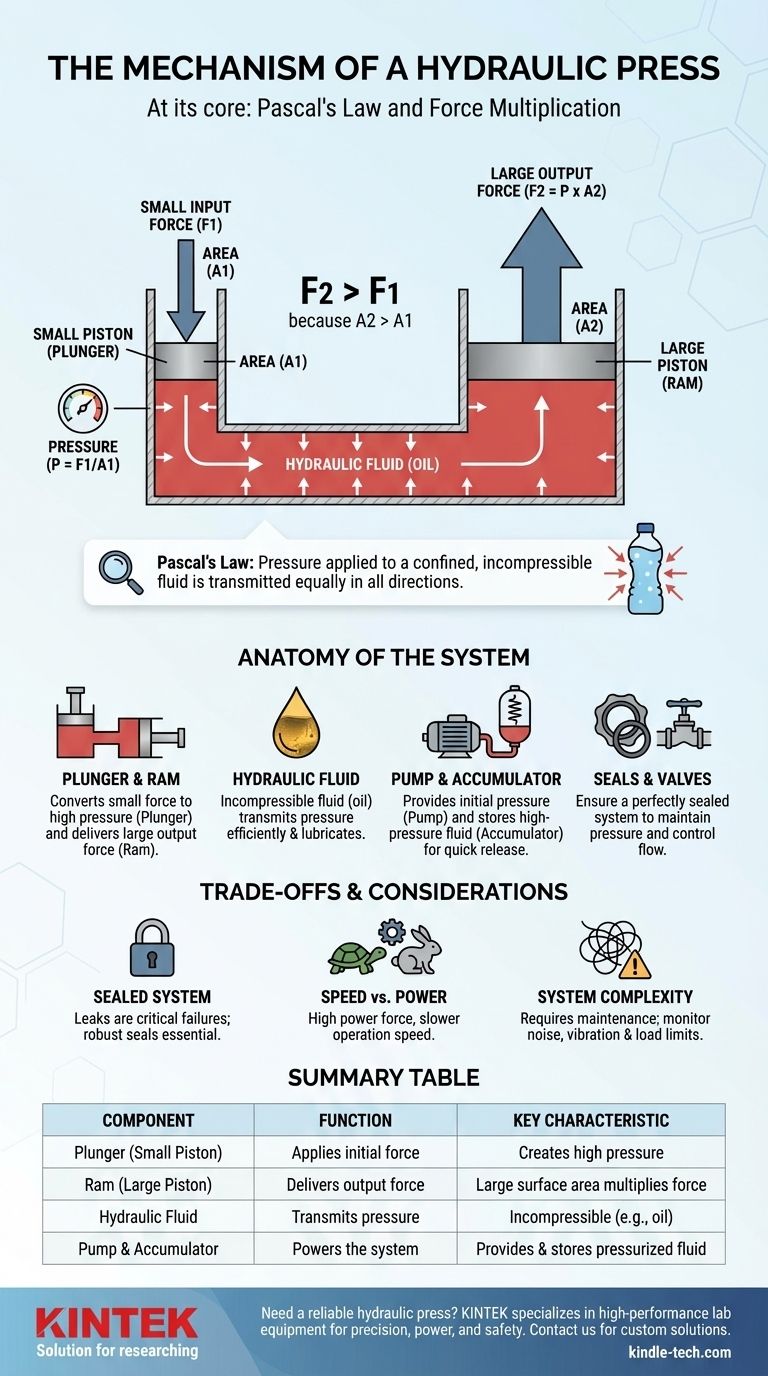
At its core, a hydraulic press operates on a simple yet powerful principle known as Pascal's Law. It uses a confined liquid, typically oil, to convert a small amount of applied force into an exceptionally large output force. By applying pressure to a small piston (the plunger), that same pressure is transmitted through the fluid to a much larger piston (the ram), multiplying the initial force significantly.
The fundamental mechanism is force multiplication through fluid pressure. A small force applied over a small area creates a specific pressure in a confined fluid, and that same pressure acting on a much larger area generates a proportionally massive output force.

The Core Principle: Pascal's Law Explained
The entire function of a hydraulic press hinges on understanding one key concept from fluid mechanics. This principle is what allows a force that a person could apply by hand to become powerful enough to shape solid steel.
What is Pascal's Law?
Pascal's Law states that pressure applied to a confined, incompressible fluid is transmitted equally in all directions throughout the fluid.
Imagine squeezing a sealed water bottle. The pressure you apply with your hand isn't just felt directly under your fingers; it increases everywhere inside the bottle. A hydraulic system harnesses this effect in a controlled way.
How Pressure Multiplies Force
The magic of the hydraulic press lies in its two-piston design. It has a small piston (plunger) and a much larger piston (ram), connected by a cylinder filled with hydraulic fluid.
Since Pressure = Force / Area, a small force applied to the small plunger creates a specific pressure within the fluid. According to Pascal's Law, this exact same pressure is then exerted on the large ram.
Because the ram has a much larger surface area, the resulting output force is enormous. For example, if the ram's area is 100 times larger than the plunger's area, the output force will be 100 times greater than the input force.
Anatomy of a Hydraulic Press System
While the two-piston system is the heart of the press, a few other components are required to make it a functional machine.
The Two-Piston System (Plunger and Ram)
The plunger is the small cylinder where the initial, smaller force is applied. The ram is the large cylinder that moves as a result of the pressure, delivering the immense compressive force onto the workpiece.
The Hydraulic Fluid
The system relies on an incompressible fluid, most commonly a specialized hydraulic oil. Oil is used because it cannot be easily compressed, ensuring that the pressure is transmitted efficiently, and it also helps lubricate the moving parts.
The Power Source and Storage
In industrial applications, an electric pump provides the initial pressure on the fluid. This high-pressure liquid is often stored in a hydraulic accumulator.
The accumulator acts like a rechargeable battery for pressure, storing the fluid under high pressure so it can be released quickly when a strong, sudden thrust is needed for an operation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
The immense power of a hydraulic press comes with specific operational considerations and potential points of failure. Understanding these is critical for its safe and effective use.
The Need for a Perfectly Sealed System
The entire principle relies on the fluid being confined. Any oil leakage is a critical failure point, as it reduces the pressure and compromises the force output. This is why robust seals and regular maintenance are essential.
Speed vs. Power
The trade-off for force multiplication is distance and speed. To move the large ram a short distance, the small plunger must travel a much longer distance. This means hydraulic presses are incredibly powerful but often operate more slowly than mechanical presses.
System Complexity and Safety
Industrial hydraulic systems are complex, involving pumps, valves, and high-pressure lines. Issues like loud noise, excessive vibration, or operating beyond the machine's load limits are signs of serious problems that require an immediate shutdown to prevent catastrophic failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The unique characteristics of a hydraulic press make it the ideal tool for specific industrial applications, particularly where raw power and fine control are paramount.
- If your primary focus is generating immense compressive force: The hydraulic press is unparalleled for tasks like forging large metal ingots, crushing materials, or deep-drawing sheet metal.
- If your primary focus is precise control over the forming process: The ability to finely regulate pressure and ram speed allows operators to create complex and unique geometries that would be impossible with other types of presses.
Ultimately, the hydraulic press is a testament to how a fundamental law of physics can be engineered into a machine of incredible power and precision.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Plunger (Small Piston) | Applies initial force | Creates high pressure in the fluid |
| Ram (Large Piston) | Delivers output force | Large surface area multiplies the force |
| Hydraulic Fluid | Transmits pressure | Incompressible (e.g., oil) |
| Pump & Accumulator | Powers the system | Provides and stores pressurized fluid |
Need a reliable hydraulic press for your lab or production line? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including hydraulic presses designed for precision, power, and safety. Our experts can help you select the perfect press for your specific application, from material testing to sample preparation. Contact our team today to discuss your requirements and discover the KINTEK difference!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Automatic High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
People Also Ask
- What is KBr disc method? A Complete Guide to IR Spectroscopy Sample Prep
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press used to compress powders into pellets? Enhance Solid-State Reaction Kinetics
- What is an example of a hydraulic press? Discover the Power of Laboratory Sample Preparation
- What role does a laboratory hydraulic press play in all-solid-state battery fabrication? Enhancing Ion Conductivity
- Why is a laboratory hydraulic press required during the preparation of Ti3AlC2 precursor pellets?



















