnaces
This method stands in stark contrast to a direct arc furnace (DAF), the workhorse of steel recycling.
In a DAF, the electrodes are lowered to make contact with the scrap metal, and the powerful electric arc passes directly through the conductive charge itself. This is incredibly efficient but also intensely violent, making it unsuitable for more delicate materials.
Why Indirect Heating Matters: Key Applications
The choice to use an indirect furnace is driven entirely by the specific properties of the material being melted.
Melting Non-Ferrous Alloys
This is the furnace's main application. Alloys like brass (copper-zinc) and bronze (copper-tin) benefit immensely from indirect heat.
The intense, localized hotspot of a direct arc would cause the zinc, which has a much lower boiling point than copper, to vaporize and escape as fume. Indirect heating melts the alloy gently, preserving its chemical composition.
Ensuring High Purity
In a direct arc furnace, the electrodes are consumed and can introduce carbon into the molten metal. For certain high-purity metals or alloys where carbon is an unwanted impurity, the indirect furnace provides crucial separation between the arc and the melt.
Processing Non-Conductive Materials
A direct arc requires an electrically conductive path to function. An indirect arc furnace can be used to heat materials that do not conduct electricity well, as it relies solely on radiated heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While specialized, the indirect arc furnace is not a universal solution. Its design comes with inherent limitations.
Lower Thermal Efficiency
Heating a material through radiation is fundamentally less efficient than passing a current directly through it. More energy is lost to the furnace structure and the surrounding environment, leading to higher energy consumption per ton of metal melted.
Slower Melting Rates
As a consequence of its lower efficiency and more gentle heating method, melting a batch of material in an indirect furnace takes significantly longer than in a direct arc furnace of comparable size.
Smaller Capacity
Due to these factors, indirect arc furnaces are typically much smaller than the massive direct arc furnaces used for steel production. They are designed for smaller, specialized batches rather than high-volume, commodity-grade output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace technology depends entirely on balancing material properties with production requirements.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous alloys like brass or bronze: The indirect arc furnace is the superior choice to prevent the loss of volatile zinc and maintain alloy integrity.
- If your primary focus is high-volume steel recycling: A direct arc furnace is the undisputed industry standard for its raw power, speed, and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is melting materials sensitive to carbon contamination: The indirect method provides the necessary isolation from the graphite electrodes to ensure purity.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace is about matching the heating method to the specific needs of the material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Direct Arc Furnace | Indirect Arc Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Bulk steel recycling | Non-ferrous alloys (brass, bronze) |
| Heating Method | Arc passes through conductive charge | Radiant heat from arc above the charge |
| Key Advantage | High efficiency, fast melting | Gentle heating, preserves volatile elements |
| Ideal For | High-volume production | Sensitive materials, high-purity requirements |
Optimize your non-ferrous alloy melting process with KINTEK's expertise.
Struggling with zinc loss in brass or tin oxidation in bronze? Our specialized lab equipment solutions ensure precise temperature control and maximum material integrity. Whether you're in R&D or small-batch production, KINTEK provides the reliable, gentle heating technology you need for sensitive metals and high-purity applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific melting challenges and discover the perfect furnace for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the VAR melting process? The Ultimate Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting
- What is the vacuum arc remelting process? Producing Ultra-Pure, High-Performance Metal Alloys
- What is the benefit of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Structural Integrity
- What is var in metals? A Guide to Vacuum Arc Remelting for Superior Alloys
- What is the process of vacuum arc remelting? Achieve Ultimate Purity for High-Performance Alloys



















