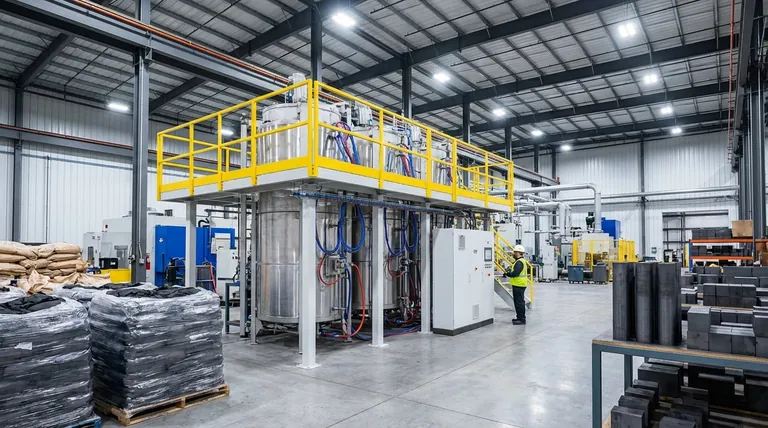
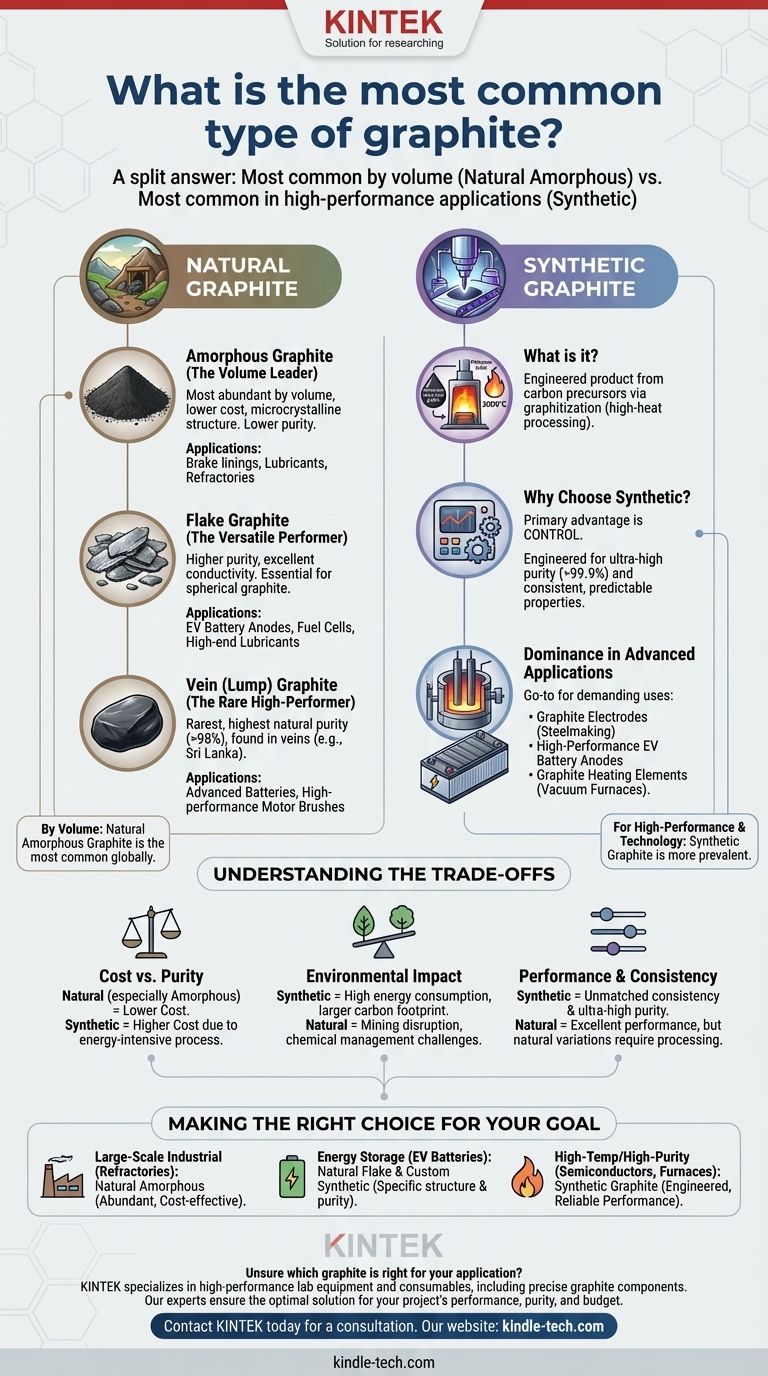
By volume, the most common type of graphite is natural amorphous graphite, which accounts for the majority of the world's natural graphite production tonnage. However, for high-performance and technology-driven applications, synthetic graphite is more prevalent and is produced in massive quantities for specific industries like steelmaking and electric vehicle batteries.
The question of "most common" is best answered by understanding the fundamental split between natural and synthetic graphite. While a low-grade natural form is most common by sheer volume, high-purity synthetic graphite dominates the most critical and advanced industrial applications.

The Two Pillars of Graphite: Natural vs. Synthetic
Graphite is not a single material but a family of materials separated into two primary categories. Understanding this distinction is the first step toward understanding the graphite market and its applications.
Natural Graphite: Mined from the Earth
Natural graphite is a mineral composed of graphitic carbon. It is mined directly and categorized into three main subtypes based on its geology and morphology.
Amorphous Graphite: The Volume Leader
This is the most abundant and lowest-cost form of natural graphite. It is not truly amorphous but microcrystalline, meaning its crystal structures are extremely small.
It is typically lower in carbon content and is used in applications where high purity is not the primary concern, such as in brake linings, lubricants, and refractories (heat-resistant materials) for the steel industry.
Flake Graphite: The Versatile Performer
Flake graphite occurs as distinct, flat particles. It has a higher carbon content and better crystalline perfection than amorphous graphite, giving it superior electrical and thermal conductivity.
Its unique structure makes it essential for manufacturing spherical graphite, the primary anode material in the lithium-ion batteries that power electric vehicles (EVs). It is also used in fuel cells and high-end lubricants.
Vein (Lump) Graphite: The Rare High-Performer
This is the rarest and highest-quality form of natural graphite, found in underground veins. It is known for its exceptional purity (often over 98% carbon) and is mined almost exclusively in Sri Lanka.
Due to its rarity and high cost, its use is limited to niche applications that demand supreme thermal and electrical conductivity, such as in advanced battery research and high-performance motor brushes.
The Rise of Synthetic Graphite
While natural graphite is mined, synthetic graphite is an engineered product manufactured from other carbon-rich materials.
What is Synthetic Graphite?
Synthetic graphite is produced by heating carbonaceous precursors, most commonly petroleum coke or coal tar pitch, to extremely high temperatures (around 3,000°C) in a specialized furnace. This process, known as graphitization, re-orders the carbon atoms into a precise, layered graphite structure.
Why Choose Synthetic?
The primary advantage of synthetic graphite is control. Manufacturers can engineer it to have exceptionally high purity (over 99.9%) and consistent, predictable properties. This level of quality and uniformity is impossible to guarantee with mined natural graphite.
Dominance in Advanced Applications
This control makes synthetic graphite the go-to material for the most demanding applications. It is used to create the massive graphite electrodes that melt scrap metal in electric arc furnaces (EAFs) for steel recycling.
It is also the dominant anode material in high-performance lithium-ion batteries and is critical for high-temperature equipment, such as the graphite heating elements used in vacuum furnaces, where purity and predictable performance are non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between natural and synthetic graphite involves a clear set of trade-offs tied directly to the final application's requirements.
Cost vs. Purity
Natural graphite, particularly the amorphous type, is significantly cheaper to produce than synthetic graphite. The energy-intensive graphitization process makes synthetic graphite a premium, higher-cost material.
Environmental Impact
The production of synthetic graphite is highly energy-intensive, contributing to a larger carbon footprint. Conversely, natural graphite mining has its own environmental challenges, including land disruption and processing chemical management.
Performance and Consistency
For applications where absolute consistency and ultra-high purity are critical, synthetic graphite is the only option. Natural flake graphite performance is excellent but can have minor variations between deposits, requiring more intensive processing for high-tech uses like batteries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific technical and commercial requirements will determine which type of graphite is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial use (like refractories): Natural amorphous graphite is the most common and cost-effective solution due to its sheer abundance and low price.
- If your primary focus is energy storage (like EV batteries): Specially processed natural flake and custom-engineered synthetic graphite both dominate this market, chosen for their specific structural and purity characteristics.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or high-purity applications (like semiconductor manufacturing or furnace electrodes): Synthetic graphite is the indispensable choice because its properties can be precisely engineered for extreme performance and reliability.
Ultimately, the right graphite is the one that meets your specific performance, purity, and cost requirements.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Natural Amorphous | Most abundant by volume, lower cost, microcrystalline | Brake linings, lubricants, refractories |
| Natural Flake | Higher purity, excellent conductivity | EV battery anodes, fuel cells, lubricants |
| Natural Vein (Lump) | Highest natural purity, rare and expensive | Advanced batteries, high-performance motor brushes |
| Synthetic Graphite | Engineered for ultra-high purity (>99.9%) and consistency | Graphite electrodes for steelmaking, EV battery anodes, furnace heating elements |
Unsure which graphite is right for your application?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables, including the precise graphite components critical for high-temperature processes and advanced material research. Our expertise ensures you get the right material for your specific needs, whether you require the consistency of synthetic graphite or the cost-effectiveness of natural grades.
Let our experts guide you to the optimal solution for your project's performance, purity, and budget requirements.
Contact KINTEL today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Is graphite affected by heat? Discover Its Remarkable Strength and Stability at High Temperatures
- What are the physical and chemical properties of graphite? A Unique Material for Extreme Applications
- How is synthetic graphite manufactured? A Deep Dive into the High-Temperature Process
- Is graphite good in high temperature? Unlocking Its Extreme Heat Potential
- How well does graphite transfer heat? Unlock Superior Thermal Management for Your Electronics



















