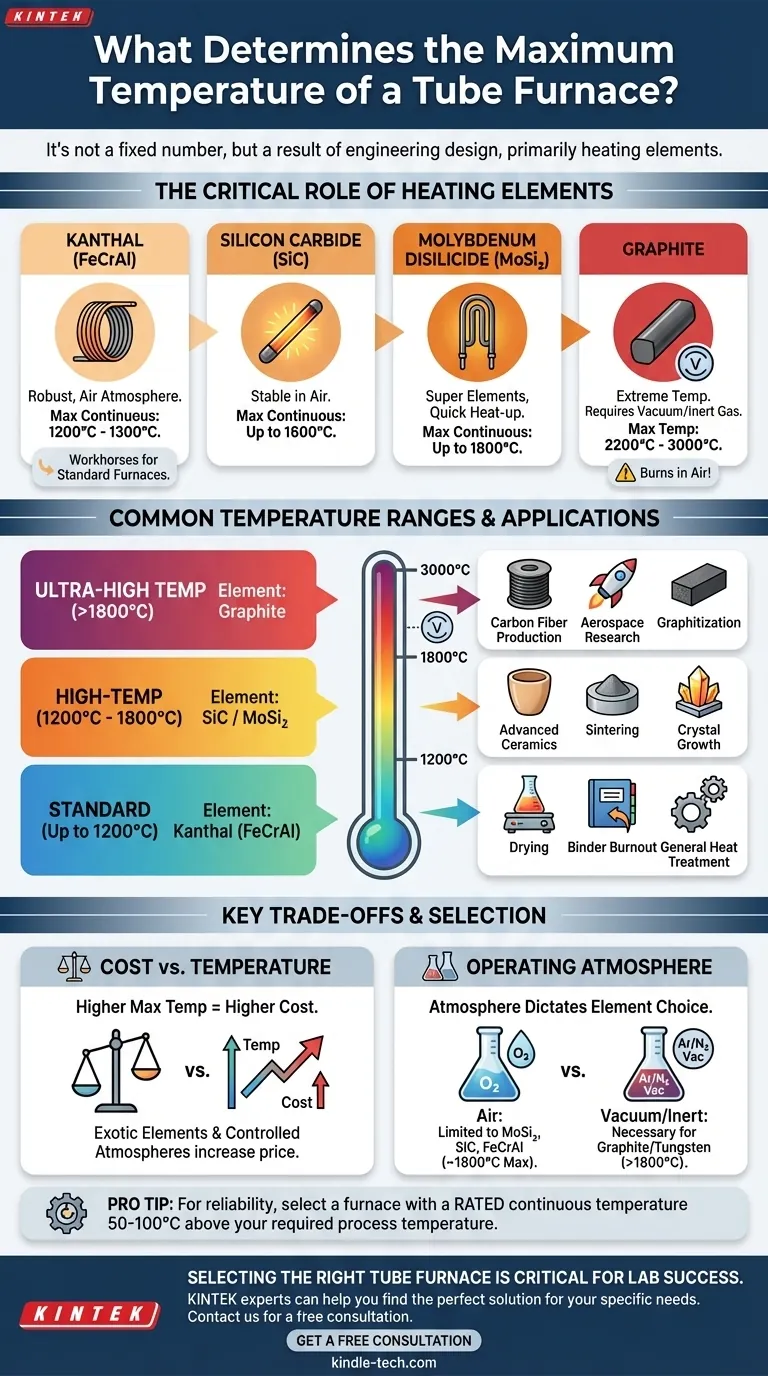
There is no single maximum temperature for a tube furnace. Instead, the maximum temperature is dictated entirely by its specific design, particularly the materials used for its heating elements and insulation. Common laboratory tube furnaces operate up to 1200°C, while high-temperature models can reach 1800°C, and highly specialized graphite-element furnaces can achieve temperatures as high as 3000°C.
The crucial takeaway is that a tube furnace's temperature limit is not a fixed property but a direct consequence of its engineering. The question is not "how hot can a tube furnace get?" but rather "which furnace is designed to safely and reliably reach my required temperature?"

What Determines a Tube Furnace's Maximum Temperature?
A furnace is a system of components, and its performance is limited by its weakest link. For maximum temperature, the heating element is almost always the primary determining factor.
The Critical Role of the Heating Element
The heating element is the heart of the furnace, converting electrical energy into heat. Different materials have vastly different temperature capabilities and atmospheric requirements.
-
Kanthal (FeCrAl) Alloys: These are the workhorses for standard furnaces. They are robust, relatively inexpensive, and work well in air, typically reaching a maximum continuous operating temperature of 1200°C to 1300°C.
-
Silicon Carbide (SiC): For higher temperatures, SiC elements are a common choice. They can operate in air and provide stable performance up to 1600°C.
-
Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂): These "super" elements are used in many high-temperature lab furnaces. They can reach very high temperatures quickly, operating continuously in air up to 1800°C.
-
Graphite: To achieve the highest possible temperatures, graphite elements are used. However, they readily oxidize and burn up in air. Therefore, graphite furnaces must operate in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to reach their maximum temperature of 2200°C to 3000°C.
Furnace Construction and Insulation
The body of the furnace must be able to contain the extreme heat generated by the elements. High-purity ceramic fiber insulation is used to prevent heat loss and protect the outer casing. The process tube itself, which holds the sample, also has a temperature limit (e.g., quartz is limited to ~1100°C, while high-purity alumina can handle over 1700°C).
Common Temperature Ranges and Their Applications
Tube furnaces can be grouped into three general tiers based on their temperature range and intended use.
Standard Furnaces (Up to 1200°C)
These are the most common and versatile furnaces found in general laboratories. They use FeCrAl elements and are ideal for applications like drying, binder burnout, general heat treatment, and synthesis of many materials.
High-Temperature Furnaces (1200°C to 1800°C)
These furnaces rely on SiC or MoSi₂ elements. They are required for processing advanced ceramics, sintering metal powders, growing certain crystals, and testing materials at elevated temperatures.
Ultra-High Temperature Furnaces (Above 1800°C)
These are highly specialized systems using graphite or refractory metal (tungsten, molybdenum) elements. Their use is confined to advanced research and industrial processes like graphitization, carbon fiber production, and testing materials for aerospace applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace is about balancing performance with practical constraints. A higher maximum temperature is not always better.
Cost vs. Temperature
There is a direct and steep correlation between maximum temperature and cost. Exotic heating elements, advanced insulation, and the complex systems required for controlled atmospheres (like vacuum pumps and gas controllers) significantly increase the price of the furnace.
Operating Atmosphere Limitations
This is a critical pitfall. Elements like graphite and tungsten are destroyed by oxygen at high temperatures. If your process requires an air atmosphere, your choice is immediately limited to furnaces with MoSi₂, SiC, or FeCrAl elements, capping your practical maximum temperature around 1800°C.
Rated Temperature vs. Absolute Maximum
Every furnace has a rated continuous operating temperature. It is poor practice to run a furnace at its absolute maximum limit for extended periods, as this drastically shortens the lifespan of the heating elements and other components. For reliability and longevity, select a furnace whose rated continuous temperature is at least 50-100°C above your required process temperature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your selection on the specific requirements of your process, not on achieving the highest possible number.
- If your primary focus is general lab work or annealing below 1200°C: A standard furnace with FeCrAl (Kanthal) elements is the most cost-effective and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced ceramics or alloys up to 1800°C: You must invest in a high-temperature furnace with Silicon Carbide (SiC) or Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements.
- If your primary focus is research requiring extreme temperatures above 1800°C: A specialized graphite or tungsten furnace operating under a vacuum or inert atmosphere is your only option.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about matching the tool's defined capabilities to your specific processing needs.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Heating Element | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 1200°C | Kanthal (FeCrAl) | Drying, binder burnout, general heat treatment |
| 1200°C to 1800°C | Silicon Carbide (SiC) / Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) | Advanced ceramics, sintering, crystal growth |
| Above 1800°C | Graphite (requires inert/vacuum atmosphere) | Graphitization, carbon fiber, aerospace research |
Selecting the right tube furnace is critical for your lab's success. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including tube furnaces tailored to your specific temperature and application requirements. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature, cost, and atmosphere to find the perfect solution for your research or production needs. Contact us today to ensure your lab has the reliable, high-performance equipment it deserves.
Get a Free Consultation for Your Tube Furnace Needs
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control
- What is the technical value of using a quartz tube reaction chamber for static corrosion testing? Achieve Precision.
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- What materials are used for the tubes in tube furnaces? A Guide to Selecting the Right Tube for Your Process



















