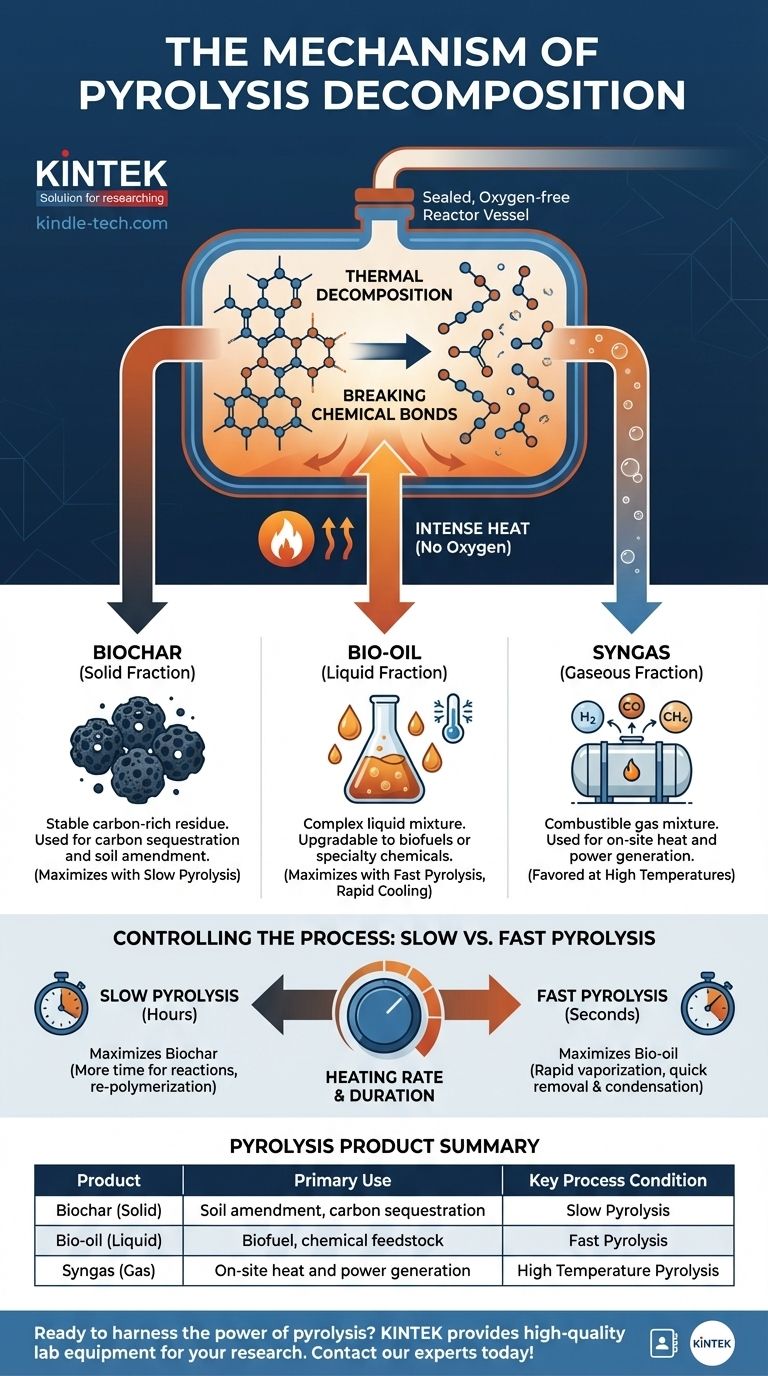
At its core, the mechanism of pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of a material in a completely oxygen-free environment. Instead of burning, the intense heat provides the energy to break the chemical bonds within large, complex molecules, causing them to fracture into a mixture of smaller, simpler molecules in solid, liquid, and gaseous forms.
The essential mechanism of pyrolysis is not combustion but a controlled chemical separation. By applying heat without oxygen, you force large organic molecules to break apart, re-forming into a valuable suite of products: a solid carbon char, a liquid bio-oil, and a combustible syngas.

The Core Principle: Breaking Bonds Without Burning
Pyrolysis is a fundamental thermochemical process, distinguished by one critical condition: the absence of oxygen. This single factor changes the outcome from combustion (burning) to controlled decomposition.
The Role of Heat
Heat is the catalyst for the entire process. It provides the necessary activation energy to overcome the strength of the chemical bonds holding large polymer chains together in materials like biomass, plastics, or tires.
The Absence of Oxygen
This is the defining feature of pyrolysis. Without oxygen, the material cannot combust. Instead of reacting with oxygen to produce ash, carbon dioxide, and water, the molecules simply break down into smaller, often more valuable, volatile components and a stable carbon residue.
From Large Molecules to Smaller Fractions
The process begins as the material is heated. The long, complex molecular chains become unstable and begin to vibrate, eventually fracturing into smaller, more volatile molecules. These smaller molecules are released as vapors, leaving behind a solid, carbon-rich material known as biochar. The released vapors are then collected and cooled.
The Three Primary Products of Pyrolysis
The decomposition process results in three distinct product streams, the proportions of which can be controlled by adjusting the pyrolysis conditions.
Biochar (The Solid Fraction)
This is the stable, carbon-rich solid residue left behind after the volatile components have been driven off. It is essentially a form of charcoal and is prized for its ability to sequester carbon and improve soil quality.
Bio-oil (The Liquid Fraction)
When the hot vapor stream is rapidly cooled, it condenses into a liquid known as bio-oil or pyrolysis oil. This is a complex mixture of hundreds of different organic compounds and can be upgraded into transportation fuels or used as a source for specialty chemicals.
Syngas (The Gaseous Fraction)
Not all of the vapor can be condensed into a liquid. The remaining non-condensable gases, such as hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane, form a mixture called syngas. This gas is combustible and can be used to generate heat or electricity, often to power the pyrolysis process itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Slow vs. Fast Pyrolysis
The mechanism can be manipulated by controlling the heating rate and duration, which dramatically changes the final product distribution. This control is the key to tailoring pyrolysis for specific industrial applications.
Slow Pyrolysis: Maximizing Biochar
By heating the material slowly over several hours, the process favors the formation of a stable carbon structure. This gives volatile gases time to react and re-polymerize, maximizing the yield of solid biochar. This was the principle behind ancient charcoal production.
Fast Pyrolysis: Maximizing Bio-oil
By heating the material extremely quickly (in seconds), the large molecules are broken down and vaporized almost instantly. These vapors are then rapidly removed from the hot zone and condensed before they have a chance to undergo secondary reactions, maximizing the yield of liquid bio-oil (up to 60%).
Matching the Mechanism to Your Goal
Understanding the relationship between process conditions and the resulting products is essential for applying pyrolysis effectively. Your primary objective will determine the ideal operational parameters.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration or soil amendment: Employ slow pyrolysis to maximize the production of stable, carbon-rich biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid biofuels or chemical feedstocks: Utilize fast pyrolysis to maximize the yield of condensable bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is generating a combustible fuel gas on-site: Tune the process to higher temperatures to favor thermal cracking and increase the output of syngas.
By controlling the fundamental mechanism of heat transfer in an oxygen-free environment, you can precisely dictate the transformation of low-value materials into high-value products.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Primary Use | Key Process Condition |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration | Slow Pyrolysis |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Biofuel, chemical feedstock | Fast Pyrolysis |
| Syngas (Gas) | On-site heat and power generation | High Temperature Pyrolysis |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab or operation?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and analysis. Whether you are developing new biofuels, studying carbon sequestration with biochar, or optimizing process conditions, our reliable equipment is designed to support your innovative work.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's solutions can help you achieve precise and efficient pyrolysis results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















