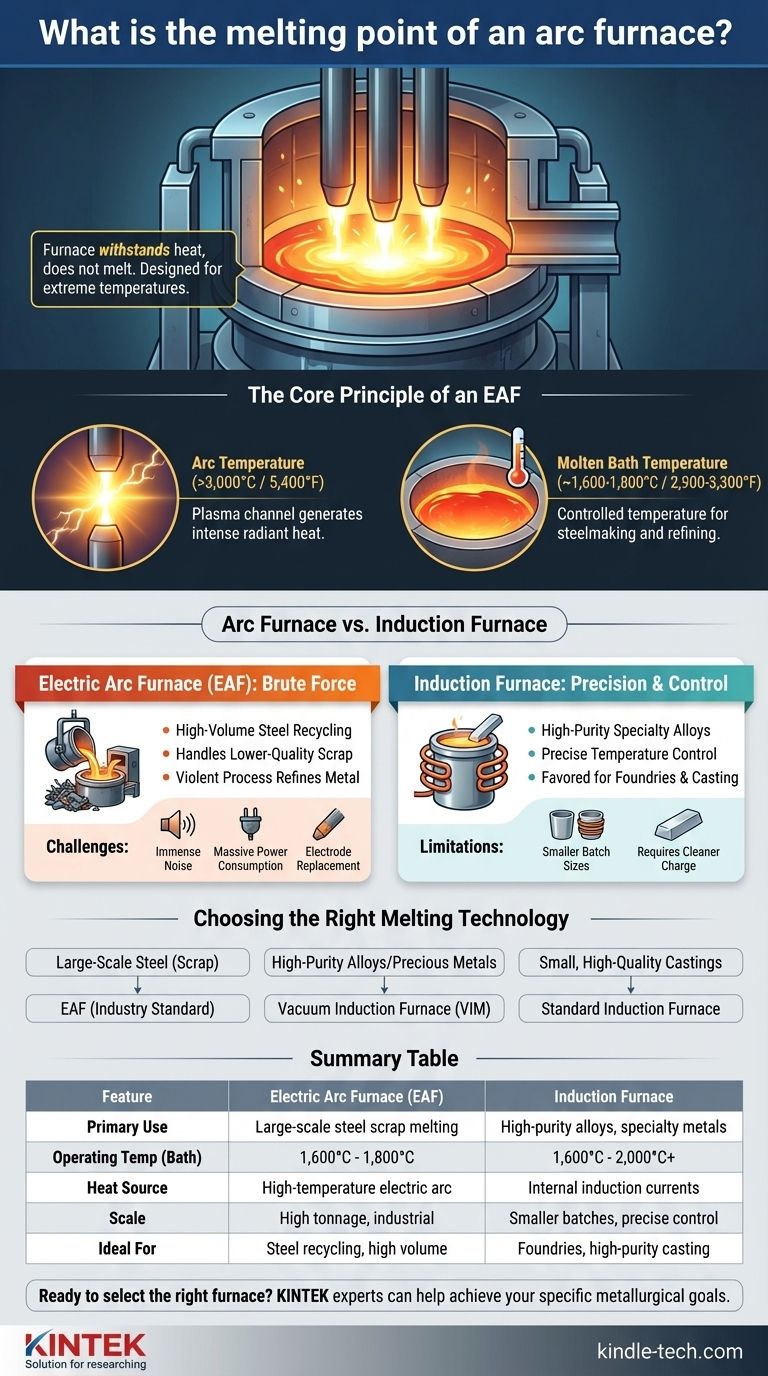
To be precise, an arc furnace itself does not have a melting point; it is a device designed to withstand extreme heat to melt materials inside it. The electric arc it generates, which does the actual melting, can reach temperatures far exceeding 3,000°C (5,400°F). However, the furnace is typically operated to maintain a molten metal bath at a controlled temperature, such as 1,600 to 1,800°C (2,900 to 3,300°F) for steelmaking.
The crucial insight is not the melting point of the furnace, but the difference in how heat is generated and for what purpose. An electric arc furnace (EAF) uses the brute force of a high-temperature electric arc for large-scale melting, primarily of steel scrap. This is a fundamentally different technology from an induction furnace, which uses electromagnetic fields for more controlled melting of specialty metals.
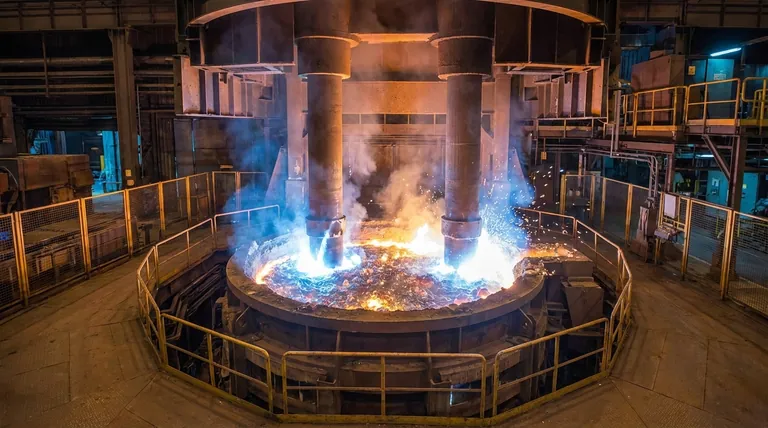

The Core Principle of an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF)
An EAF works by passing an enormous electrical current through large graphite electrodes. This is a technology of immense power and scale.
How an Electric Arc Generates Heat
The tips of the electrodes are brought close to the metal charge inside the furnace, creating a high-energy electric arc. This arc is a channel of plasma—a super-heated, electrically conductive gas.
This plasma arc is a source of intense radiant heat, functionally like a miniature lightning storm inside the furnace, which rapidly melts the scrap metal.
Operating Temperature vs. Arc Temperature
It is critical to distinguish between the temperature of the arc itself and the working temperature of the molten metal.
While the arc can theoretically exceed 3,000°C, the pool of molten metal (the "bath") is carefully managed. For steel production, this bath is controlled at the temperatures needed for melting and refining, typically around 1,600°C to 1,800°C.
Arc Furnace vs. Induction Furnace: A Key Distinction
The reference materials provided describe induction furnaces, which are a different, though equally important, melting technology. Understanding the difference clarifies their distinct applications.
The Arc Furnace: Brute Force for High Volumes
The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the workhorse of modern steel recycling. Its primary strength इज its ability to melt huge quantities of scrap steel, known as "charge," quickly and efficiently.
It is designed for high-tonnage production and can handle lower-quality, less-sorted scrap material because the intense heat and violent process help refine the metal.
The Induction Furnace: Precision and Control
An Induction Furnace operates on a completely different principle. It uses powerful, alternating magnetic fields to induce electrical currents within the metal itself, causing it to heat up and melt from the inside out.
As noted in the references, these furnaces can reach temperatures of 1,600°C to 2,000°C. They are favored for producing high-purity specialty alloys, precious metals, and for applications in foundries where precise temperature control and a clean melt are paramount. Vacuum induction furnaces (VIM) offer even greater purity by melting in a vacuum.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is universally superior; they are optimized for different tasks and come with distinct operational challenges.
Arc Furnace Challenges
The EAF process is extremely harsh. It produces immense noise, requires massive amounts of electrical power, and consumes the large graphite electrodes, which must be replaced periodically. It is a tool of industrial brute force, not fine control.
Induction Furnace Limitations
Induction furnaces are generally limited to smaller batch sizes compared to EAFs. They also require a cleaner, more well-defined charge material, as the process offers fewer opportunities for refining out impurities compared to the violent chemical reactions in an EAF.
Choosing the Right Melting Technology
Your choice of furnace technology depends entirely on your material, scale, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production from scrap: The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) is the definitive industry standard for its high throughput and efficiency at volume.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity specialty alloys or precious metals: A vacuum induction furnace (VIM) offers the precise temperature and atmospheric control needed for superior metallurgical quality.
- If your primary focus is operating a foundry for smaller, high-quality castings: A standard induction furnace provides the clean melting and precise control required for casting complex parts.
Understanding these core differences empowers you to select the precise tool required for your specific metallurgical goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) | Induction Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Large-scale steel scrap melting | High-purity alloys, specialty metals |
| Operating Temp | 1,600°C - 1,800°C (molten bath) | 1,600°C - 2,000°C+ |
| Heat Source | High-temperature electric arc | Internal induction currents |
| Scale | High tonnage, industrial | Smaller batches, precise control |
| Ideal For | Steel recycling, high volume | Foundries, high-purity casting |
Ready to select the right furnace for your lab or production needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose between arc and induction furnace technologies to achieve your specific metallurgical goals, from high-volume steel processing to precision alloy creation. Contact us today to discuss your project and get a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How do you clean a tubular furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Maintenance
- What temperature is tube annealing? A Guide to Material-Specific Ranges for Optimal Results
- What is the temperature of a quartz tube furnace? Master the Limits for Safe, High-Temp Operation
- Why does heating increase temperature? Understanding the Molecular Dance of Energy Transfer
- What is the process of annealing tubes? Achieve Optimal Softness and Ductility for Your Tubing



















