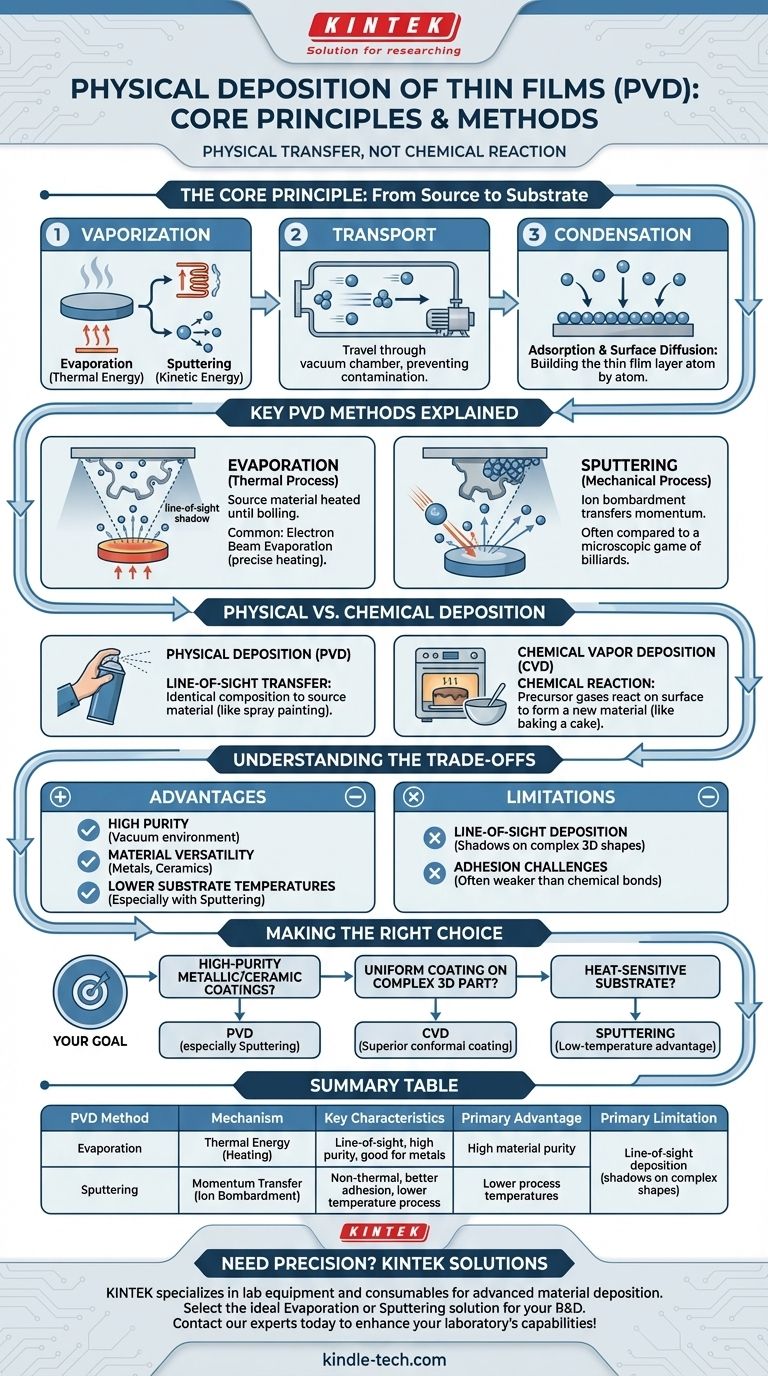
In materials science, physical deposition refers to a family of techniques used to create a thin film of material on a surface, known as a substrate. These methods involve physically transforming a solid source material into a vapor phase, which then travels through a low-pressure environment and condenses onto the substrate, atom by atom. The two primary methods are evaporation, which uses heat, and sputtering, which uses momentum transfer.
The core principle differentiating physical deposition from other methods is its mechanism: it is a process of physical transfer, not chemical reaction. Atoms are moved from a source to a substrate without changing their fundamental chemical identity.

The Core Principle: From Source to Substrate
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is fundamentally a three-step process that occurs within a vacuum chamber to ensure purity and control.
The Vaporization Step
The first step is to convert the solid source material, or "target," into a gas. This is accomplished either by heating the material until its atoms evaporate (thermal energy) or by bombarding it with high-energy ions to knock atoms loose (kinetic energy).
The Transport Step
Once in a vapor phase, the atoms travel through the vacuum chamber from the source to the substrate. The vacuum is critical as it prevents these atoms from colliding with and reacting to particles in the air, ensuring a pure film.
The Condensation Step
When the vaporized atoms reach the cooler substrate, they condense back into a solid state. This process, known as adsorption, is followed by surface diffusion, where the atoms move across the surface to find stable energy sites, gradually building the thin film layer.
Key PVD Methods Explained
While there are many variations, nearly all PVD techniques fall into two main categories: evaporation and sputtering.
Evaporation
Evaporation is a thermal process. A source material is heated in a vacuum until it begins to boil and release atoms in a gaseous state.
These atoms then travel in a straight line and coat whatever is in their path, including the intended substrate. A common technique is electron beam evaporation, which uses a focused beam of electrons to heat the source material with high precision.
Sputtering
Sputtering is a mechanical, non-thermal process. It is often compared to a microscopic game of billiards.
High-energy ions, typically from an inert gas like argon, are accelerated to strike the target material. This collision transfers momentum and physically ejects, or "sputters," atoms from the target, which then deposit onto the substrate.
The Critical Distinction: Physical vs. Chemical Deposition
Understanding what physical deposition is not is key to grasping its unique role. The main alternative is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Physical Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a line-of-sight process. Think of it like spray painting: you are physically transferring particles of an existing material from a source onto a surface. The composition of the final film is identical to the source material.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD uses precursor gases that undergo a chemical reaction directly on the heated substrate's surface, creating a new solid material that forms the film. This is more like baking a cake, where you mix ingredients (gases) that react with heat to form an entirely new substance (the film).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing PVD involves accepting a specific set of advantages and limitations inherent to its physical nature.
Advantage: Purity and Material Versatility
Because PVD operates in a vacuum and doesn't rely on chemical reactions, it can produce exceptionally pure films. It is also highly effective for depositing materials like metals and ceramics that are difficult to create using chemical precursors.
Advantage: Lower Process Temperatures
While evaporation requires high temperatures at the source, the substrate itself can remain relatively cool. Sputtering, in particular, can be performed at low temperatures, making it ideal for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics.
Limitation: Line-of-Sight Deposition
The physical, straight-line travel of atoms means PVD struggles to coat complex, three-dimensional shapes uniformly. Areas not in the direct line of sight from the source receive little to no coating, creating a "shadow" effect.
Limitation: Adhesion Can Be a Challenge
In some cases, the adhesion of physically deposited films to the substrate can be weaker than that of films grown via chemical reaction. This often requires additional substrate preparation or intermediate layers to solve.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best deposition method depends entirely on the material, the substrate, and the desired properties of the final film.
- If your primary focus is high-purity metallic or ceramic coatings: PVD, especially sputtering, offers excellent control over film composition and purity.
- If your primary focus is a uniform, conformal coating on a complex 3D part: CVD is almost always the superior choice due to its gas-based, non-line-of-sight nature.
- If your primary focus is depositing a film onto a heat-sensitive substrate: Sputtering offers a low-temperature processing advantage that is difficult to achieve with CVD.
- If your primary focus is simple, low-cost deposition without vacuum equipment: Non-vacuum chemical methods like sol-gel, spin coating, or chemical bath deposition are more appropriate.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental mechanism—physical transfer versus chemical reaction—is the key to selecting the ideal method for your material and application.
Summary Table:
| PVD Method | Mechanism | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Evaporation | Thermal Energy (Heating) | Line-of-sight, high purity, good for metals |
| Sputtering | Momentum Transfer (Ion Bombardment) | Non-thermal, better adhesion, lower temperature process |
| Primary Advantage | High material purity, lower process temperatures | |
| Primary Limitation | Line-of-sight deposition (shadows on complex shapes) |
Need to apply a precise, high-purity thin film to your substrate? The right PVD method is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for advanced material deposition, serving R&D and production laboratories. Our experts can help you select the ideal evaporation or sputtering solution for your specific material and application. Contact our team today to discuss your thin film requirements and enhance your laboratory's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma CVD? Unlock Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for Sensitive Materials



















