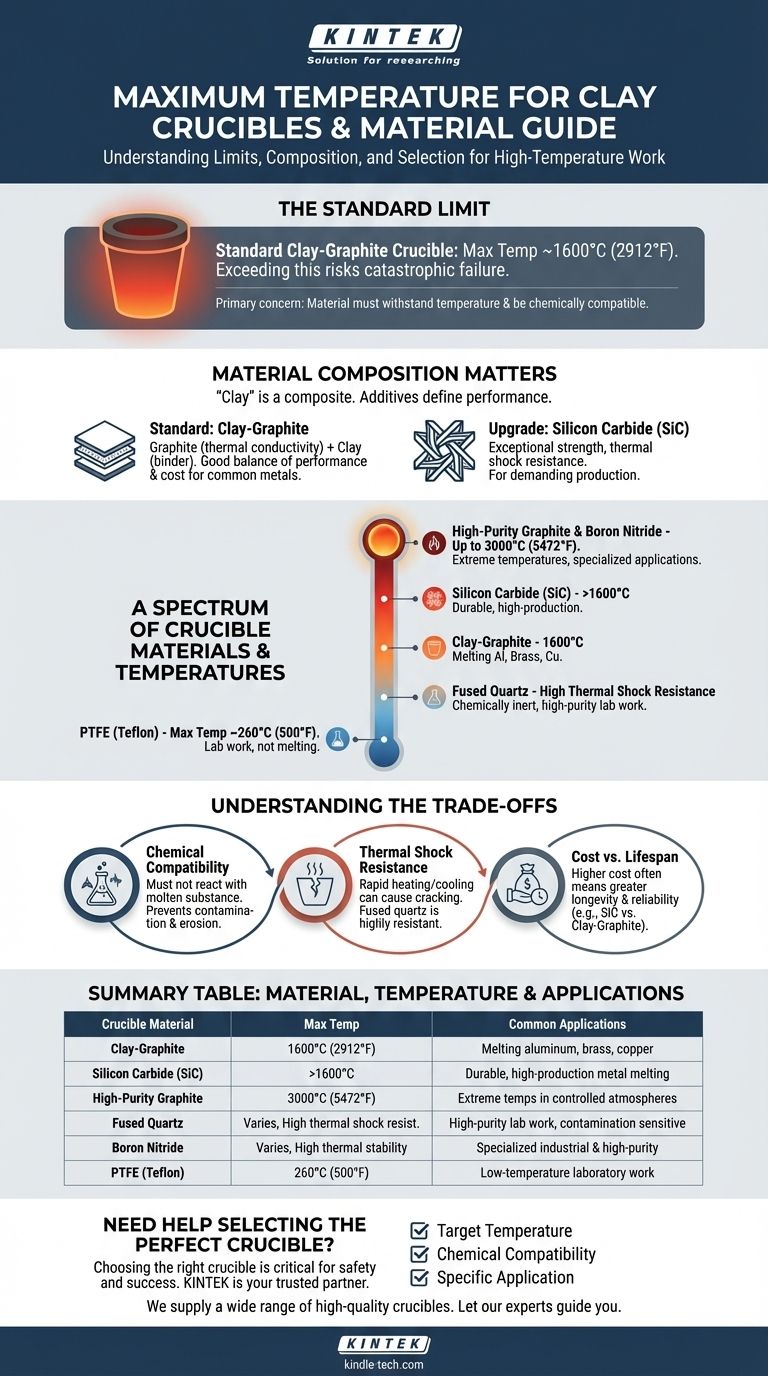
For a standard clay-graphite crucible, the type most commonly used in foundries and workshops, the maximum service temperature is typically around 1600°C (2912°F). Exceeding this limit risks crucible failure, which can be catastrophic when handling molten metal. However, the term "clay" is broad, and the true limit depends on the crucible's specific composition.
The maximum temperature is only one factor in choosing a crucible. Your primary concern should be selecting a material that can withstand your target temperature while also being chemically compatible with the substance you are heating to avoid contamination and crucible degradation.
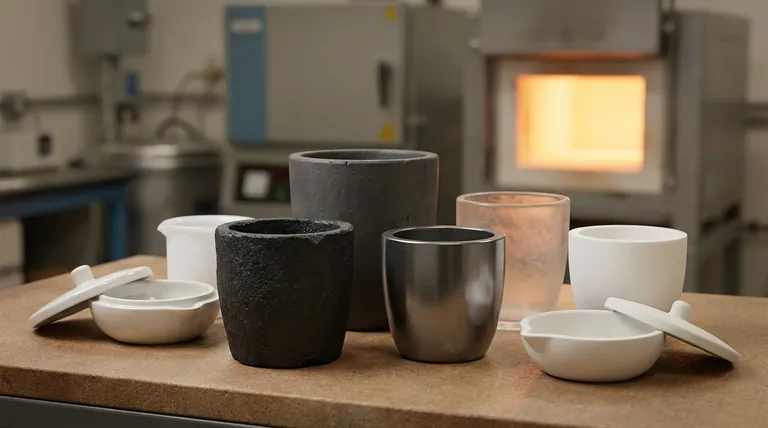

Why Material Composition is Everything
The term "clay crucible" is often a shorthand for a composite material. Pure clay is rarely used alone for high-temperature work. The additives blended with the clay are what define the crucible's performance and temperature limits.
The Standard: Clay-Graphite
Most crucibles used for melting common metals like aluminum, brass, and copper are a clay-graphite composite. Graphite provides excellent thermal conductivity for even heating, while the clay acts as a binder, giving it structural form. This combination offers a great balance of performance and cost.
The Upgrade: Silicon Carbide
For greater durability and a longer service life, silicon carbide (SiC) crucibles are a superior choice. They are often bonded with clay or other materials. SiC offers exceptional strength and resistance to thermal shock, making it a workhorse in more demanding production environments.
A Spectrum of Crucible Materials
Choosing the right crucible means matching the material to the temperature and the application. The range of materials is vast, each with a specific operational window.
Low-Temperature Polymers: PTFE
At the very low end of the spectrum, you find materials like PTFE (Teflon). These are not for melting metal but for laboratory work, with a maximum temperature of only about 260°C (500°F).
High-Temperature Ceramics: Fused Quartz
For applications requiring extreme resistance to thermal shock (rapid heating and cooling), fused quartz is an excellent choice. It is chemically inert in many situations, making it ideal for high-purity lab work where contamination is a concern.
Extreme-Temperature Synthetics: Graphite & Boron Nitride
For the highest temperatures, specialized synthetic materials are required. High-purity graphite crucibles can withstand up to 3000°C (5472°F) in a controlled atmosphere, making them suitable for a wide range of industrial processes. Boron nitride is another specialty material valued for its excellent thermal insulation and chemical stability.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a crucible based solely on its maximum temperature rating is a common mistake. You must consider the chemical and physical stresses of your specific process.
Chemical Compatibility
The most critical factor after temperature is ensuring the crucible material will not react with the molten substance inside it. An incompatible crucible can contaminate your melt or be rapidly eroded, leading to failure.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Heating or cooling a crucible too quickly induces thermal stress, which can cause cracking. Materials like fused quartz are highly resistant to this, while standard clay-graphite crucibles require a more careful pre-heating and cool-down cycle to prevent damage.
Cost vs. Lifespan
There is a direct relationship between cost and performance. A basic clay-graphite crucible is economical for hobbyists, while a silicon carbide or boron nitride crucible represents a significant investment suited for industrial or high-purity applications where longevity and reliability are paramount.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your decision on the specific demands of your work.
- If your primary focus is melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum or brass: A standard clay-graphite or silicon carbide crucible is the industry standard and the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity laboratory work or materials sensitive to contamination: A fused quartz or boron nitride crucible is necessary to ensure chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures above 2000°C: You must use a specialized material like high-purity graphite in a controlled-atmosphere furnace.
Ultimately, matching the crucible material to your specific temperature, chemistry, and process is the key to safe and successful high-temperature work.
Summary Table:
| Crucible Material | Typical Max Service Temperature | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Clay-Graphite | 1600°C (2912°F) | Melting aluminum, brass, copper |
| Silicon Carbide (SiC) | >1600°C | Durable, high-production metal melting |
| High-Purity Graphite | 3000°C (5472°F) | Extreme temperatures in controlled atmospheres |
| Fused Quartz | Varies, high thermal shock resistance | High-purity lab work, sensitive to contamination |
| Boron Nitride | Varies, high thermal stability | Specialized industrial & high-purity applications |
| PTFE (Teflon) | 260°C (500°F) | Low-temperature laboratory work |
Need Help Selecting the Perfect Crucible?
Choosing the right crucible is critical for the safety and success of your high-temperature work. The wrong material can lead to contamination, crucible failure, and dangerous situations.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory equipment and consumables. We specialize in helping our customers select the ideal crucible based on:
- Your Target Temperature: Ensuring the material can withstand the heat.
- Chemical Compatibility: Preventing contamination and crucible degradation.
- Your Application: Whether you're melting metals, conducting high-purity research, or working in an industrial setting.
We supply a wide range of high-quality crucibles, including clay-graphite, silicon carbide, and specialized materials, to meet your specific needs.
Don't risk your process or safety. Let our experts guide you to the perfect solution.
Contact KINTEK today for a personalized consultation and get the right crucible for your lab.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-purity alumina crucible preferred for high-temperature oxidation? Ensure Unmatched Data Integrity
- Why are high-purity alumina crucibles used for LATP? Preserve Purity and Conductivity in Sintering
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data



















