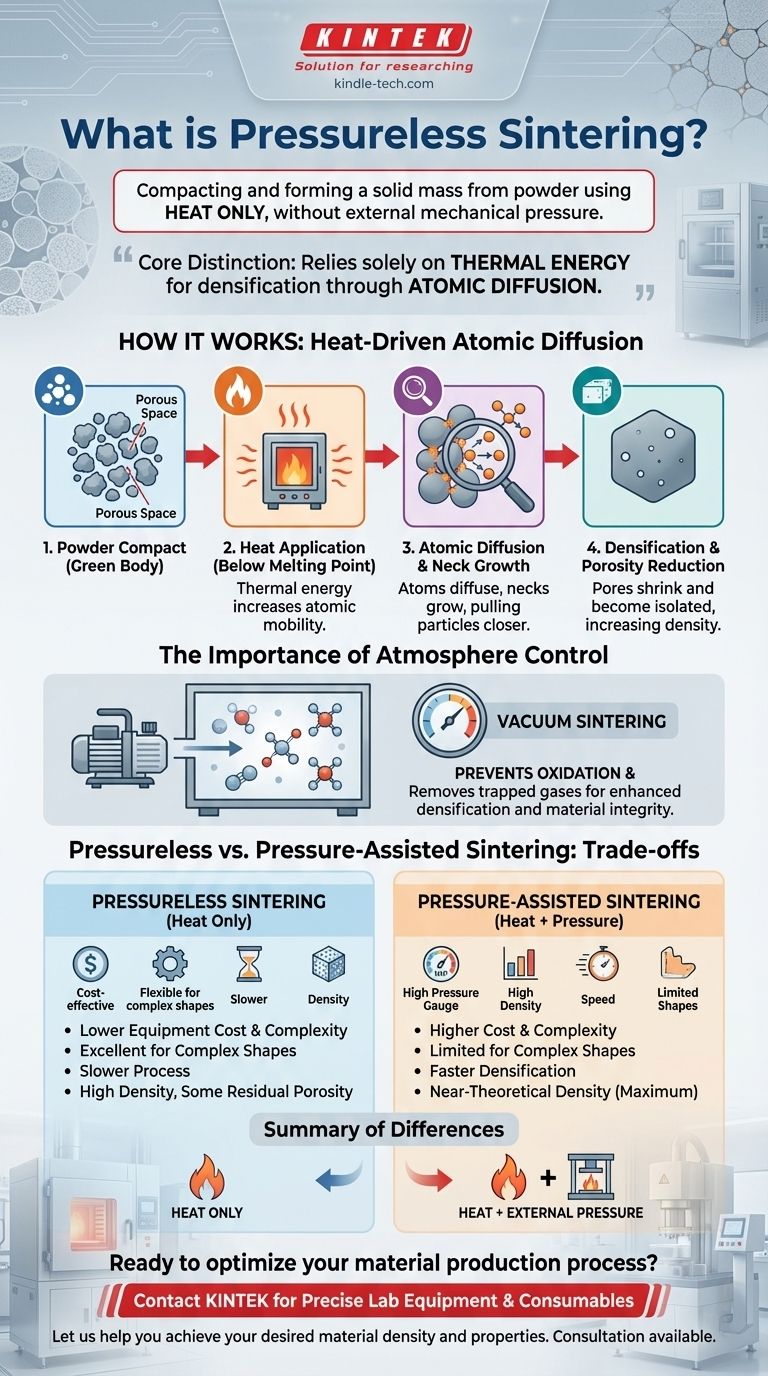
In materials science, pressureless sintering is a method of compacting and forming a solid mass from a powder by applying heat without the use of external mechanical pressure. This process relies solely on atomic diffusion, driven by thermal energy, to bond particles together and reduce the porous space between them. It is a fundamental technique for producing a wide range of ceramic and metallic components.
The core distinction of pressureless sintering is its reliance on heat alone to densify materials, in contrast to methods that use external force. This makes it a simpler and often more cost-effective process, but one that is highly dependent on material composition and precise temperature control to achieve the desired density.

How Pressureless Sintering Works
Pressureless sintering transforms a loose powder into a dense, solid object by carefully controlling temperature and atmosphere. The mechanism is based on minimizing the surface energy of the powder particles.
The Role of Thermal Energy
When a compacted powder (known as a "green body") is heated to a temperature below its melting point, the atoms gain significant thermal energy. This energy allows them to move and diffuse across the contact points between individual particles.
This atomic movement causes the necks between particles to grow, gradually pulling the particles closer together and shrinking the voids, or pores, that exist between them.
Eliminating Porosity and Increasing Density
The primary goal of sintering is to eliminate porosity and create a dense, strong final part. As the process continues, the network of interconnected pores shrinks and eventually breaks up into isolated, closed pores.
With sufficient time at the sintering temperature, these isolated pores can also shrink and disappear, leading to a product with high density and improved mechanical properties like hardness and strength.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Many pressureless sintering operations are performed in a controlled atmosphere or a vacuum. Vacuum sintering is a common and highly effective form of pressureless sintering.
By removing air and other gases, a vacuum prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions that could compromise the material's integrity. It also helps remove gases trapped within the powder compact, further aiding the densification process.
Pressureless vs. Pressure-Assisted Sintering
To fully understand pressureless sintering, it is crucial to contrast it with methods that do use external force.
The Pressureless Approach
This method is defined by the absence of external pressure. Its success depends entirely on the material's inherent ability to densify under heat. It is particularly effective for certain ceramics, powdered metals, and graded metal-ceramic composites.
The Pressure-Assisted Approach
In contrast, methods like hot isostatic pressing (HIP) or hot pressing apply both high temperature and high external pressure simultaneously. The mechanical force physically aids in collapsing pores and consolidating the powder.
This approach is used for materials that are difficult to sinter with heat alone or when achieving near-100% theoretical density is critical for performance.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between pressureless and pressure-assisted methods involves evaluating a clear set of trade-offs related to cost, complexity, and final part properties.
Advantages of Pressureless Sintering
Because it does not require complex and expensive high-pressure equipment, pressureless sintering is generally more cost-effective.
The process is also highly flexible, allowing for the production of complex shapes that would be difficult or impossible to form inside a mechanical press. Modern furnaces offer high levels of automation and precise process control.
Limitations and Challenges
The primary limitation is that pressureless sintering may not achieve the same final density as pressure-assisted methods. Some residual porosity can remain, which might be unacceptable for high-performance applications.
The process can also be slower, requiring longer hold times at high temperatures. Furthermore, its success is highly dependent on the quality and characteristics of the starting powder.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use pressureless sintering hinges on the specific requirements of your material and final component.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness and producing complex shapes: Pressureless sintering is often the superior choice, provided your material can achieve the required density with heat alone.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density or processing difficult-to-sinter materials: A pressure-assisted method will likely be necessary to force consolidation and eliminate all residual porosity.
Understanding this fundamental difference between using heat alone versus heat with force is the key to selecting the optimal manufacturing process for your material.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pressureless Sintering | Pressure-Assisted Sintering (e.g., HIP) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Driving Force | Heat (Atomic Diffusion) | Heat + External Mechanical Pressure |
| Typical Density Achieved | High, but may have residual porosity | Near-theoretical density (Very high) |
| Equipment Cost & Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| Suitability for Complex Shapes | Excellent | Limited |
| Ideal For | Cost-effective production of ceramics, many metals | High-performance applications requiring maximum density |
Ready to optimize your material production process?
Pressureless sintering is a powerful, cost-effective solution for creating complex components from powders. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables needed to perfect your sintering process, from furnaces with exact temperature control to vacuum systems for atmosphere management.
Let us help you achieve the material density and properties your application demands. Contact our team today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What are the parameters for spark plasma sintering? Master Speed, Pressure & Temperature Control
- What are the steps in spark plasma sintering? Achieve Rapid, Low-Temperature Densification
- What is the plasma sintering technique? Achieve Rapid, High-Density Material Fabrication
- Can aluminum be sintered? Overcome the Oxide Barrier for Complex, Lightweight Parts
- What is the vapor phase material? Unlock Faster, Denser Sintering with SPS Technology



















