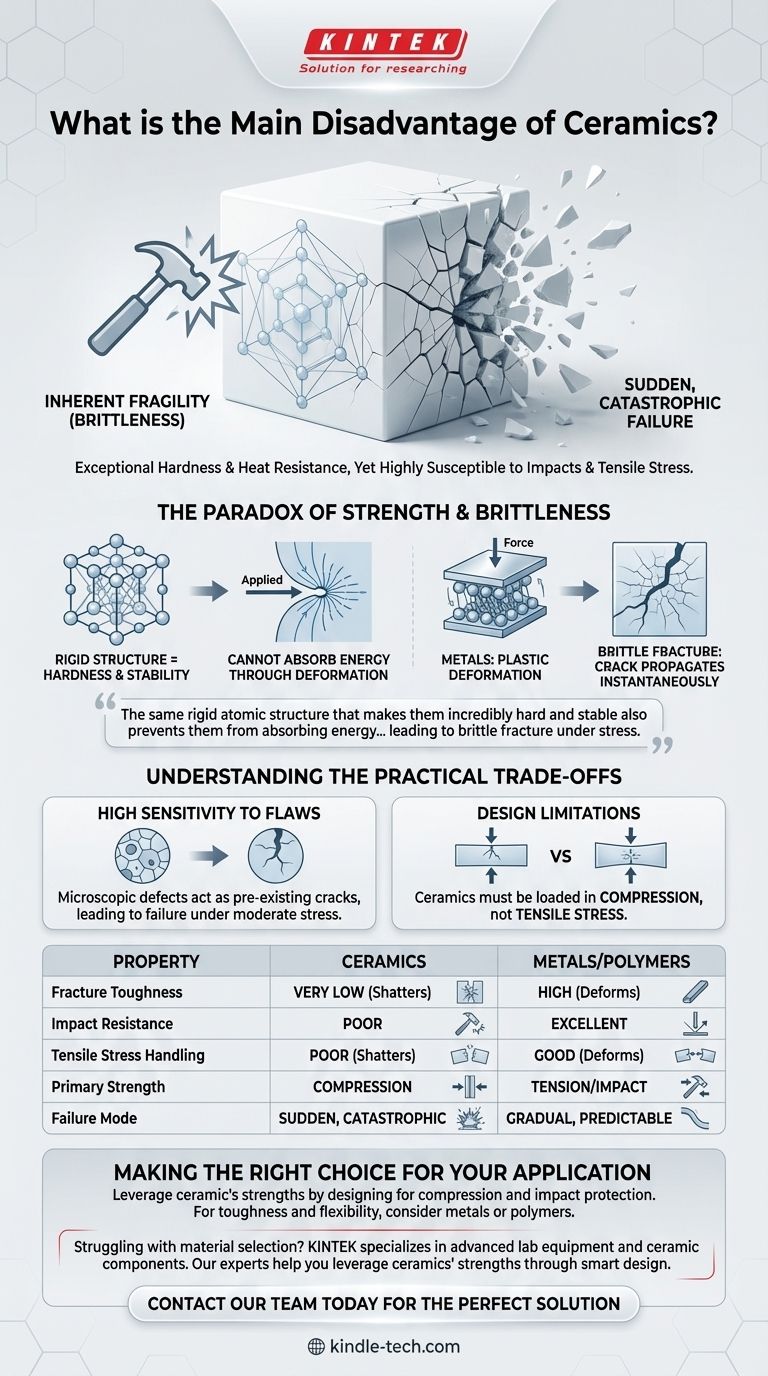
Without question, the single greatest disadvantage of most ceramic materials is their inherent fragility, or brittleness. While they possess exceptional hardness and resistance to heat and chemical attack, they are highly susceptible to catastrophic failure when subjected to sharp impacts or tensile stress. This means they can shatter suddenly without any prior warning or deformation.
The core issue with ceramics is a paradox: the same rigid atomic structure that makes them incredibly hard and stable also prevents them from absorbing energy through bending or deforming, leading to brittle fracture under stress.
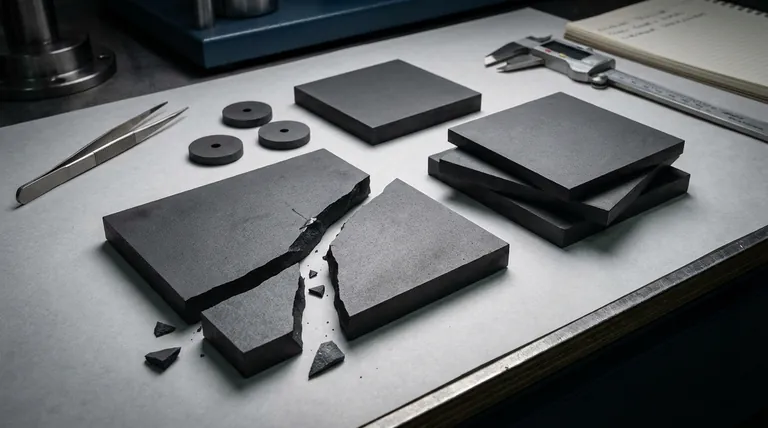

The Paradox of Strength and Brittleness
Ceramics present a unique engineering challenge. Their most valued properties are directly linked to their most significant weakness. Understanding this relationship is crucial for using them effectively.
What Makes Ceramics So Hard?
The atoms in ceramic materials are held together by extremely strong and rigid ionic and covalent bonds.
This rigid crystalline structure is very difficult to disrupt. It is what gives ceramics their characteristic hardness, high compressive strength (resistance to being squeezed), and stability at high temperatures.
Why Does Hardness Lead to Brittleness?
When a force is applied to a metal, its atomic layers can slip past one another, allowing the material to deform and absorb energy. This is called plastic deformation.
Ceramics cannot do this. Their rigid bonds resist any slipping. Instead, when a force creates a tiny surface crack, all of that energy becomes concentrated at the tip of the crack. This intense stress breaks the bonds at the crack's tip, causing it to propagate almost instantaneously through the material, resulting in a sudden, complete fracture.
The Concept of Fracture Toughness
This property is measured as fracture toughness—a material's ability to resist the propagation of a crack.
Metals and polymers generally have high fracture toughness, while most traditional ceramics have very low fracture toughness. They simply cannot absorb much energy before failing.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
This fundamental brittleness has significant real-world consequences that must be managed in any application.
High Sensitivity to Flaws
The manufacturing process can introduce microscopic flaws, such as pores, grain boundaries, or tiny cracks, into the ceramic body.
These tiny, often invisible, defects act as pre-existing cracks. They become the starting points for catastrophic failure, even under moderate stress that a "perfect" component could easily withstand.
Challenges in Handling and Installation
The low fracture toughness of ceramics makes them extremely vulnerable during transportation and installation.
A dropped tool, an accidental collision, or even stress from bolting a ceramic part to a misaligned surface can be enough to initiate a crack and cause the entire component to fail.
Design Limitations
Engineers must design systems that specifically protect ceramic components from impact and tensile stress (pulling forces).
Ceramic parts are almost always designed to be loaded in compression (pushing forces), which works to close any potential cracks rather than pull them apart.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the choice to use a ceramic material depends entirely on whether you can leverage its strengths while mitigating its fundamental weakness.
- If your primary focus is hardness, wear resistance, or high-temperature stability: Ceramics are an exceptional choice, provided you can design the component to exist primarily in a state of compression and protect it from impact.
- If your primary focus is impact resistance, toughness, or the ability to bend without breaking: You must consider metals, polymers, or composite materials, as ceramics are fundamentally unsuited for these requirements.
Understanding the brittle nature of ceramics is the first step to harnessing their remarkable capabilities.
Summary Table:
| Property | Ceramics | Metals/Polymers |
|---|---|---|
| Fracture Toughness | Very Low | High |
| Impact Resistance | Poor | Excellent |
| Tensile Stress Handling | Poor (Shatters) | Good (Deforms) |
| Primary Strength | Compression | Tension/Impact |
| Failure Mode | Sudden, Catastrophic | Gradual, Predictable |
Struggling to choose the right material for your high-temperature or high-wear application? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including ceramic components engineered for maximum performance. Our experts can help you leverage the strengths of ceramics while mitigating their brittleness through smart design and material selection. Contact our team today to find the perfect solution for your laboratory's unique challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide (SIC) Ceramic Sheet Wear-Resistant Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Rod Insulated for Industrial Applications
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Precision Machined Zirconia Ceramic Ball for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Hexagonal Boron Nitride HBN Ceramic Ring
People Also Ask
- Which is harder silicon carbide or tungsten carbide? Discover the Key to Material Selection
- What are the characteristics of SiC? Unlock High-Temp, Hard, and Chemically Inert Performance
- What are the properties of SiC? Unlock High-Temperature, High-Frequency Performance
- What is the temperature resistance of silicon carbide? Withstands Extreme Heat Up to 1500°C
- What is the resistivity of silicon carbide? It's a tunable property from <0.1 ohm-cm to highly resistive.



















