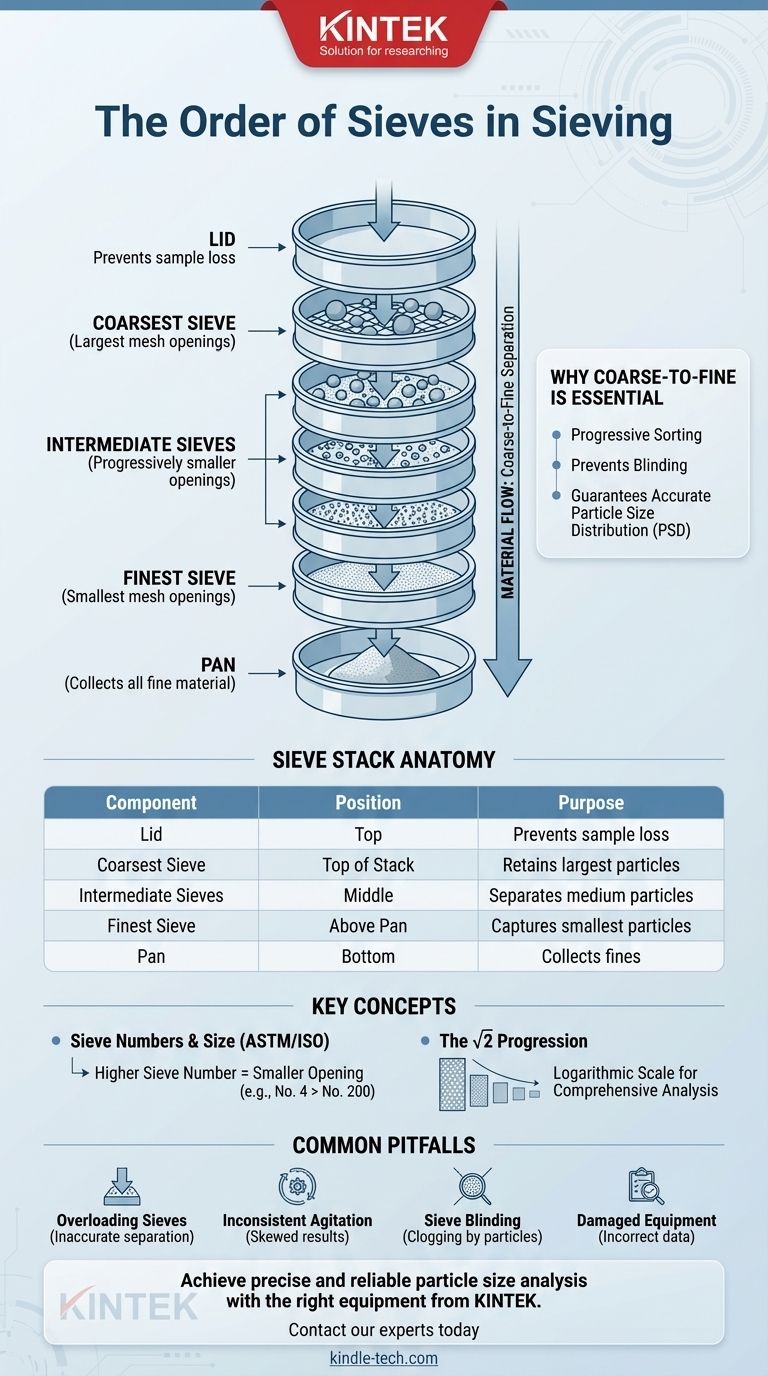
In standard laboratory practice, sieves are always arranged in a vertical stack with the coarsest sieve—the one with the largest mesh openings—at the very top. The sieves are then ordered sequentially by decreasing opening size, with the finest sieve—the one with the smallest mesh openings—placed just above a solid collection pan at the bottom.
The core principle is not just about order, but about systematic separation. Arranging sieves from coarse to fine ensures that particles are progressively sorted by size, preventing the finer screens from becoming clogged and guaranteeing an accurate measurement of the particle size distribution.

The Mechanics of a Sieve Stack
A sieve analysis is a foundational technique for determining the particle size distribution of a granular material. The physical arrangement of the equipment is critical for achieving a reliable result.
Why Coarse-to-Fine is the Only Correct Order
The top-down, coarse-to-fine arrangement is a matter of process efficiency and accuracy. When the sample is loaded onto the top sieve and agitated, the largest particles are immediately retained.
This allows the smaller particles to pass through to the next sieve below. This process repeats down the stack, with each sieve systematically removing a specific size fraction from the material.
Placing a fine sieve above a coarse one would be counterproductive. The fine mesh would immediately be covered and blocked by larger particles, a phenomenon known as blinding, preventing any smaller particles from even reaching the sieves below them.
The Anatomy of the Sieve Stack
A complete sieve stack has several distinct components, each with a specific purpose:
- Lid: Placed on the very top sieve to prevent any loss of the sample material during agitation.
- Coarsest Sieve: The first sieve at the top of the stack, which has the largest mesh opening.
- Intermediate Sieves: A series of sieves with progressively smaller openings.
- Finest Sieve: The last sieve in the series with the smallest mesh opening.
- Pan: A solid pan at the bottom of the stack that collects all the material fine enough to pass through every sieve.
Selecting the Right Sieves for Your Stack
While the coarse-to-fine order is fixed, the specific sieves you choose for the stack depends on the material you are analyzing and the data you need.
Standard Sieve Numbers
Sieves are standardized by organizations like ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ISO. The size is often designated by a sieve number.
Critically, a higher sieve number corresponds to a smaller opening size. For example, a No. 4 sieve has a 4.75 mm opening, while a No. 200 sieve has a tiny 0.075 mm (75 micron) opening.
The √2 Progression
For a comprehensive analysis, it is common to select sieves where the opening size of each sieve in the series is smaller than the one above it by a factor of the square root of 2 (approximately 1.414).
This creates a logarithmic scale of particle sizes, providing a well-distributed set of data points across the entire size range of the sample.
Common Pitfalls and Sources of Error
A correct sieve order is the first step, but several procedural errors can still invalidate your results. Understanding these helps ensure the integrity of your analysis.
Overloading the Sieves
Placing too much sample material on the top sieve is a common mistake. An excessive volume of material can prevent particles from having a fair chance to pass through the mesh openings, leading to inaccurate results.
Inconsistent Agitation
The duration and intensity of shaking must be standardized. Shaking for too short a time will not allow for complete separation, while shaking for too long can cause particle attrition (the particles breaking down), skewing the results toward finer sizes.
Sieve Blinding and Clogging
Blinding occurs when particles become trapped in the mesh openings, effectively reducing the open area of the sieve. This is common with materials that are wet, sticky, or contain near-size particles that get wedged in the mesh.
Damaged or Worn Equipment
Sieves are precision instruments. A deformed frame, a torn mesh, or a sagging screen will produce incorrect results. Regular inspection and calibration are essential for maintaining accuracy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The proper setup of your sieve stack is fundamental to generating trustworthy data. Your approach should be guided by the specific information you need to obtain.
- If your primary focus is accurate particle size distribution: Always stack sieves with the largest mesh opening (lowest sieve number) at the top, progressing to the smallest mesh opening (highest sieve number) at the bottom above the collection pan.
- If your primary focus is repeatability and standardization: Use a standard sieve series (like a √2 progression), and meticulously control the sample weight, shaking time, and agitation intensity for every test.
- If your primary focus is preventing data errors: Regularly inspect sieves for damage or blinding, ensure they are clean and dry before use, and never overload the stack with an excessive amount of sample material.
By understanding this fundamental order and the principles behind it, you ensure the integrity and accuracy of your entire particle size analysis.
Summary Table:
| Sieve Stack Component | Position | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Lid | Top | Prevents sample loss during agitation. |
| Coarsest Sieve | Top of Stack | Retains the largest particles first. |
| Intermediate Sieves | Middle | Sequentially separate medium-sized particles. |
| Finest Sieve | Above Pan | Captures the smallest particles. |
| Pan | Bottom | Collects material that passes all sieves. |
Achieve precise and reliable particle size analysis with the right equipment from KINTEK.
Whether you are conducting R&D, quality control, or production testing, the accuracy of your sieve analysis depends on high-quality, durable sieves and consistent methodology. KINTEK specializes in supplying a comprehensive range of standard ASTM and ISO test sieves, sieve shakers, and accessories to meet your specific laboratory needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application, get help selecting the perfect sieve series, and ensure the integrity of your particle size data.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Multifunctional Small Speed-Adjustable Horizontal Mechanical Shaker for Lab
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
People Also Ask
- What function does a sieving system perform during HPS powder pretreatment? Ensure Uniform Particle Size Distribution
- Why use a vibratory sieve shaker for PET powder? Achieve Precise Particle Size Control for Chemical Research
- Why is a precision vibratory sieving system important for Pt/Pd alloy analysis? Ensure Data Integrity & XRD Accuracy
- Why is a laboratory electromagnetic vibratory sieve shaker used? Optimize Walnut Shell Chemical Pretreatment
- What are the disadvantages of sieve machine? Key Limitations in Particle Size Analysis



















