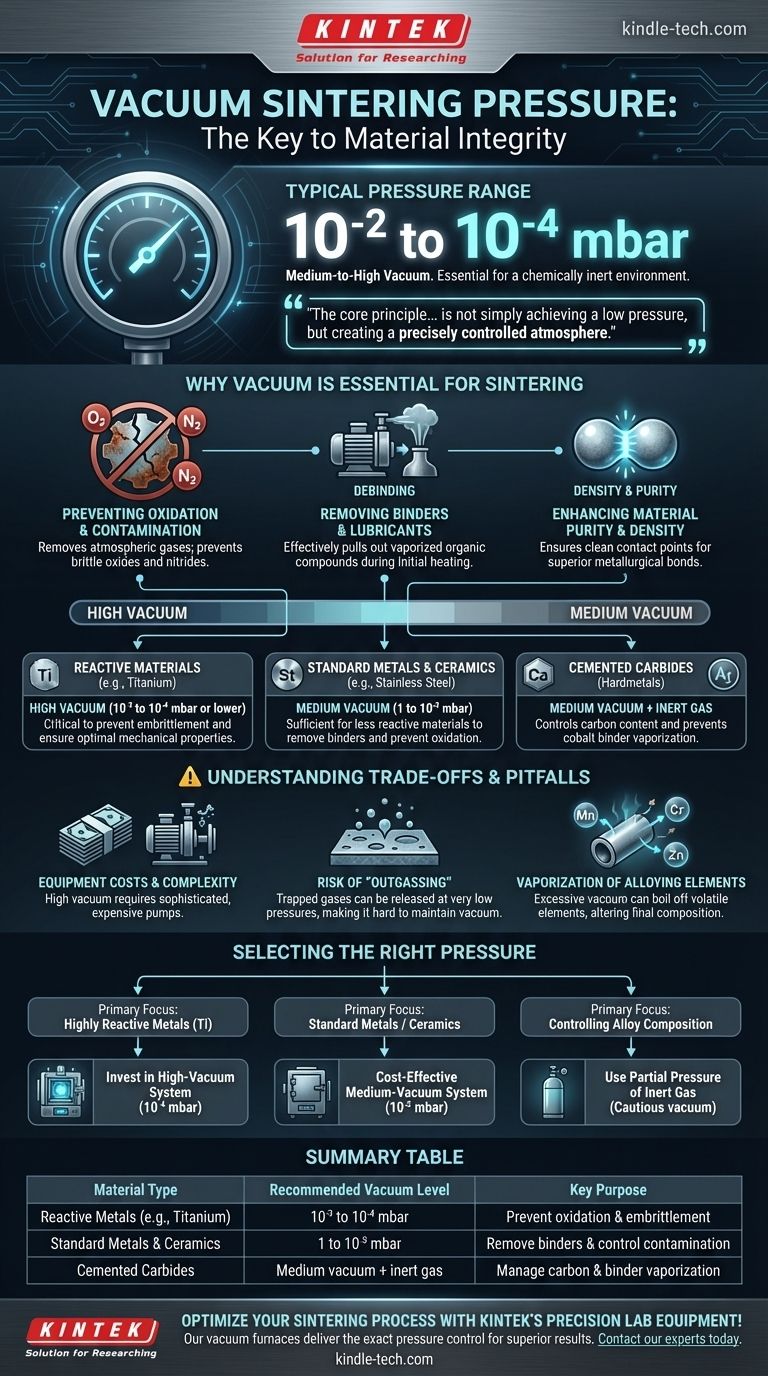
The typical pressure for vacuum sintering generally falls within a range of 10⁻² to 10⁻⁴ millibars (mbar). This places the process in the medium-to-high vacuum spectrum, a level required to create a chemically inert environment suitable for fusing powdered materials into a solid mass. For extremely reactive materials like titanium, the lower end of this range (approaching 10⁻⁴ mbar) is critical to prevent contamination.
The core principle of vacuum sintering is not simply achieving a low pressure, but creating a precisely controlled atmosphere. The ideal vacuum level is dictated entirely by the material's reactivity and the necessity of removing contaminants before the part reaches its final density.

Why Vacuum is Essential for Sintering
Achieving a specific vacuum level is fundamental to the success of the sintering process. The reduced pressure serves several critical functions that directly impact the quality of the final component.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
The primary purpose of the vacuum is to remove atmospheric gases, especially oxygen and nitrogen. At high sintering temperatures, these gases readily react with most metals, forming brittle oxides and nitrides that compromise the material's structural integrity.
Removing Binders and Lubricants
Most powdered metal parts are formed using organic binders or lubricants. During the initial heating phase of the sintering cycle, these compounds vaporize. A vacuum environment is crucial for effectively pulling these gaseous byproducts out of the furnace, a process known as debinding.
Enhancing Material Purity and Density
By eliminating reactive gases and outgassed binders, the vacuum ensures that the contact points between material particles are perfectly clean. This allows for superior metallurgical bonds to form, leading to a denser, stronger, and more pure final product with minimal porosity.
Matching Vacuum Level to Material Needs
There is no single pressure value that works for all applications. The required vacuum level is a direct function of the material being processed and the desired outcome.
Reactive Materials (e.g., Titanium)
Materials like titanium, niobium, and certain superalloys are exceptionally reactive at high temperatures. For these, a high vacuum (10⁻³ to 10⁻⁴ mbar or lower) is non-negotiable. This minimizes the presence of residual oxygen to prevent embrittlement and ensure optimal mechanical properties.
Standard Metals and Ceramics
For less reactive materials like stainless steel or many industrial ceramics, a medium vacuum (1 to 10⁻³ mbar) is often sufficient. The goal here is still to prevent oxidation and remove binders, but the material is more forgiving of trace amounts of residual gases.
Cemented Carbides
Sintering cemented carbides (hardmetals) often involves complex cycles that may use a medium vacuum during debinding, followed by a low-pressure inert gas (like argon) during the final high-temperature phase to control carbon content and prevent the vaporization of the cobalt binder.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Pitfalls
While a lower pressure seems better, pursuing the deepest possible vacuum is not always the best or most practical approach. Understanding the trade-offs is key to an efficient and successful process.
Equipment Costs and Complexity
Achieving a high or ultra-high vacuum requires sophisticated and expensive equipment, such as turbomolecular or diffusion pumps. These systems have higher operational and maintenance costs compared to the simpler mechanical or diaphragm pumps used for medium vacuum levels.
The Risk of "Outgassing"
At very low pressures, gases trapped within the material itself or adsorbed on the furnace walls can be released—a phenomenon called outgassing. This can make it difficult and time-consuming to reach and maintain the target vacuum level.
Vaporization of Alloying Elements
One of the most significant risks of an excessively high vacuum is the vaporization of volatile alloying elements. Elements with a high vapor pressure, such as manganese, chromium, or zinc, can literally boil off the surface of the part, altering its final chemical composition and properties.
Selecting the Right Pressure for Your Application
Choosing the correct vacuum level requires balancing material requirements with practical process constraints. The following guidelines can help direct your decision.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive metals like titanium: You must invest in a high-vacuum system capable of reaching the 10⁻⁴ mbar range to guarantee material purity.
- If your primary focus is sintering standard stainless steels or non-reactive ceramics: A robust medium-vacuum system (around 10⁻² mbar) is often the most cost-effective and reliable solution.
- If your primary focus is controlling the final alloy composition: Be cautious of pulling too hard a vacuum, which could vaporize key elements. You may need to use a partial pressure of an inert gas.
Ultimately, the correct vacuum level is the one that protects your material's integrity while enabling complete densification.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Recommended Vacuum Level | Key Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive Metals (e.g., Titanium) | 10⁻³ to 10⁻⁴ mbar | Prevent oxidation and embrittlement |
| Standard Metals & Ceramics | 1 to 10⁻³ mbar | Remove binders and control contamination |
| Cemented Carbides | Medium vacuum + inert gas | Manage carbon content and binder vaporization |
Optimize your sintering process with KINTEK’s precision lab equipment! Whether you work with reactive metals, ceramics, or cemented carbides, our vacuum furnaces and consumables are engineered to deliver the exact pressure control you need for superior material purity, density, and performance. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can enhance your laboratory’s efficiency and results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why must ZnS powder undergo furnace heat treatment before sintering? Eliminate Impurities for Superior Ceramics
- How is a vacuum oven used in the preparation of gel polymer electrolyte (GPE) membranes? Master Your Battery Research
- What is the contamination in heat treatment? Control Surface Reactions for Superior Component Performance
- What is the temperature for a furnace? It Depends on Your Material and Process Goal
- What are the benefits of using HIP equipment for high-entropy alloys? Achieve Near-Theoretical Density & Durability
- What is the specific application of a vacuum oven in removing trace moisture from PEO? Ensure Battery Stability
- What is the main advantage of vacuum evaporation over atmospheric evaporation? Achieve Low-Temperature, High-Purity Processing
- What is the significance of maintaining a high vacuum environment during the sintering of ODS iron-based alloys?



















